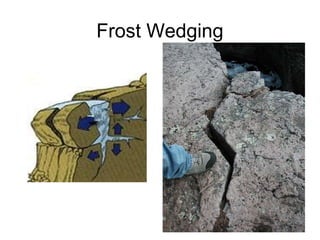
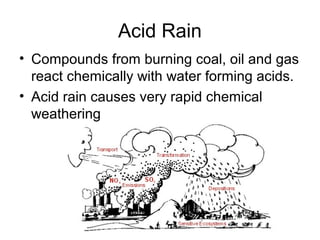
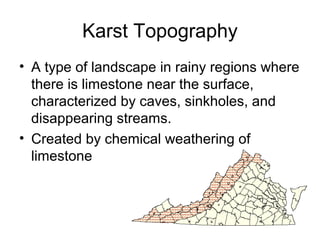
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces through either physical or chemical processes. Physical weathering breaks rocks mechanically through processes like frost wedging or plant roots, while chemical weathering uses chemical agents like water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and acids to decompose the minerals within rocks. Erosion is the process by which weathered material is transported by forces such as water, wind, ice or gravity. It shapes the landscape by wearing down exposed rock and carrying sediments to new locations.