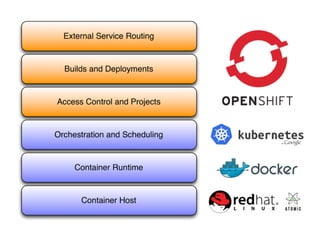
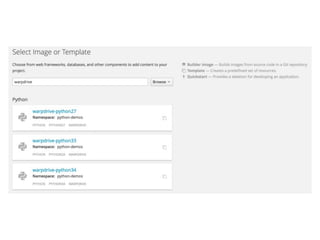
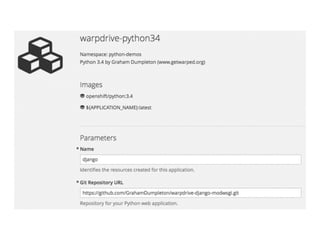
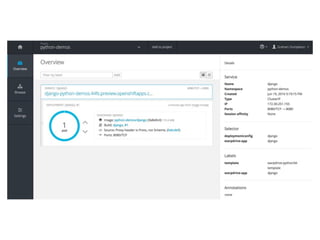
The document outlines 'warpdrive', a tool designed to simplify the deployment of Python web applications, particularly using Django. It details the steps for setting up a virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring a WSGI server for both local development and production. The document also emphasizes integration possibilities with various hosting platforms and seeks feedback from users.






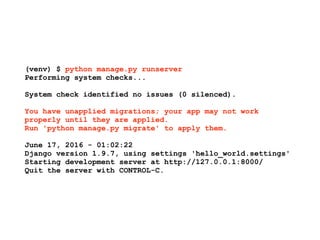















![Configure and start the
WSGI server
(warpdrive+django) $ warpdrive start
-----> Configuring for deployment type of 'auto'
-----> Default WSGI server type is 'mod_wsgi'
-----> Running server script start-mod_wsgi
-----> Executing server command 'mod_wsgi-express start-server
--log-to-terminal --startup-log --port 8080 --application-type
module --entry-point hello_world.wsgi --callable-object
application --url-alias /static/ /usr/local/www/mysite/static'
[Sun Jun 19 22:00:59.819762 2016] [mpm_prefork:notice] [pid
67483] AH00163: Apache/2.4.18 (Unix) mod_wsgi/4.5.2 Python/2.7.10
configured -- resuming normal operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warpdrivemakingpythonwebapplicationdeploymentmagicallyeasy-160815030801/85/warpdrive-making-Python-web-application-deployment-magically-easy-25-320.jpg)









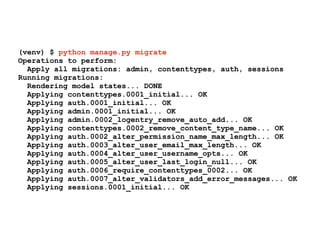
![Create Docker image
(warpdrive+django) $ warpdrive image django
I0619 22:14:22.783544 67609 install.go:251] Using "assemble" installed from
"image:///opt/app-root/s2i/bin/assemble"
I0619 22:14:22.783688 67609 install.go:251] Using "run" installed from
"image:///opt/app-root/s2i/bin/run"
I0619 22:14:22.783712 67609 install.go:251] Using "save-artifacts" installed
from "image:///opt/app-root/s2i/bin/save-artifacts"
---> Installing application source
---> Building application from source
-----> Installing dependencies with pip (requirements.txt)
Collecting Django (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading Django-1.9.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (6.6MB)
Installing collected packages: Django
Successfully installed Django-1.9.7
-----> Collecting static files for Django
Copying ‘…/urlify.js’
…
56 static files copied to '/opt/app-root/src/static'.
---> Fix permissions on application source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warpdrivemakingpythonwebapplicationdeploymentmagicallyeasy-160815030801/85/warpdrive-making-Python-web-application-deployment-magically-easy-35-320.jpg)
![Run Docker image
$ docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 django
---> Executing the start up script
-----> Configuring for deployment type of 'auto'
-----> Default WSGI server type is 'mod_wsgi'
-----> Running server script start-mod_wsgi
-----> Executing server command 'mod_wsgi-express start-server --log-to-terminal --
startup-log --port 8080 --application-type module --entry-point hello_world.wsgi --
callable-object application --url-alias /static/ /opt/app-root/src/static/'
[Sun Jun 19 07:44:57.955455 2016] [mpm_event:notice] [pid 48:tid 139683988789312]
AH00489: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) mod_wsgi/4.5.2 Python/3.4.2 configured -- resuming
normal operations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warpdrivemakingpythonwebapplicationdeploymentmagicallyeasy-160815030801/85/warpdrive-making-Python-web-application-deployment-magically-easy-36-320.jpg)
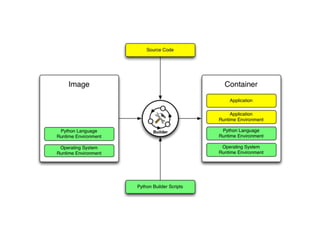
![Manually build image
FROM grahamdumpleton/warp0-centos7-python34
COPY . ${WARPDRIVE_SRC_ROOT}
RUN warpdrive build
CMD [ "warpdrive", "start" ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warpdrivemakingpythonwebapplicationdeploymentmagicallyeasy-160815030801/85/warpdrive-making-Python-web-application-deployment-magically-easy-38-320.jpg)
![Source to Image (S2I)
https://github.com/openshift/source-to-image
$ s2i build https://github.com/GrahamDumpleton/warpdrive-django-auto.git
grahamdumpleton/warp0-centos7-python34 django
I0619 17:34:38.784337 66356 docker.go:352] Image "grahamdumpleton/warp0-centos7-
python34:latest" not available locally, pulling ...
I0619 17:40:23.793610 66356 clone.go:32] Downloading "https://github.com/
GrahamDumpleton/warpdrive-django-modwsgi.git" ...
I0619 17:40:25.979028 66356 install.go:251] Using "assemble" installed from
"image:///opt/app-root/s2i/bin/assemble"
I0619 17:40:25.979075 66356 install.go:251] Using "run" installed from "image:///
opt/app-root/s2i/bin/run"
I0619 17:40:25.979099 66356 install.go:251] Using "save-artifacts" installed from
"image:///opt/app-root/s2i/bin/save-artifacts"
---> Installing application source
---> Building application from source
-----> Installing dependencies with pip (requirements.txt)
Collecting Django (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading Django-1.9.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (6.6MB)
…
E0619 17:40:51.152317 66356 util.go:91] + python manage.py collectstatic --noinput
-----> Collecting static files for Django
Copying ‘/…/urlify.js’
…
56 static files copied to '/opt/app-root/src/static'.
---> Fix permissions on application source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warpdrivemakingpythonwebapplicationdeploymentmagicallyeasy-160815030801/85/warpdrive-making-Python-web-application-deployment-magically-easy-39-320.jpg)