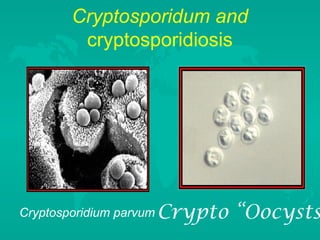
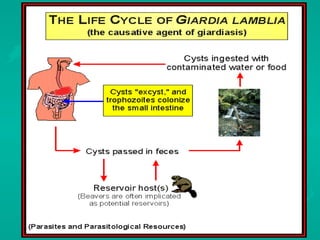
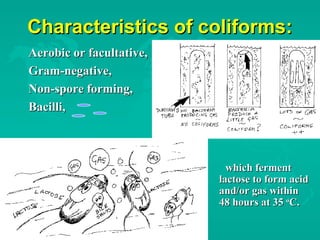
This document discusses microbial pathogens and indicators in water. It describes common waterborne pathogens like Salmonella, E. coli, Vibrio cholerae, and parasites Cryptosporidium and Giardia lamblia. Indicator bacteria like coliforms and E. coli are used to indicate fecal contamination in drinking water. Total coliforms are ubiquitous and can proliferate in distribution systems, while fecal coliforms and E. coli are more specific indicators of recent fecal contamination but are less resistant to disinfection. The document also discusses microbial indicators for recreational waters.