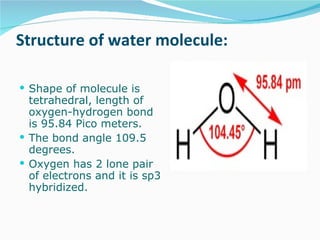
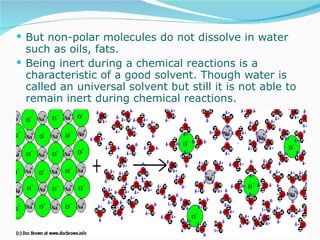
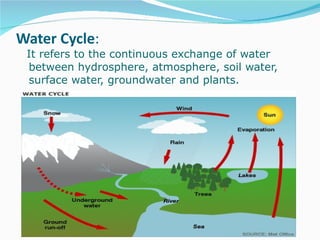
Water has the chemical formula H2O and IUPAC name of dihydrogen monoxide. It can act as both an acid and a base, donating or accepting protons in chemical reactions. Water has a tetrahedral molecular structure and is polar due to the greater electronegativity of oxygen. It has many unique physical and chemical properties, including being a liquid at room temperature, having high surface tension, and acting as a solvent for many other substances due to its polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds. Water plays a vital role in Earth's processes through the water cycle and is essential for life.