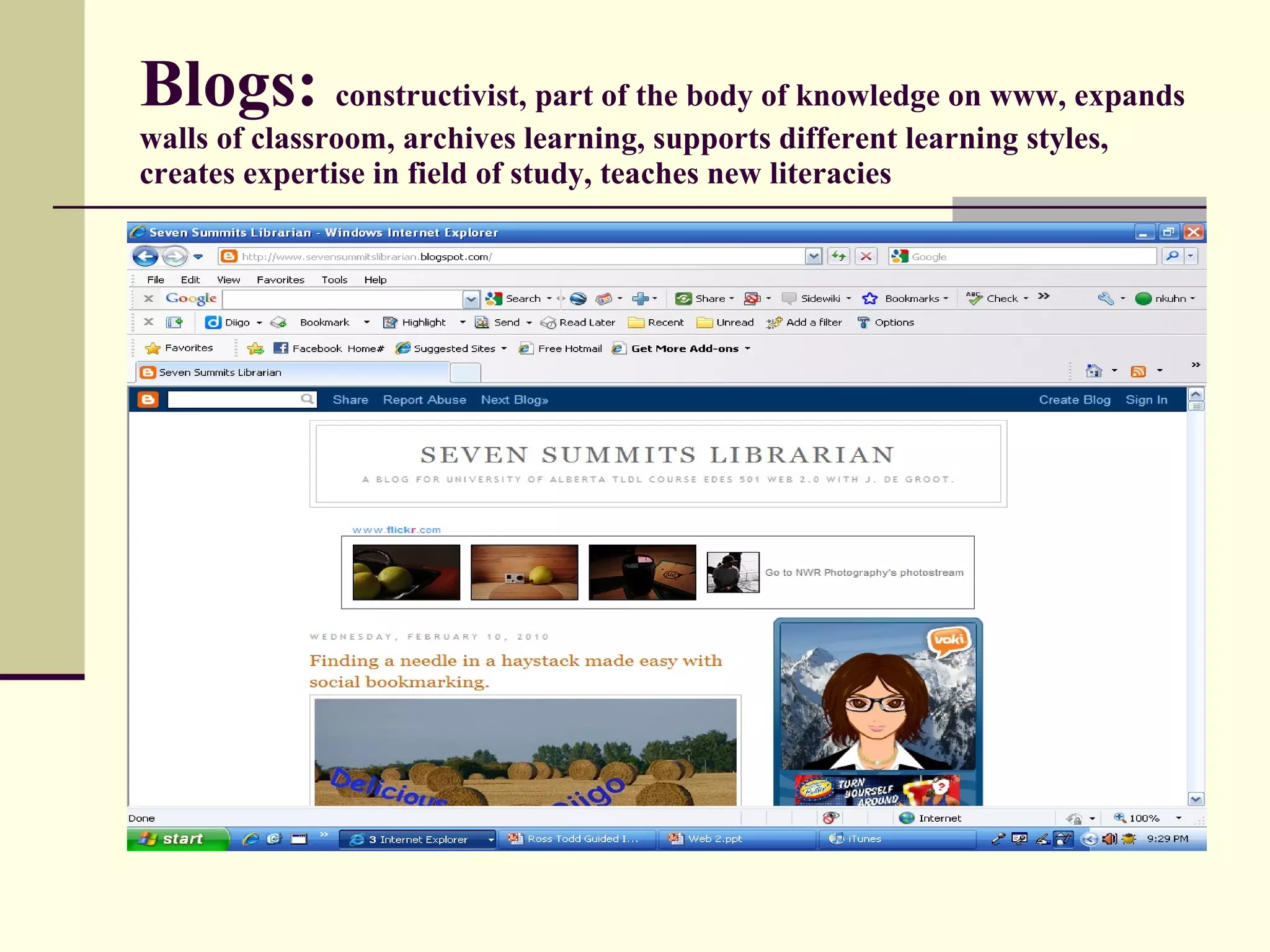
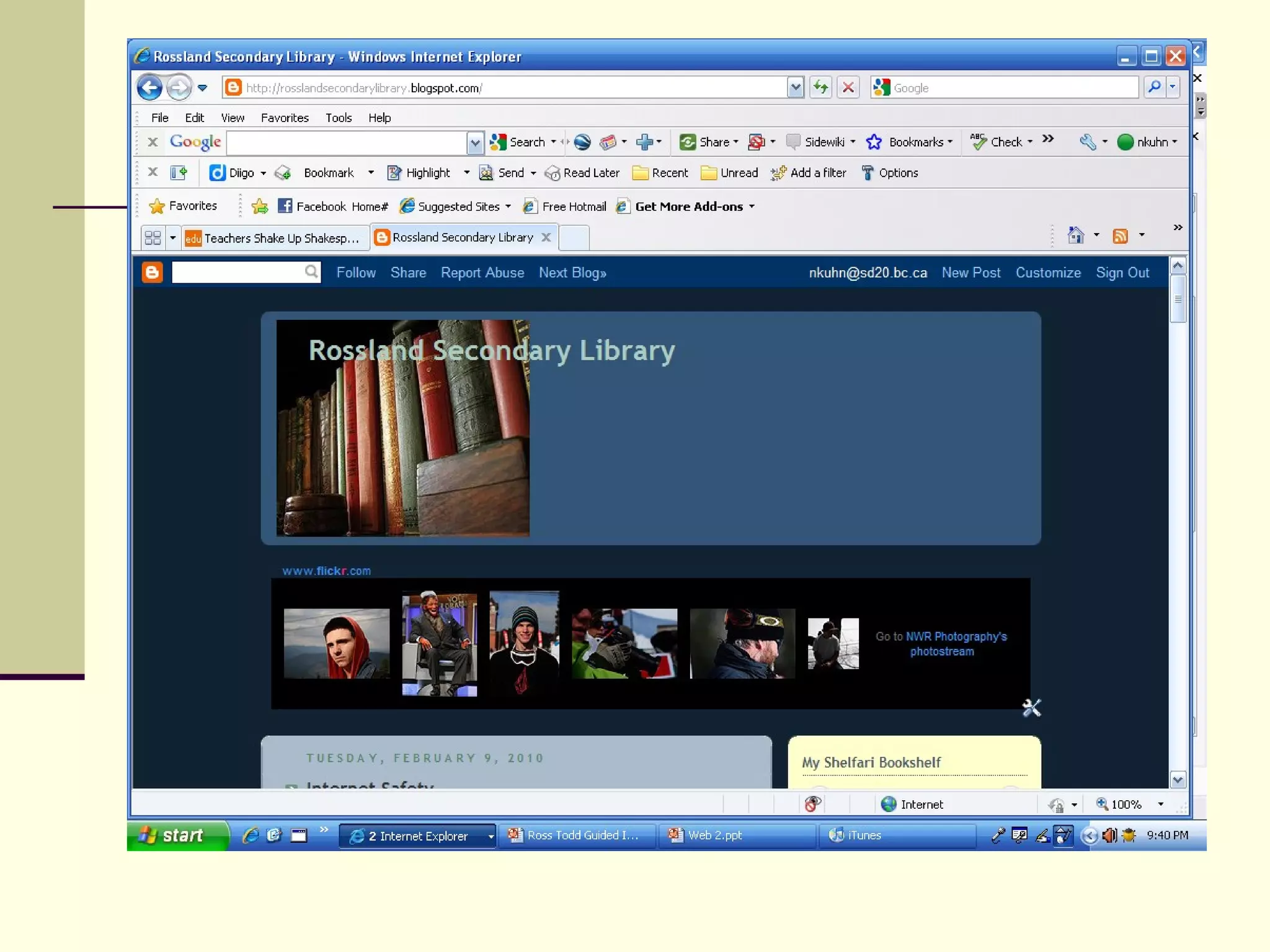
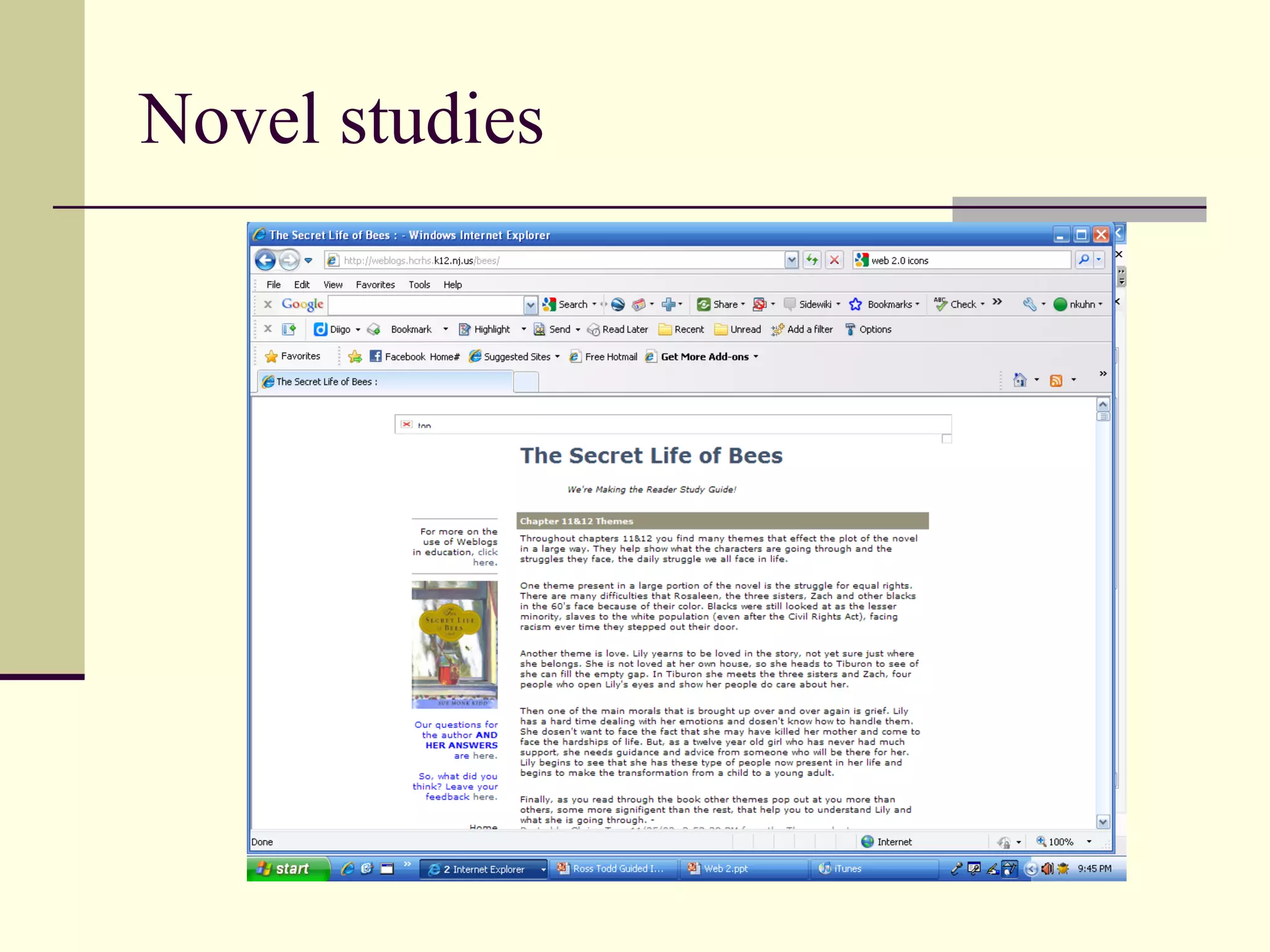
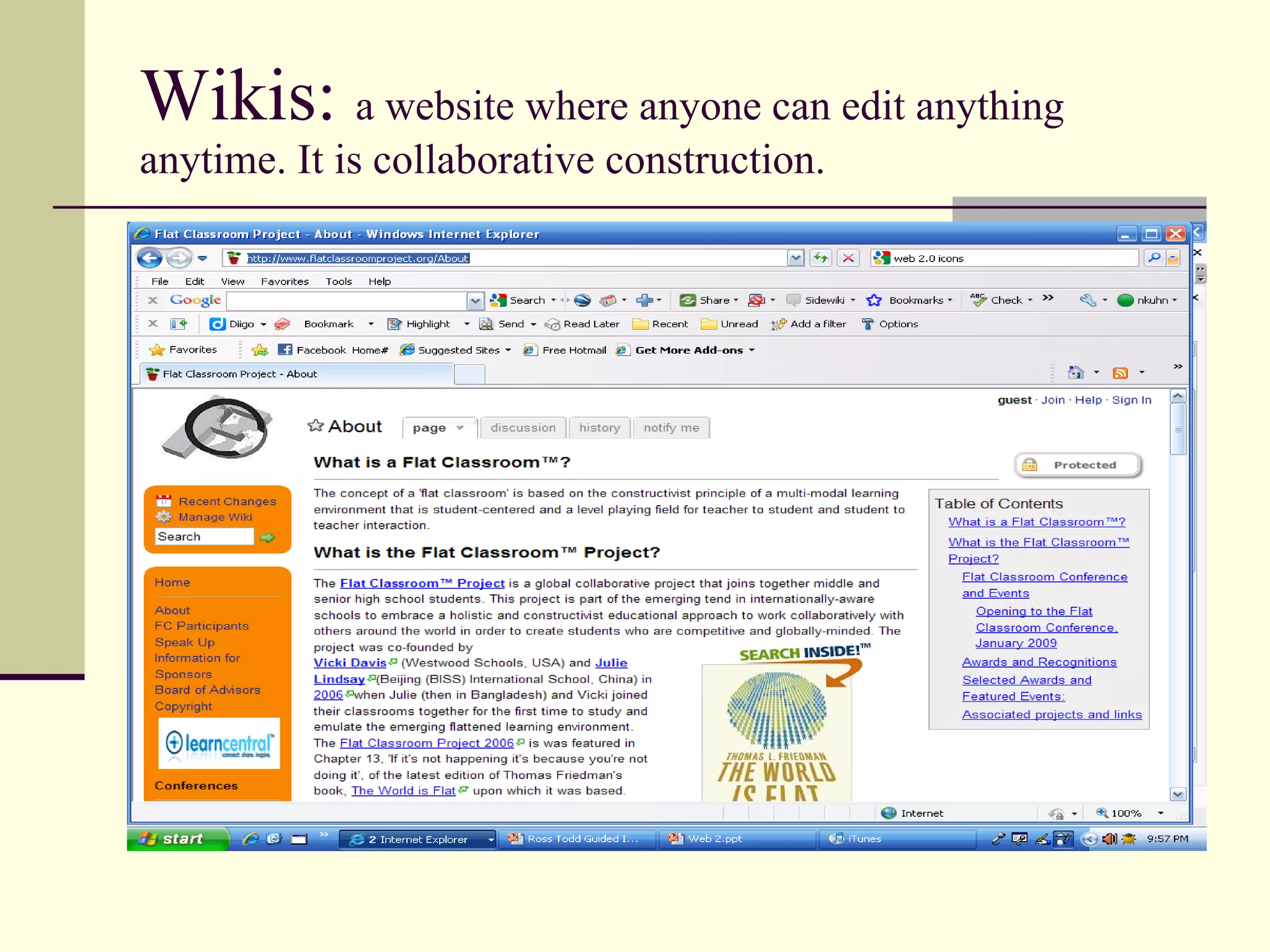
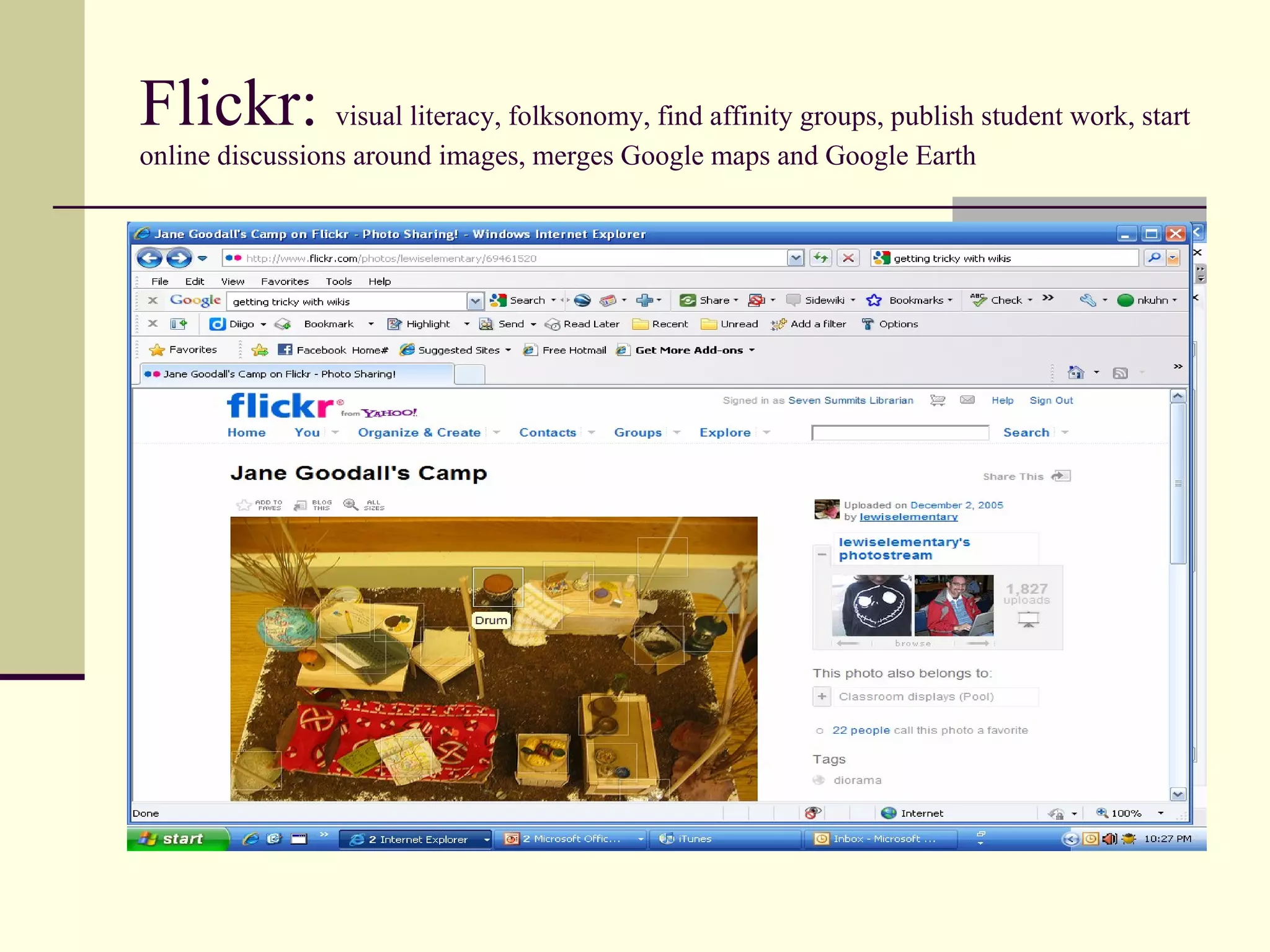
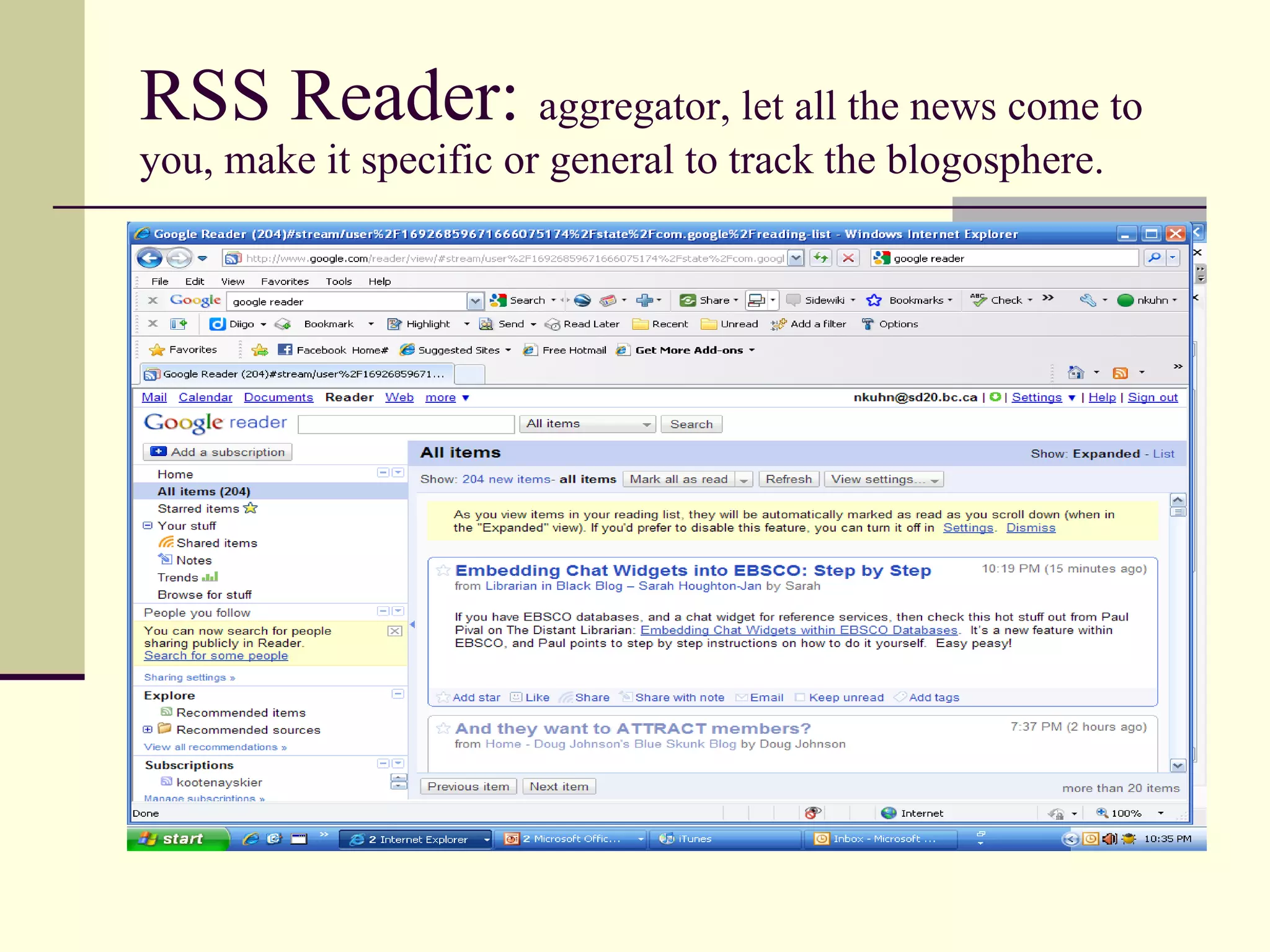
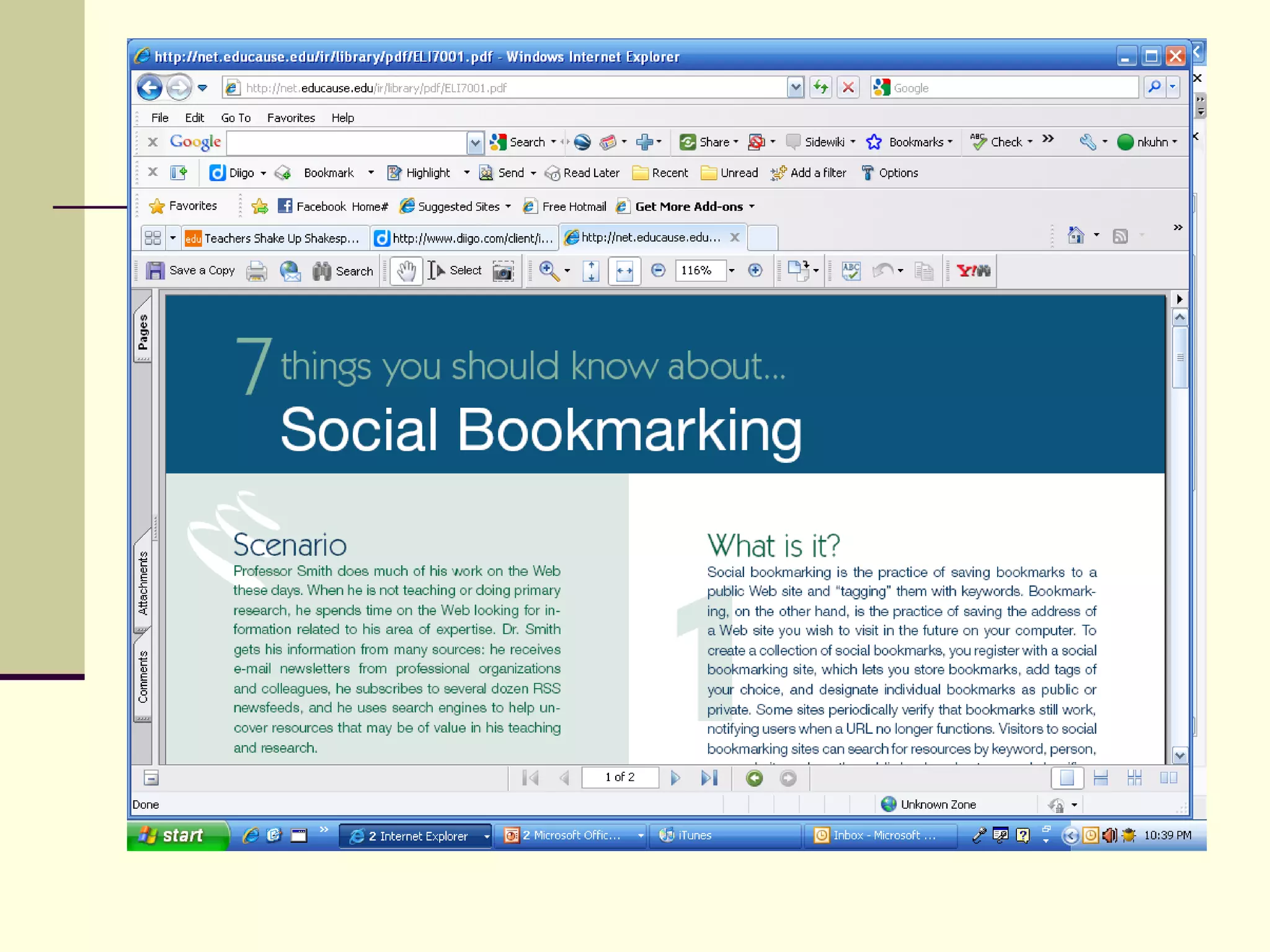
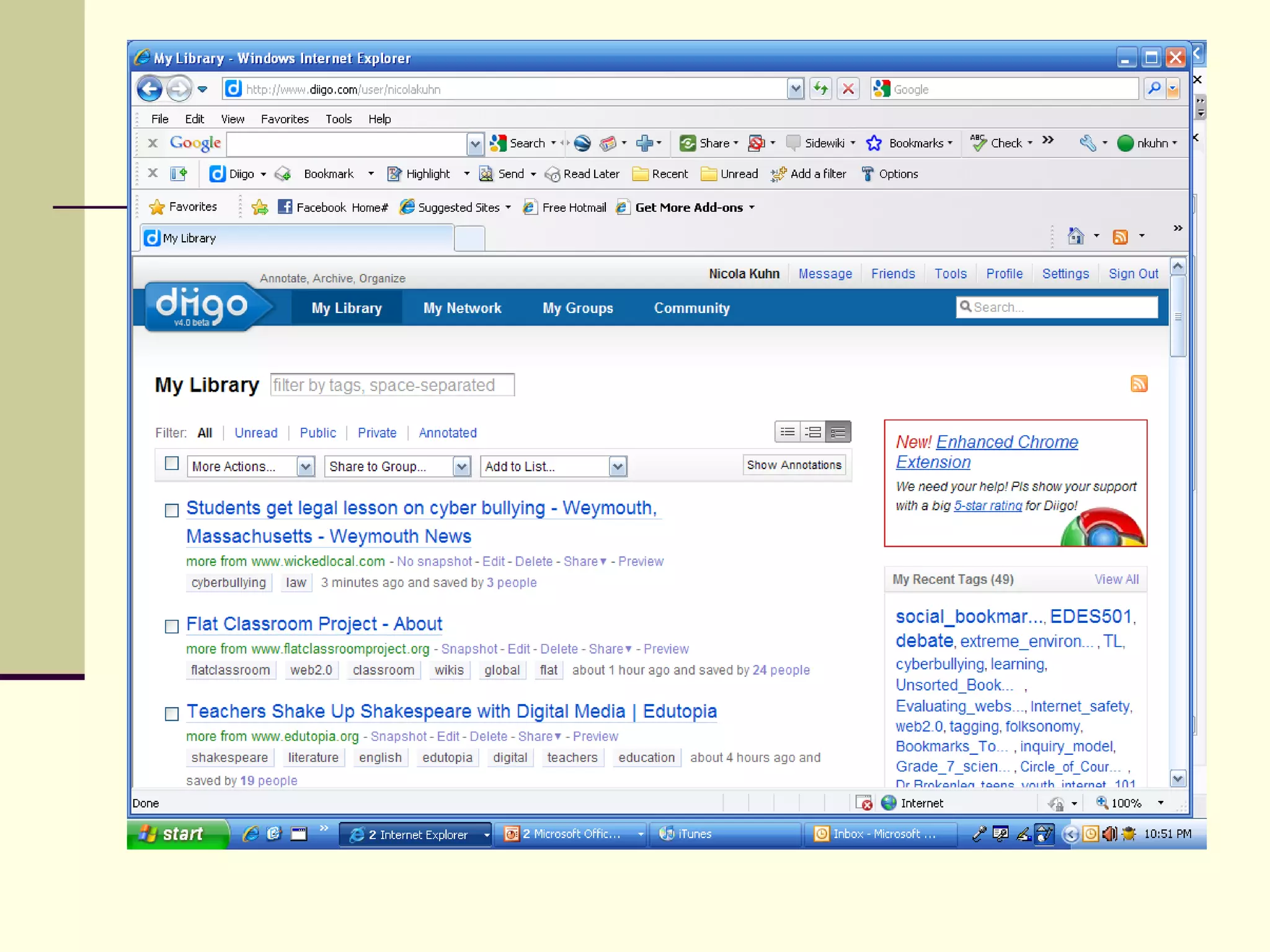
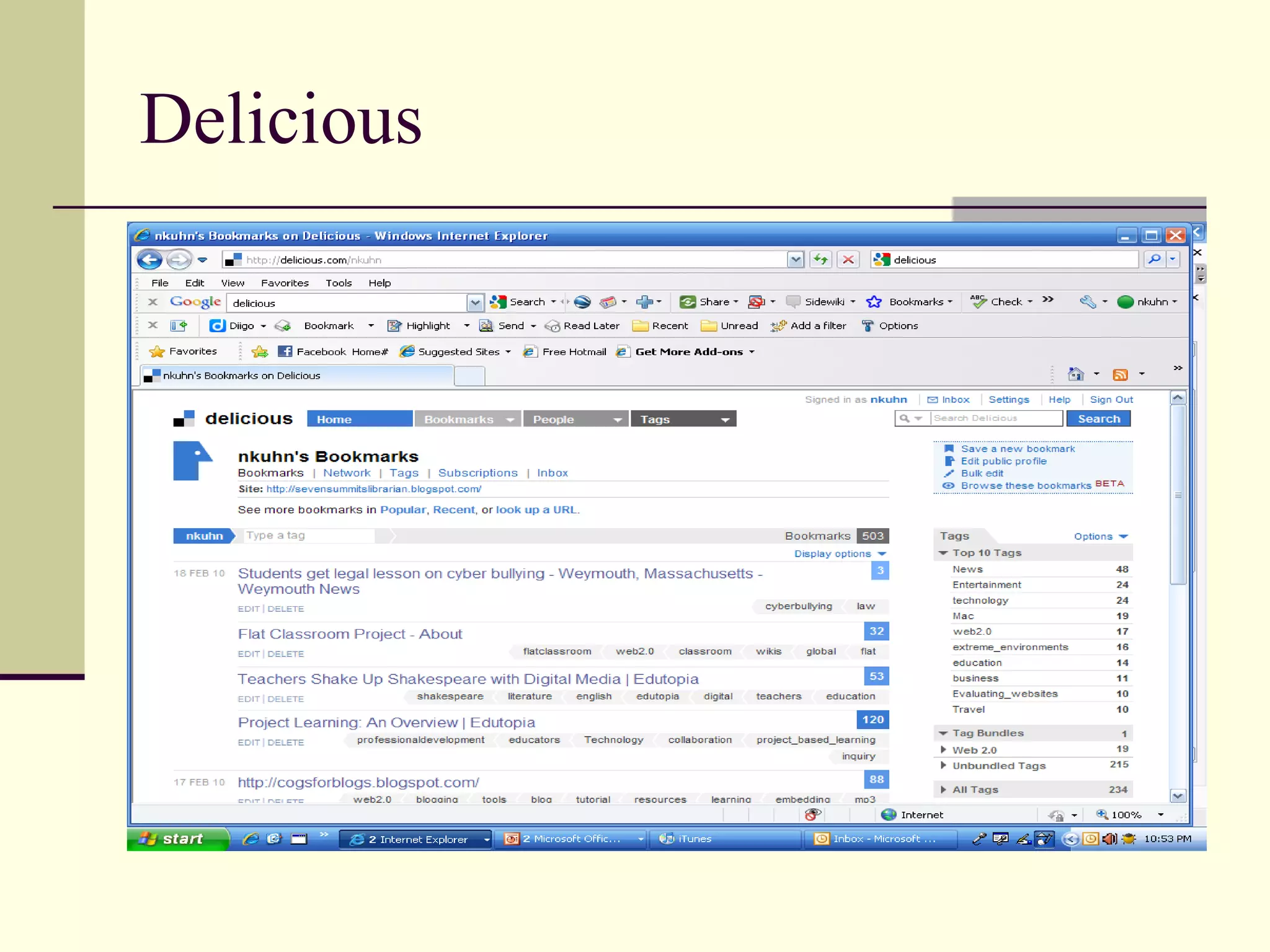
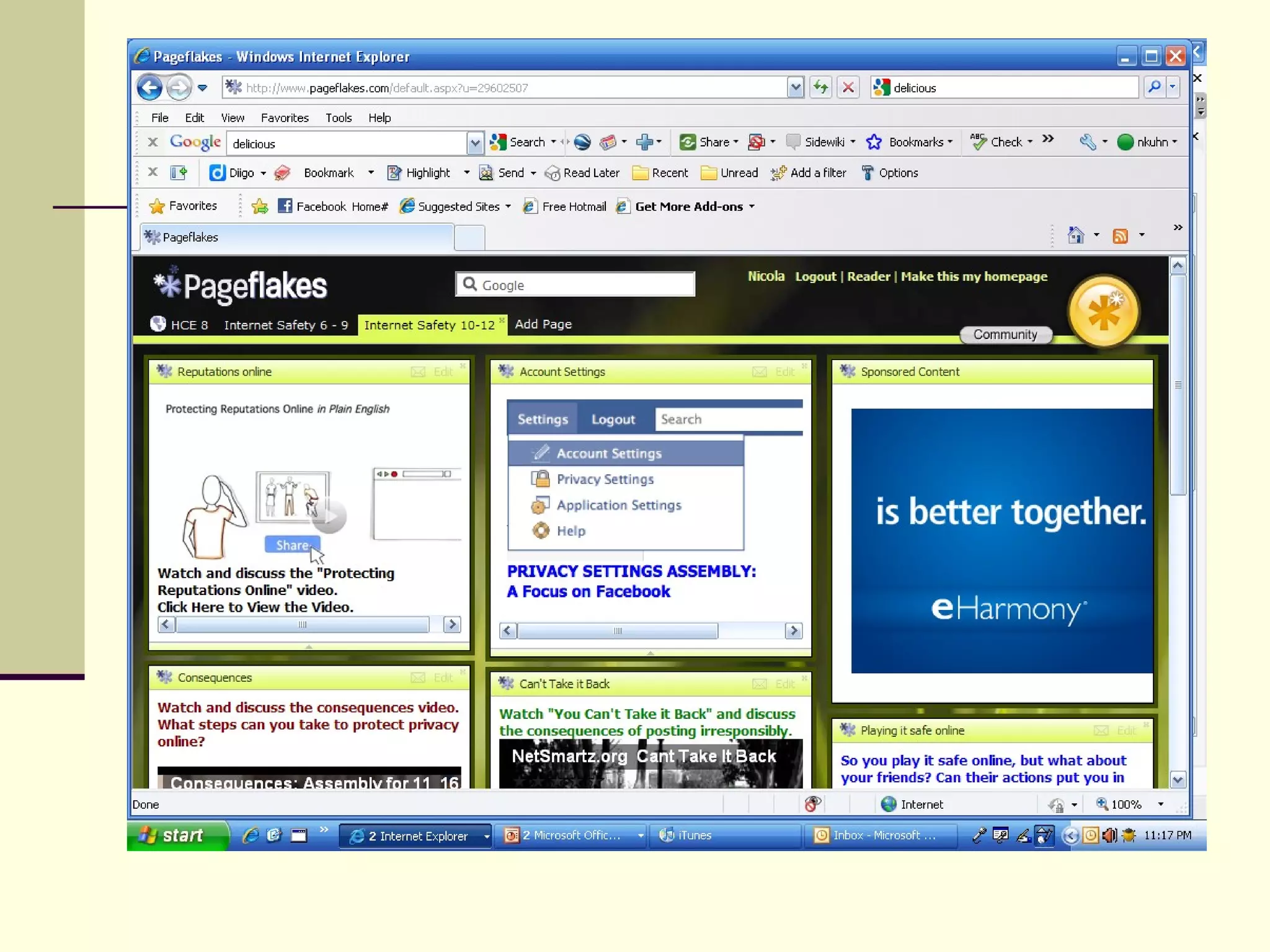
Web 2.0 allows for user-generated content and collaboration in online communities, challenging traditional education. It enables easy sharing of content with a global audience anywhere, anytime. Key characteristics include developing an online identity, personalizing spaces, creating and consuming user-generated content, and social participation through feedback and content development. While it promotes knowledge sharing and engagement, there are also risks like the digital divide and potential for unproductive or negative experiences online that must be addressed. Web 2.0 tools discussed for educational use include blogs, wikis, podcasts, social networking, social bookmarking, YouTube, Flickr, RSS feeds, and more.