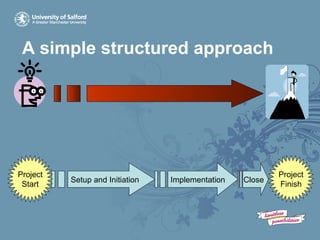
Prince2 is a methodology for project management that defines a process-based approach with clear inputs, outputs, and objectives at each stage. It emphasizes that projects should be properly controlled and flexible, with the whole project driven by business requirements. A simple structured approach can adopt Prince2 principles without complexity, such as having three stages - setup and initiation, implementation, and close - with governance, planning, risk management, and communications throughout.