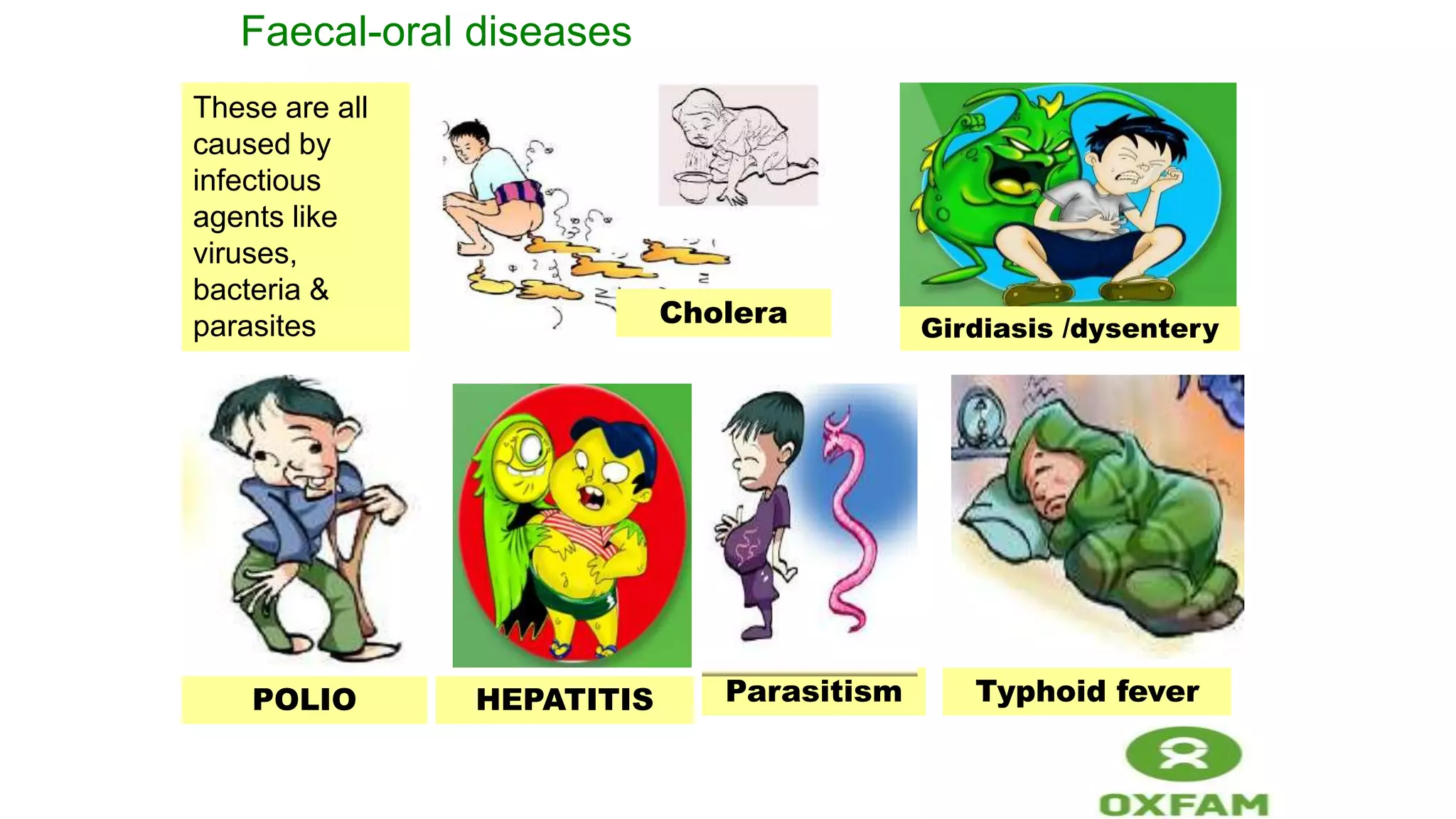
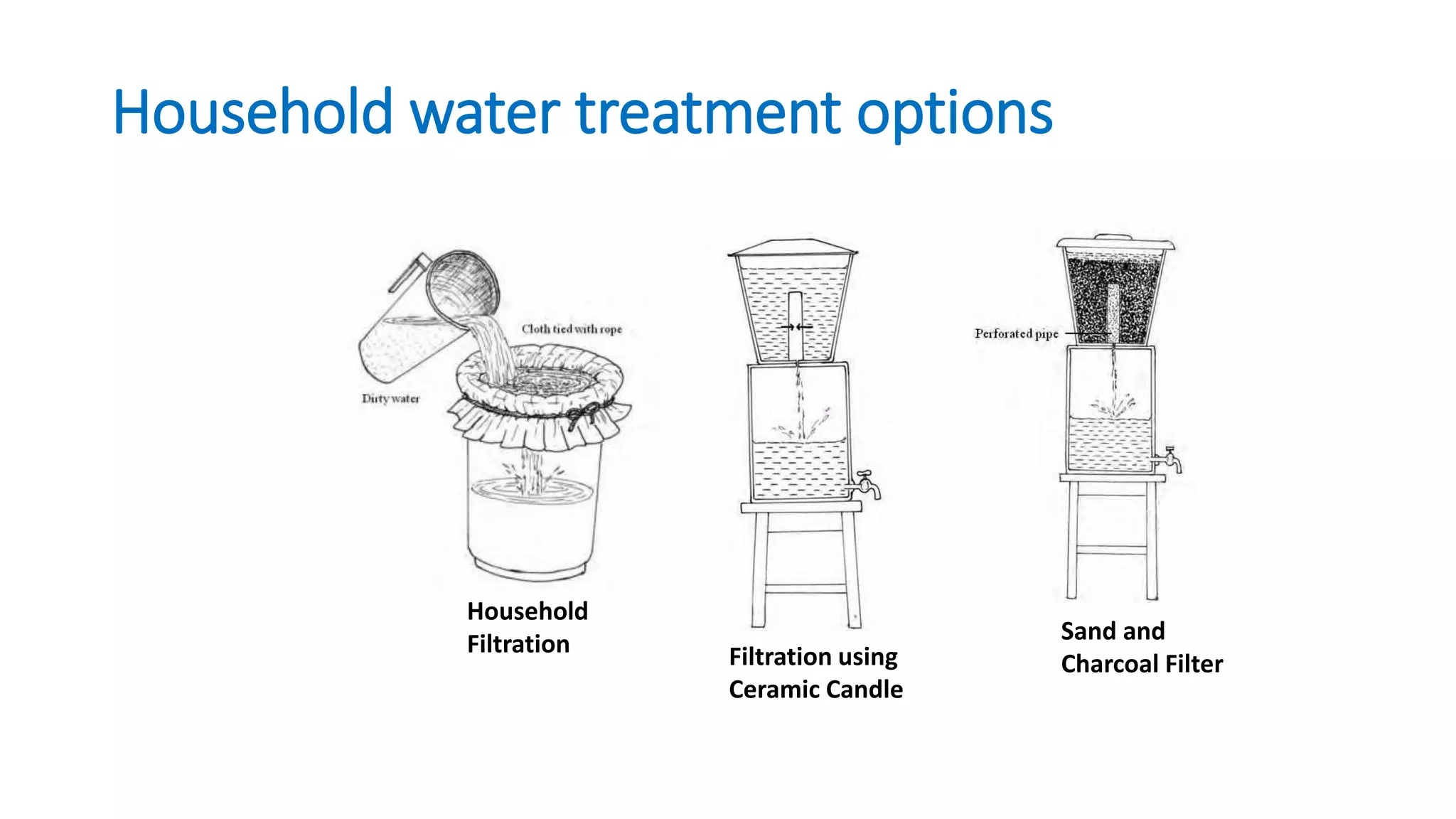
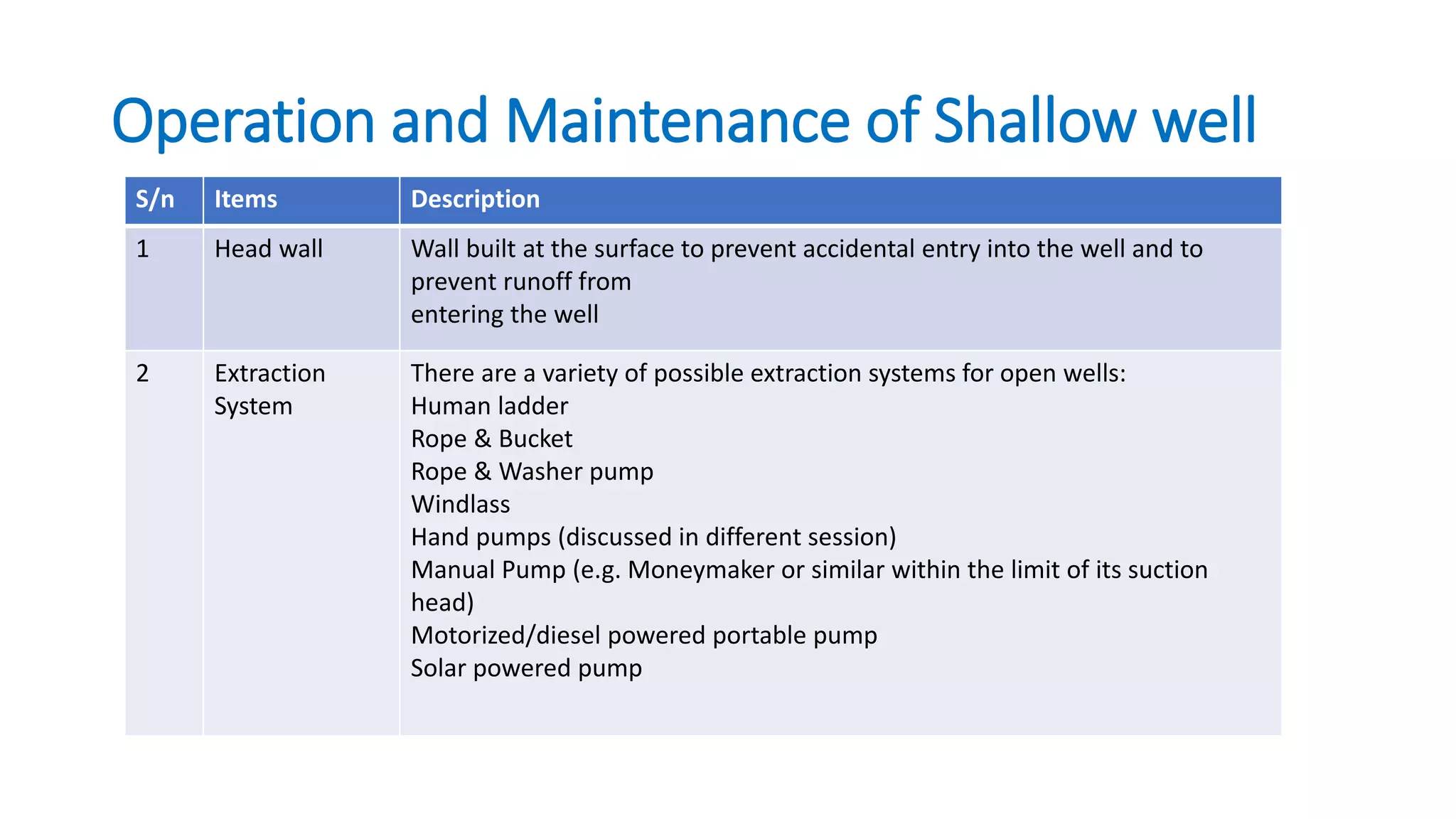
This document provides guidance for WASH committee trainings covering topics like water sources, committee roles and responsibilities, leadership, conflict management, representation, communication, sustainability, governance, financial management, and operation and maintenance of water sources. It outlines training sessions on these topics including group activities, discussions, and presentations. Key points emphasized include the importance of clean water, treating water at the household level, proper management of water points and finances, and defining leadership roles for equitable committees.