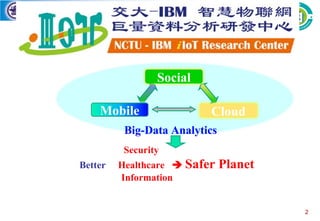
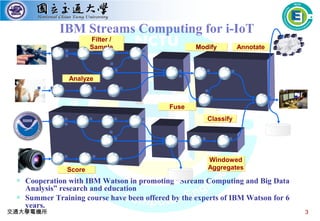
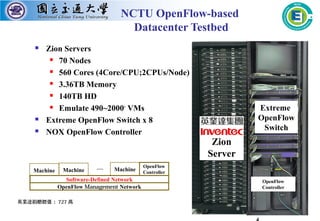
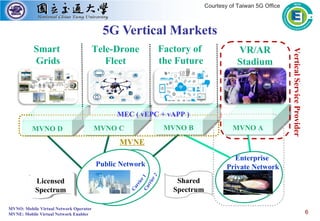
The mobile computing lab is led by Professor Li-Chun Wang whose research interests include 5G wireless communications, data-driven learning for radio resource management, and big data analytics for industrial IoT. The lab has partnerships with IBM Watson for stream computing education and research and has received funding from IBM to support an openflow-based datacenter testbed with servers, switches and controllers donated by Extreme Networks. The lab is currently working on several projects applying AI techniques to problems in drone communications networks, industrial IoT latency and reliability, and predictive maintenance for numerical control machines.







![15
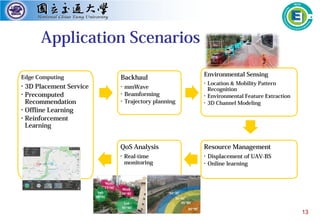
Challenge: The existing transmission mechanism can not reach the strict delay
requirements of IIoT
Network resources are limited
Traffic characteristics change dynamically
Approach: Delay-aware group-based MTC scheme
Adaptively adjust aggregation buffer size based on the change of real-time traffic
Adaptive cluster partition scheme by bin packing based on delay performance
Gain:
[Uplink transmission latency] 303 ms → 113 ms (↓62%)
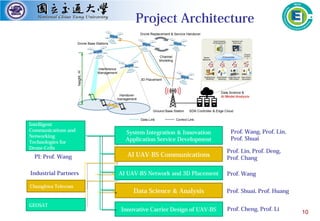
5G Machine Type Communications for Latency-Aware Industrial
Internet of Things (IIoT)
303 ms303 ms
113 ms113 ms
62%62%
Move
Reliable Device-
aggregator Associations
Fixed Aggregator
Moving
Aggregator
IIoT TestbedIIoT Testbed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wanglabintroduction12042018-190109120804/85/Wang-lab-introduction_1204_2018-15-320.jpg)
![16
Challenge: The existing 802.11ad link setup latency
can not reach the AR/VR requirement.
802.11ad link setup latency: >40 ms
AR/VR latency requirement: ~ 4 ms
Approach:
AI-based light-weight WiFi fingerprint beam search
Gain:
[Beam search latency] 10.95 ms → 1.09 ms (↓90%)
[Probability of availability] 89% → 98% (↑11%)
Low-Latency High-availability 5G Indoor Communications
Training Trajectory
Signal Mapping
Ideal Practical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wanglabintroduction12042018-190109120804/85/Wang-lab-introduction_1204_2018-16-320.jpg)
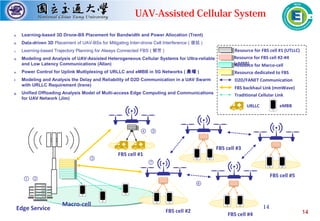
![17
UPER scheme
Almost achieve
URLLC requirement
Delay requirement (1 ms)
Challenge: How to avoid resource collision between urgent uplink URLLC
with other services (e.g., eMBB or mMTC)?
Approach:
User-initiated probabilistic elastic reservation (UPER) scheme
Probabilistic resource selection between dedicated and shared resource blocks.
K-repetition transmit in frequency domain.
Gain: (For 0.25 ms grant-free transmission interval)
[Average delay time] 0.56 ms → 0.385 ms (↓31%)
[1 ms delay reliability] 85.59% → 99.994% (↑14.404%)
Resource sharing for 5G URLLC Cellular Systems
UPER
others
URLLC
Unreserved
others
URLLC
URLLC dedicated resources
Shared resources
URLLC
UL traffic
eMBB/mMTC
UL traffic
Resource blocks
Reserved resources
UL UL UL UL UL UL UL
0.25 ms
URLLC:
Ultra Reliable Ultra Low
Latency Communications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wanglabintroduction12042018-190109120804/85/Wang-lab-introduction_1204_2018-17-320.jpg)


