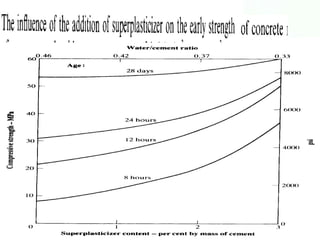
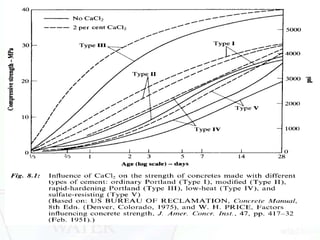
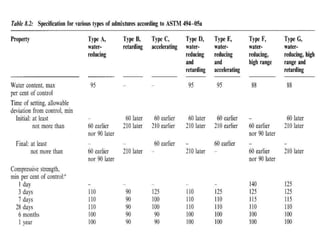
This document discusses water and admixtures used in concrete. It describes how the quality of water can impact concrete strength, durability and corrosion. It outlines acceptable limits for impurities in water and discusses the effects of seawater. It also categorizes and explains the purpose and effects of different types of admixtures (A-F) including water reducers, retarders, accelerators and superplasticizers. Specialty admixtures like air-entraining and waterproofing are also briefly covered.