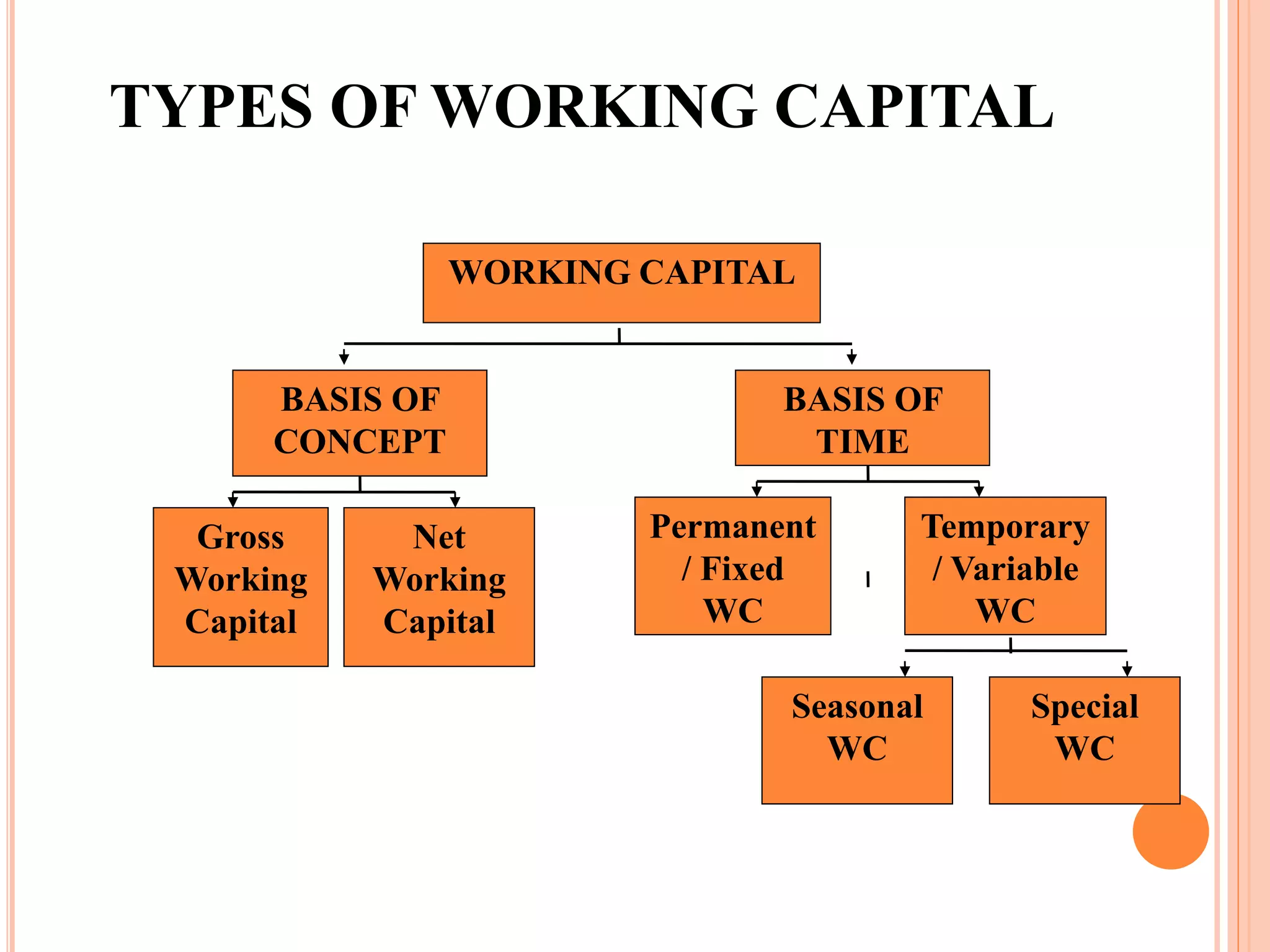
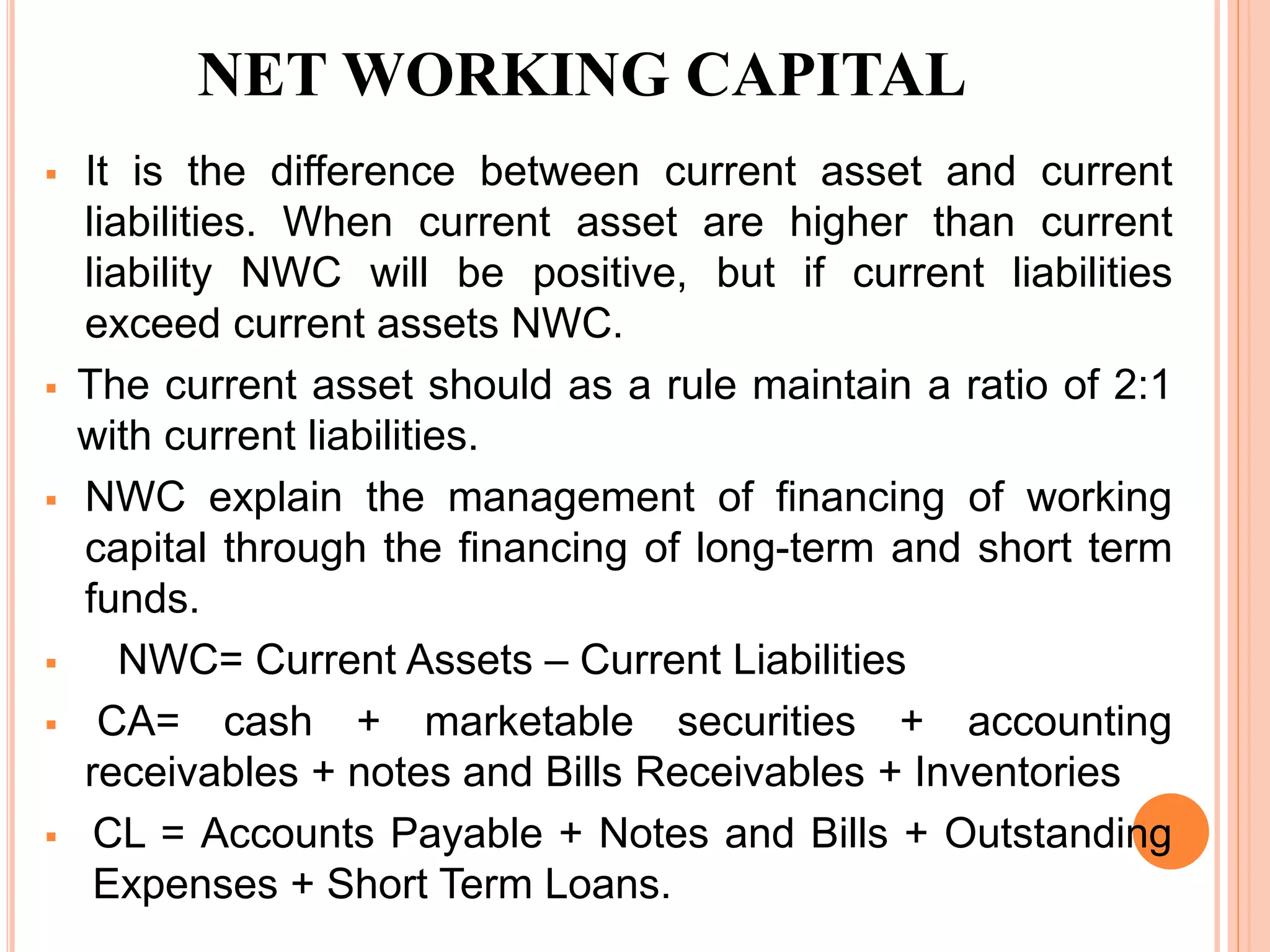
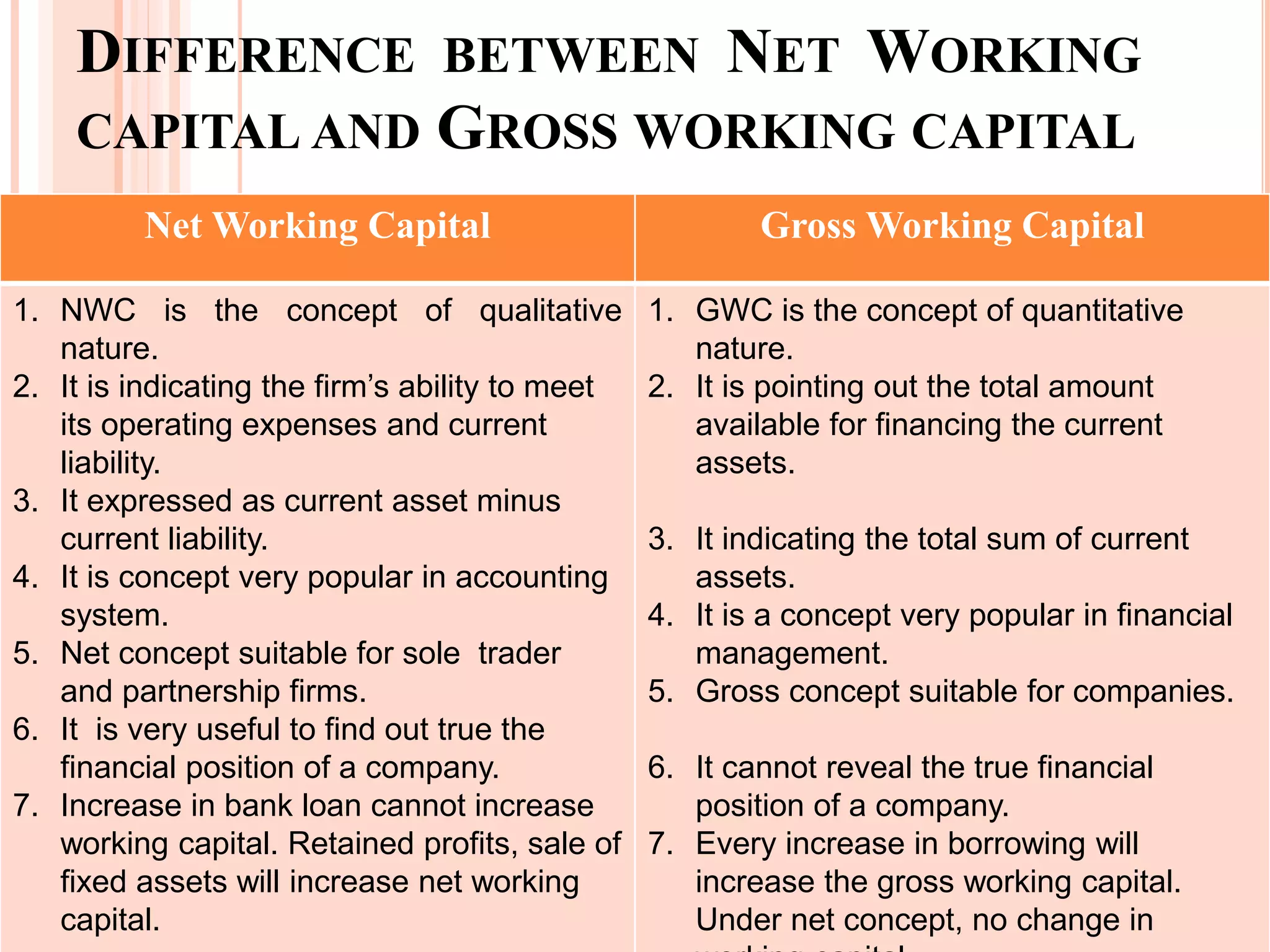
This document discusses different types of working capital. It defines working capital as the capital required to finance short-term assets like cash, inventory, and accounts receivable. There are two main types of working capital: gross working capital, which refers to the total investment in current assets, and net working capital, which is current assets minus current liabilities. Net working capital indicates a firm's ability to meet short-term obligations, while gross working capital simply measures total current assets. Working capital can also be classified as permanent/fixed or temporary/variable depending on whether it is needed continuously or fluctuates over time. Temporary working capital includes seasonal working capital needed for periodic demand fluctuations and specific working capital for unexpected needs.