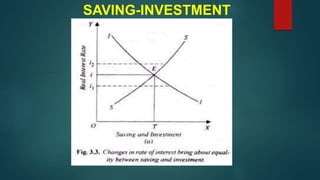
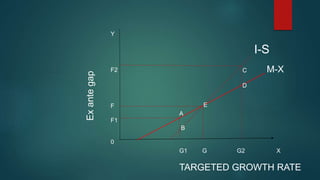
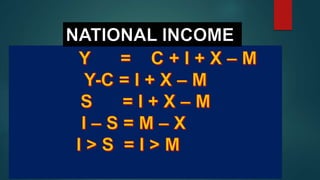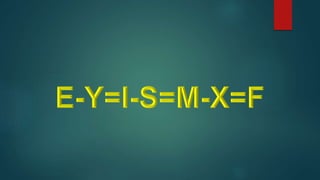This document discusses the dual gap analysis model for analyzing savings-investment gaps and foreign exchange gaps that constrain economic growth in developing countries. It explains that if a country's targeted growth rate requires higher investment than can be supported by domestic savings, there will be an ex-ante savings gap that can be filled by foreign aid inflows. Similarly, if the foreign exchange required for imports to support the targeted growth rate exceeds potential foreign exchange earnings, there will be an ex-ante foreign exchange gap that can also be filled by foreign aid. The dual gap analysis is useful for developing countries to estimate capital requirements and calculate how much investment and savings can be generated domestically versus relying on foreign resources.