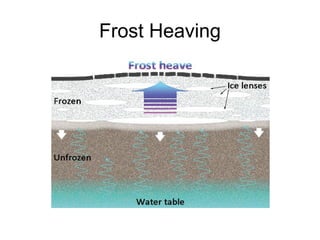
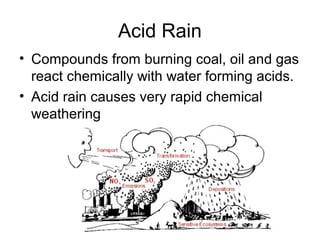
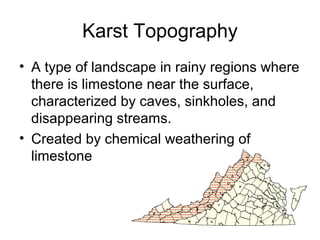
This document discusses weathering and erosion. It defines weathering as the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces through physical or chemical processes. Physical weathering breaks rocks down mechanically through processes like frost wedging or plant roots. Chemical weathering uses chemical agents like water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and acids to break rocks down chemically over time. One example of chemical weathering discussed is how carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form carbonic acid, which easily weathers limestone. The document also defines erosion as the movement of rock and soil by agents such as water, ice, wind or gravity. Specific types of erosion mentioned include water erosion through rivers/streams and runoff, ice erosion through glaciers, and wind erosion