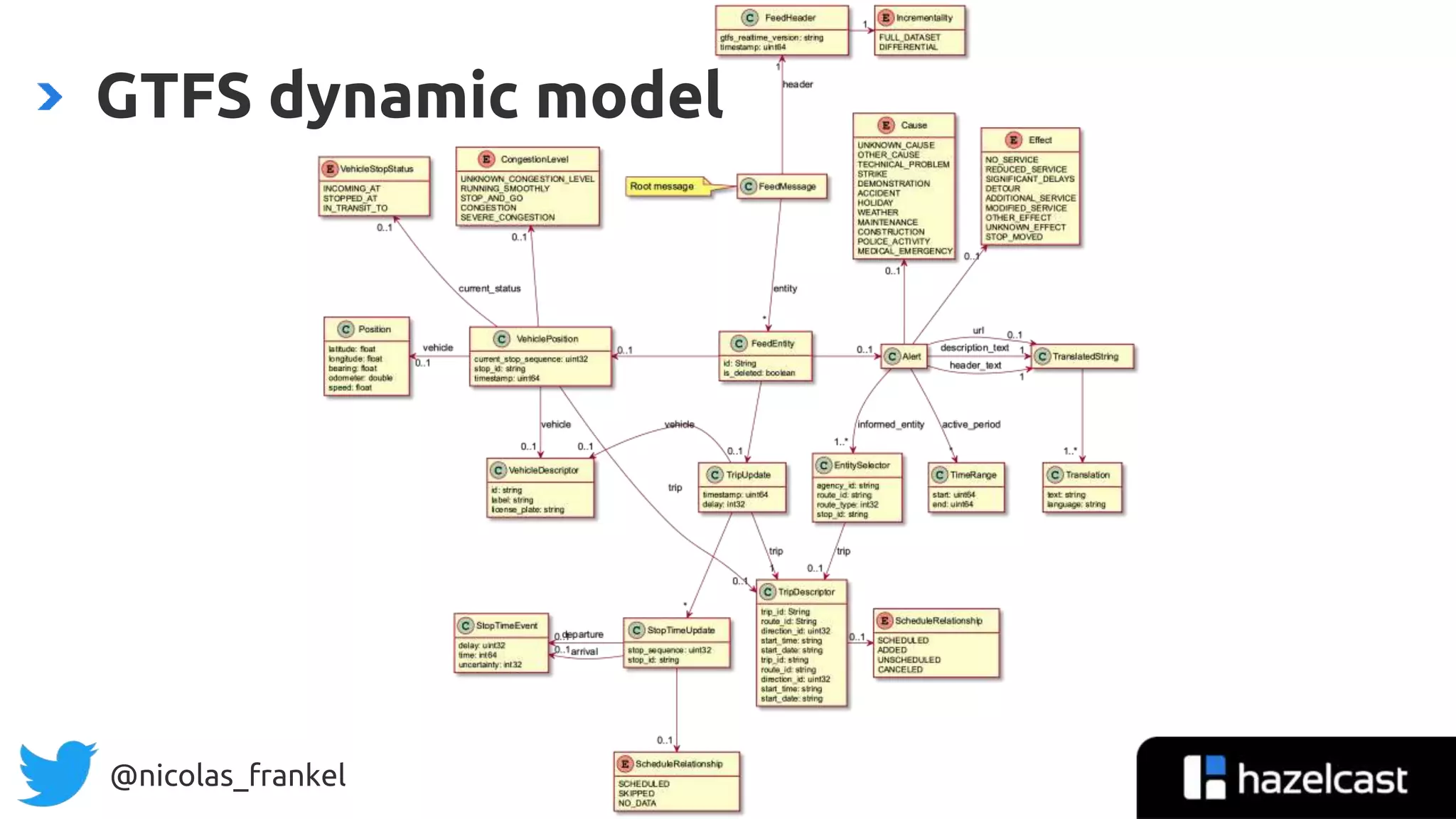
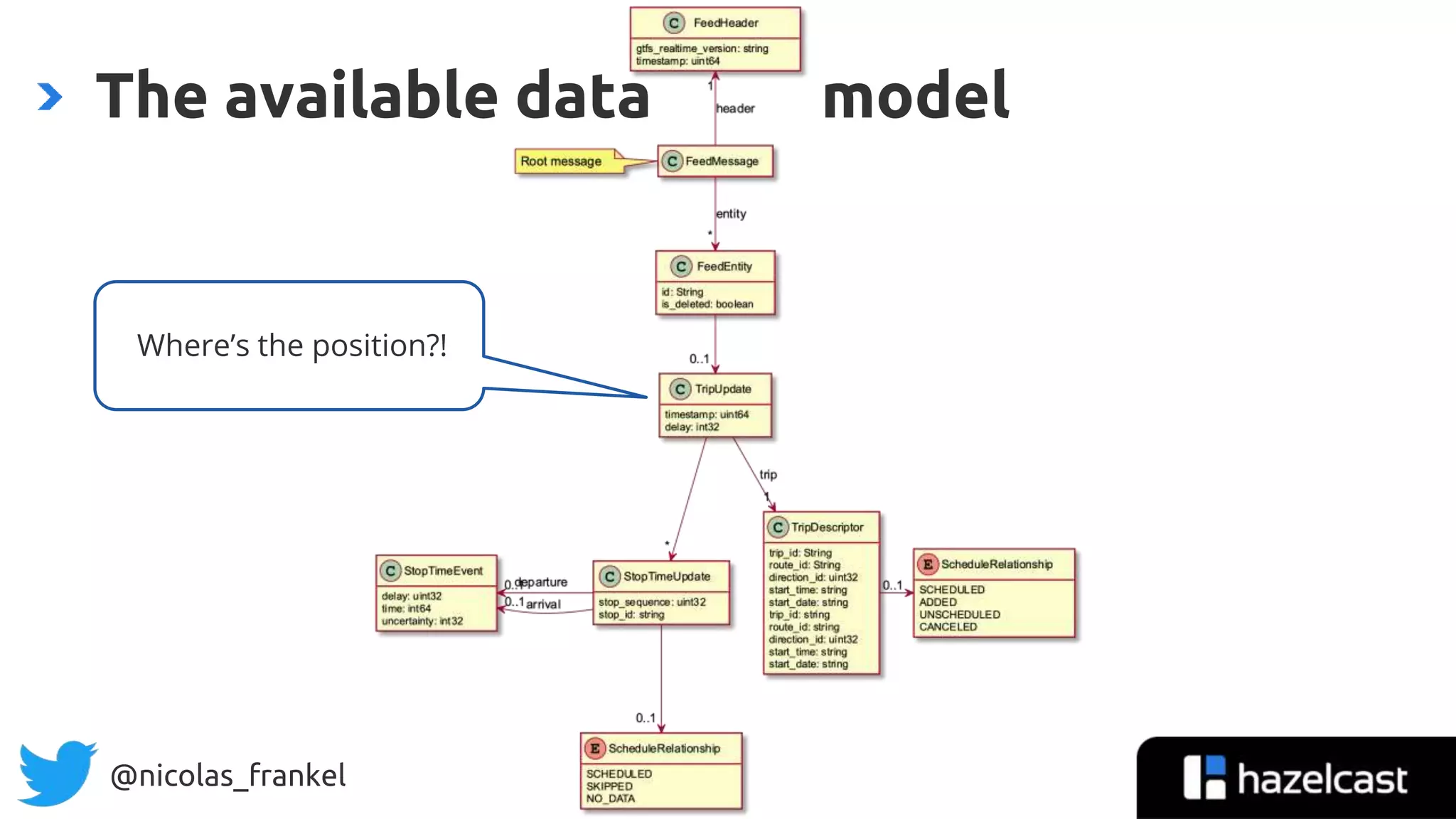
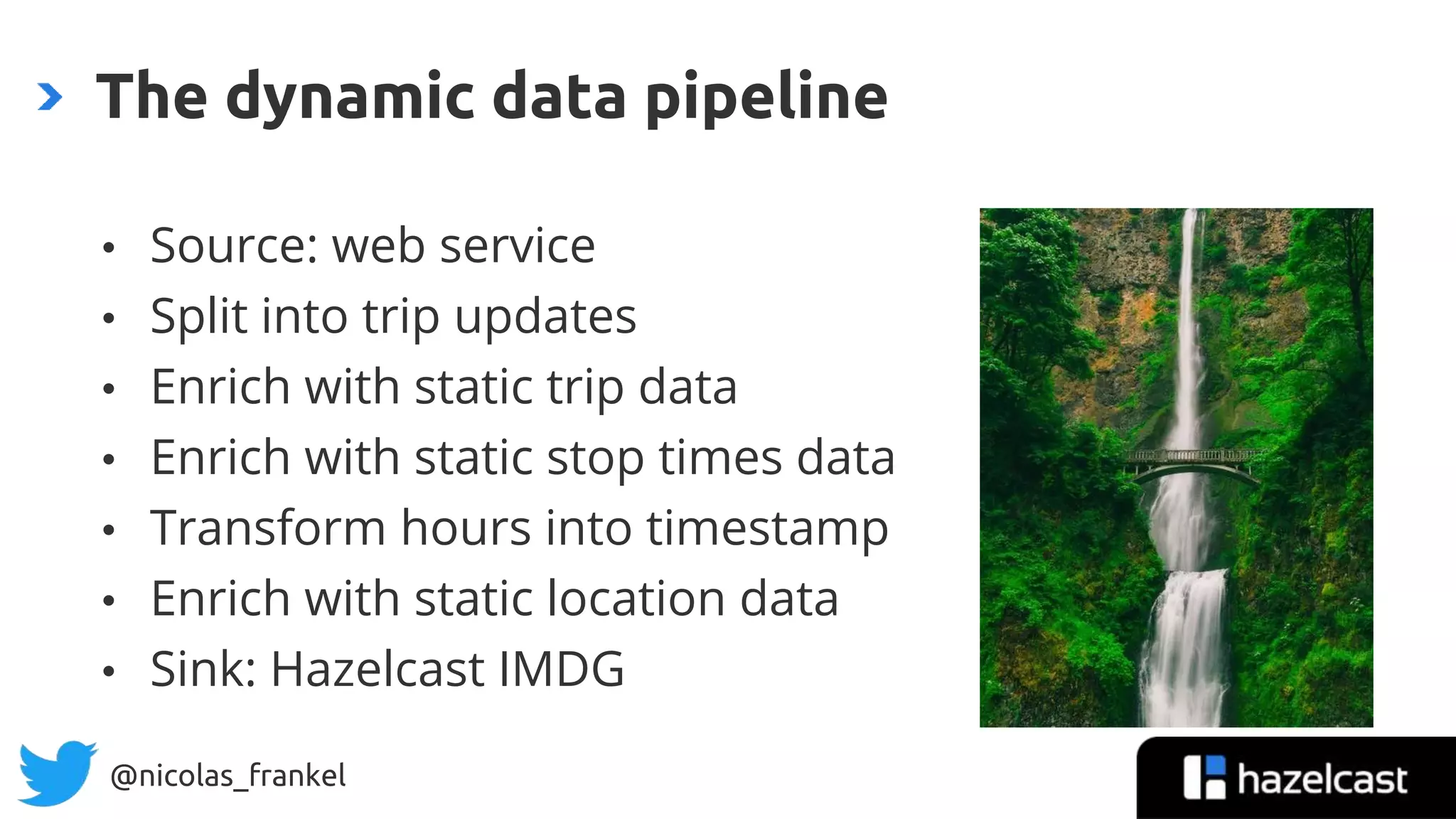
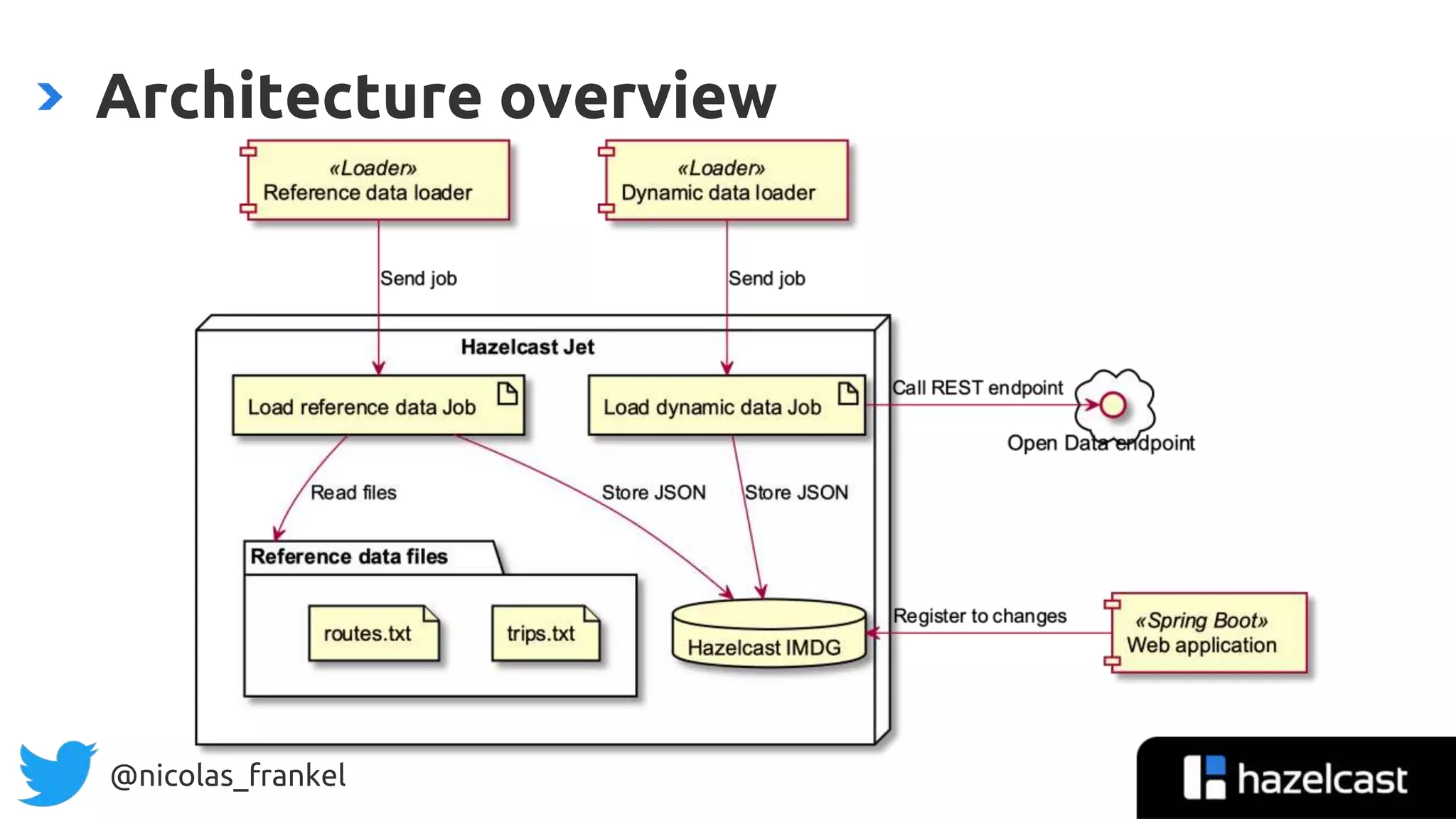
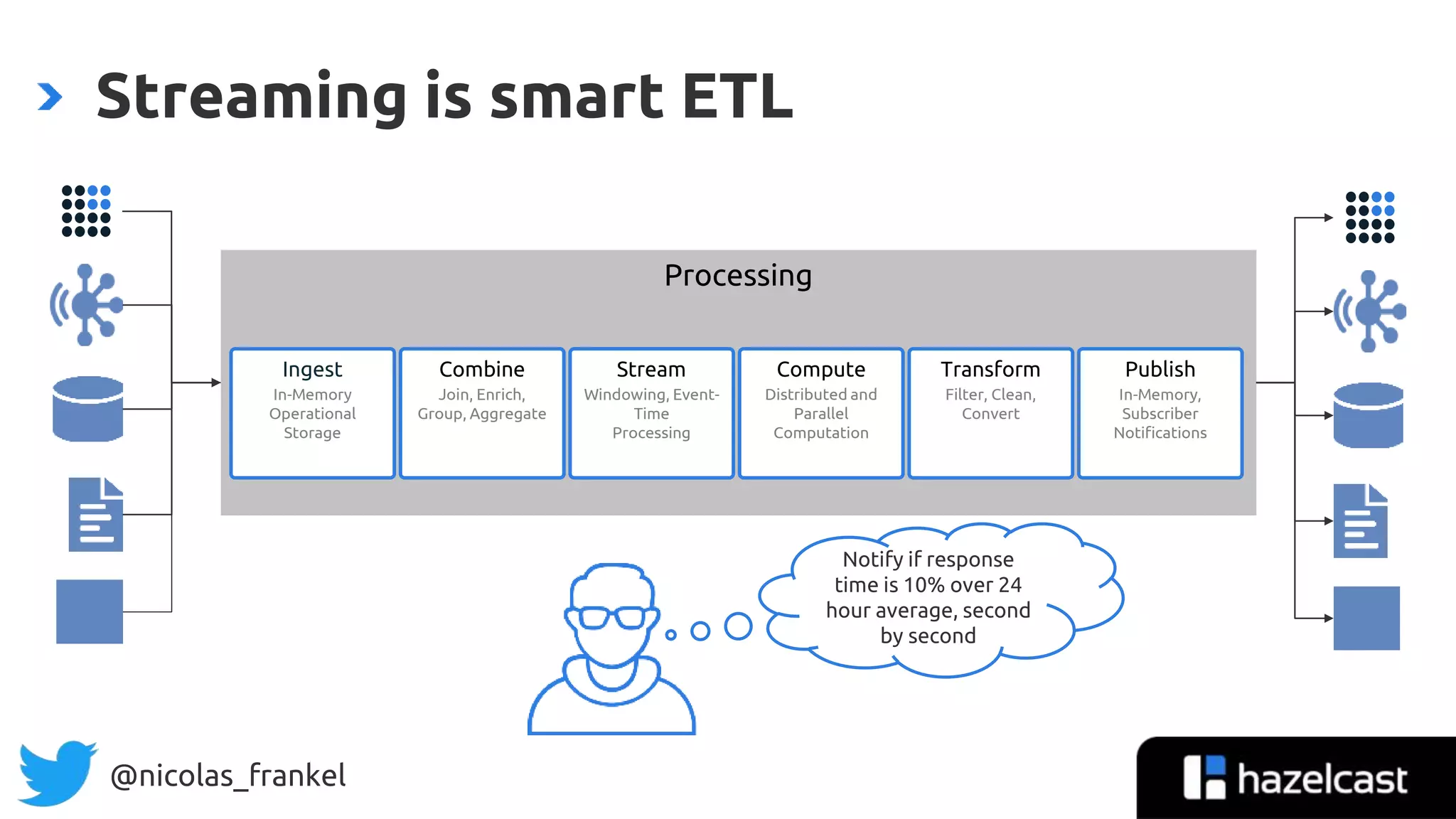
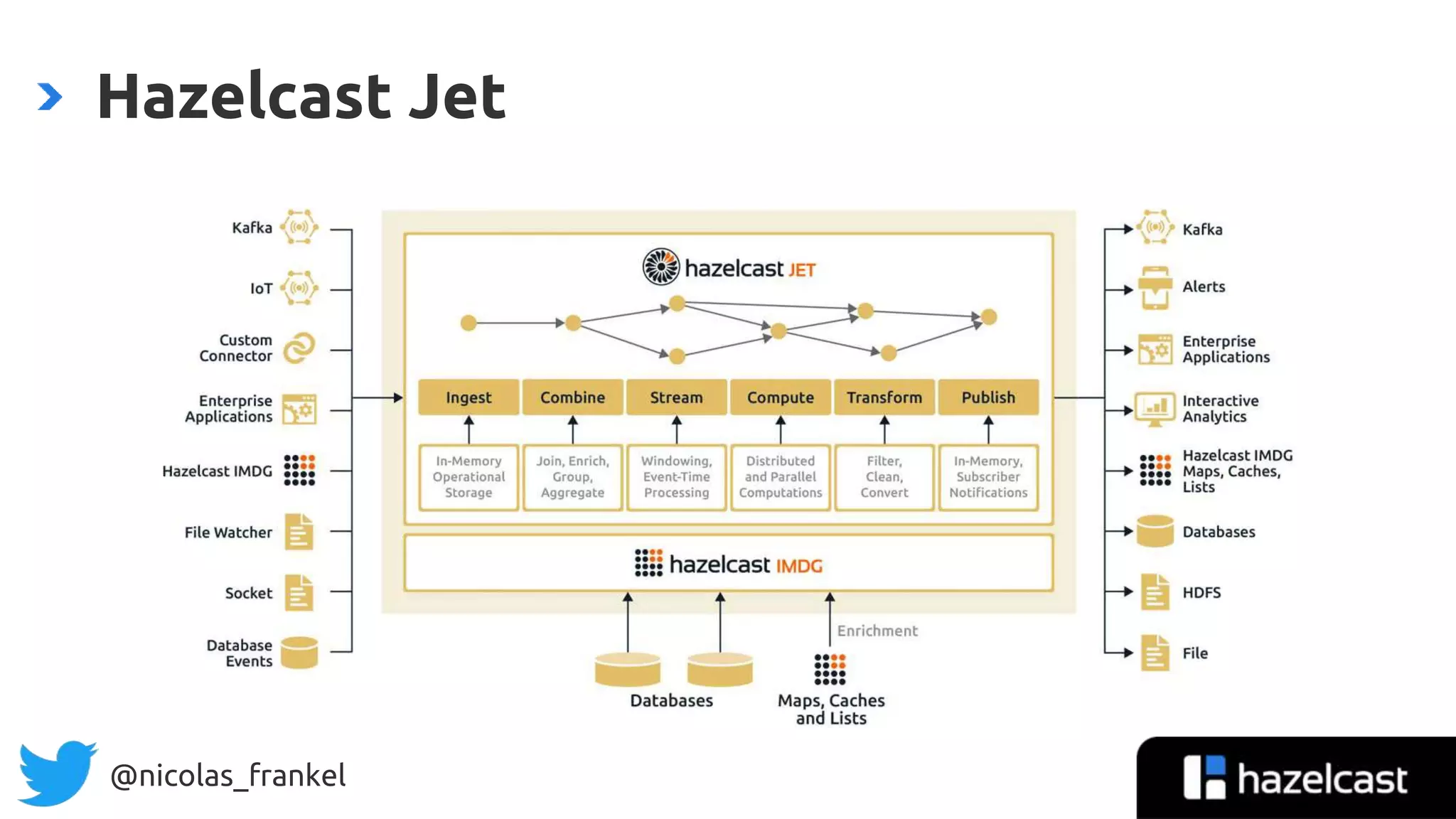
The document is an introduction to data streaming, focusing on Hazelcast's IMDG and Jet for processing. It discusses the evolution from SQL databases and batch processing to real-time streaming, emphasizing the benefits of event-driven programming and leveraging open data. Additionally, it covers key concepts such as the General Transit Feed Specification (GTFS) for public transport data and the design of dynamic data pipelines.




























![@nicolas_frankel
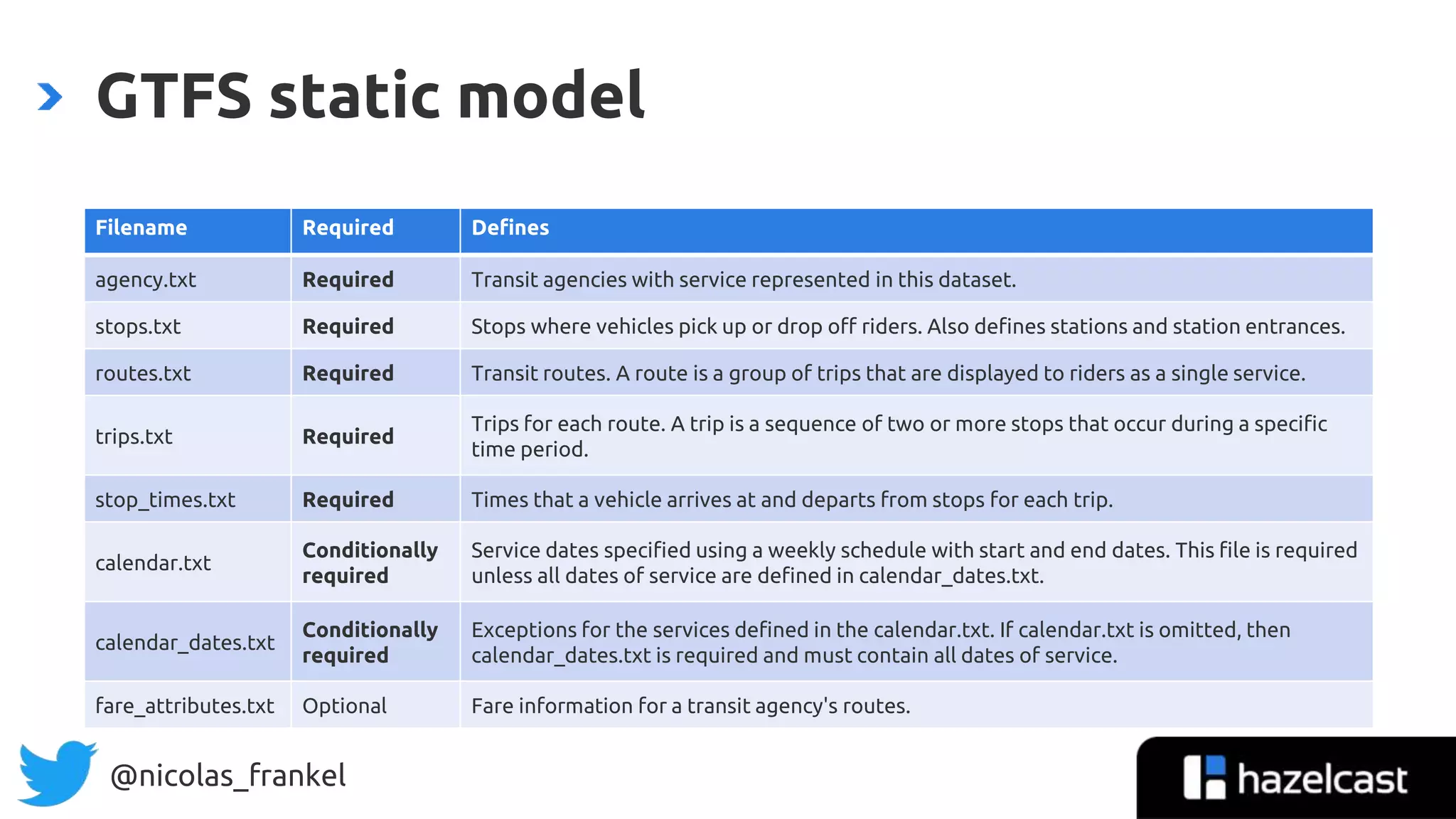
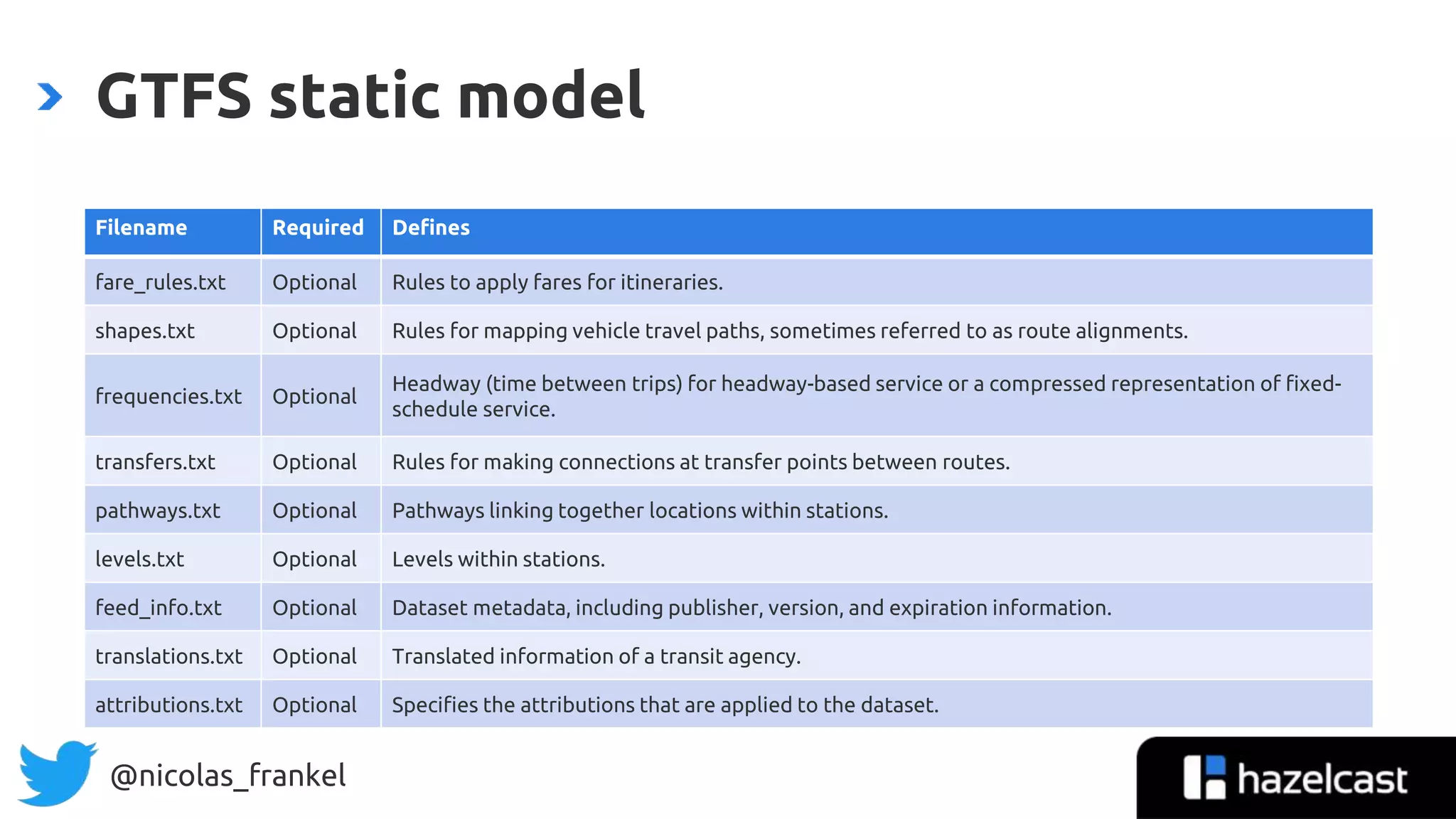
General Transit Feed Specification
”The General Transit Feed Specification (GTFS) […]
defines a common format for public transportation
schedules and associated geographic information.
GTFS feeds let public transit agencies publish their
transit data and developers write applications that
consume that data in an interoperable way.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wajug-introductiontodatastreaming-200204193329/75/WaJUG-Introduction-to-data-streaming-43-2048.jpg)