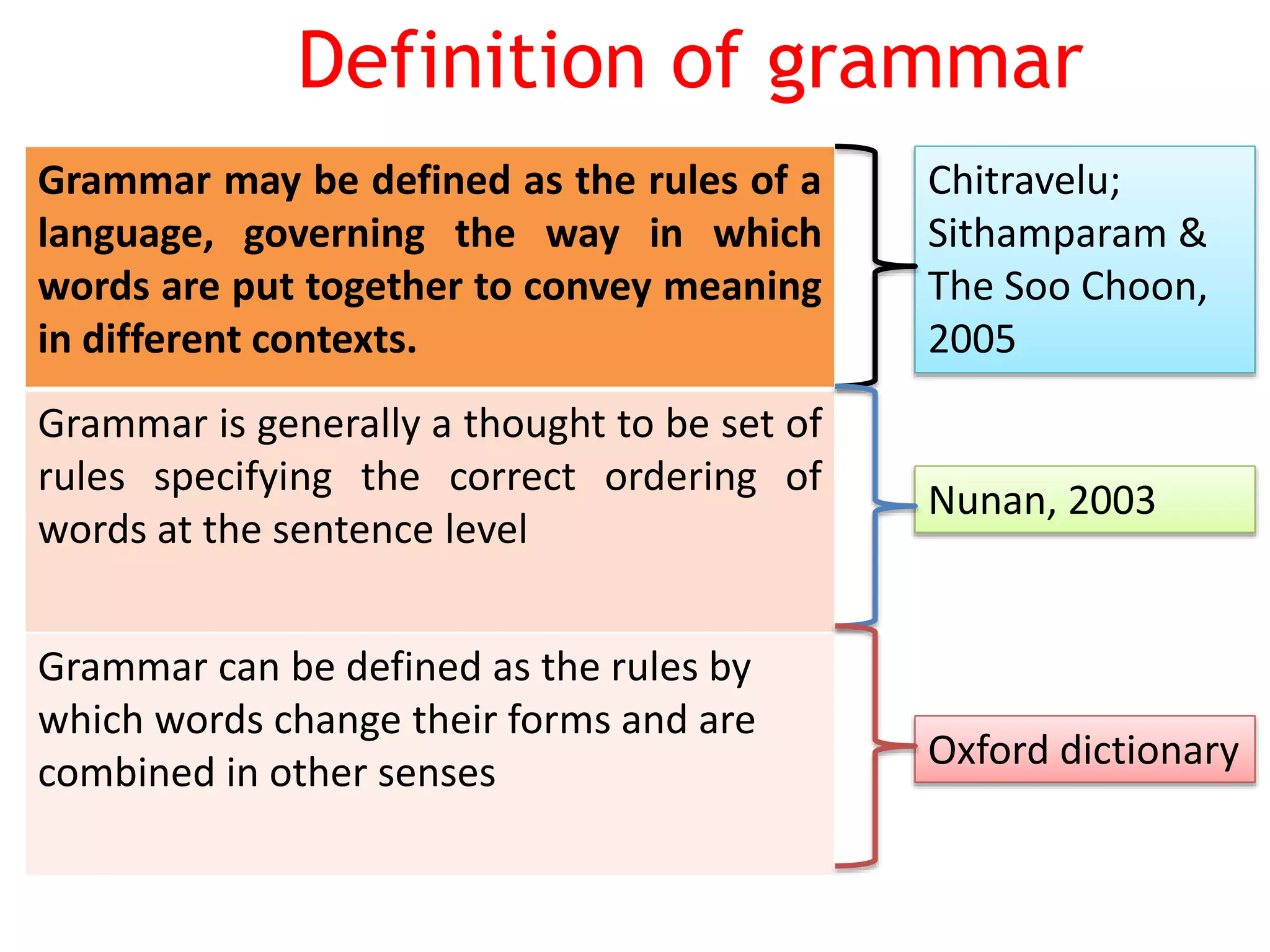
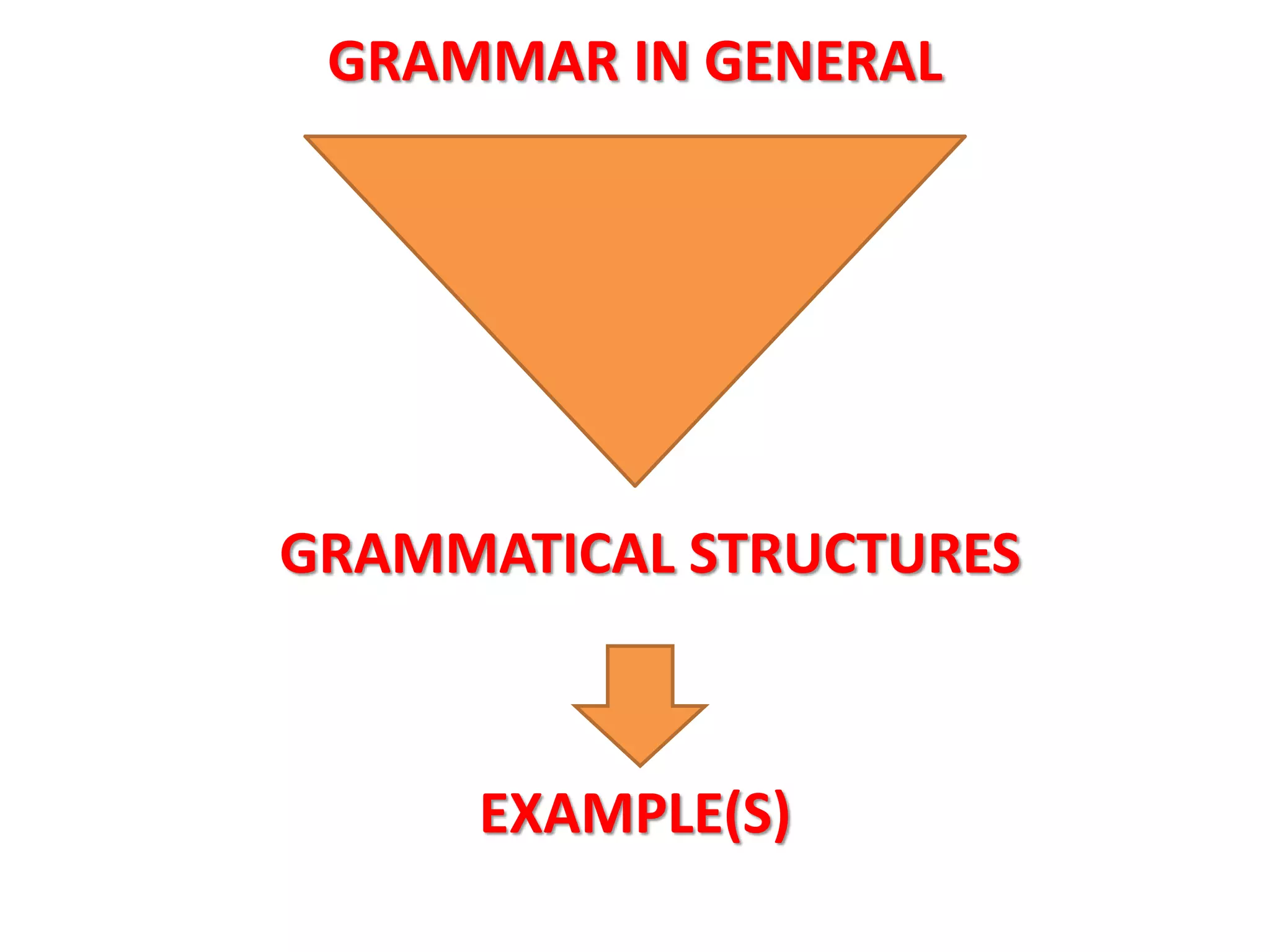
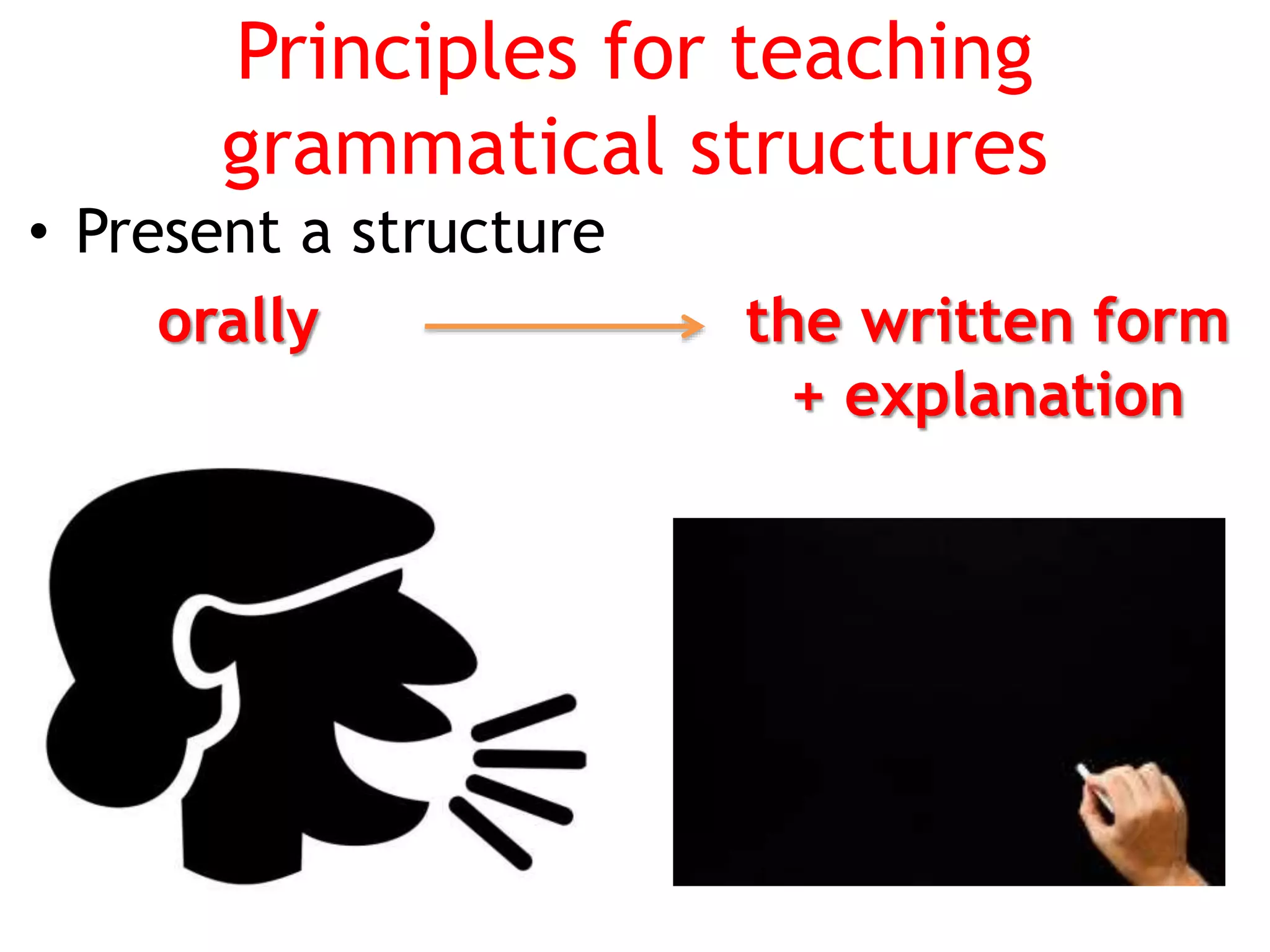
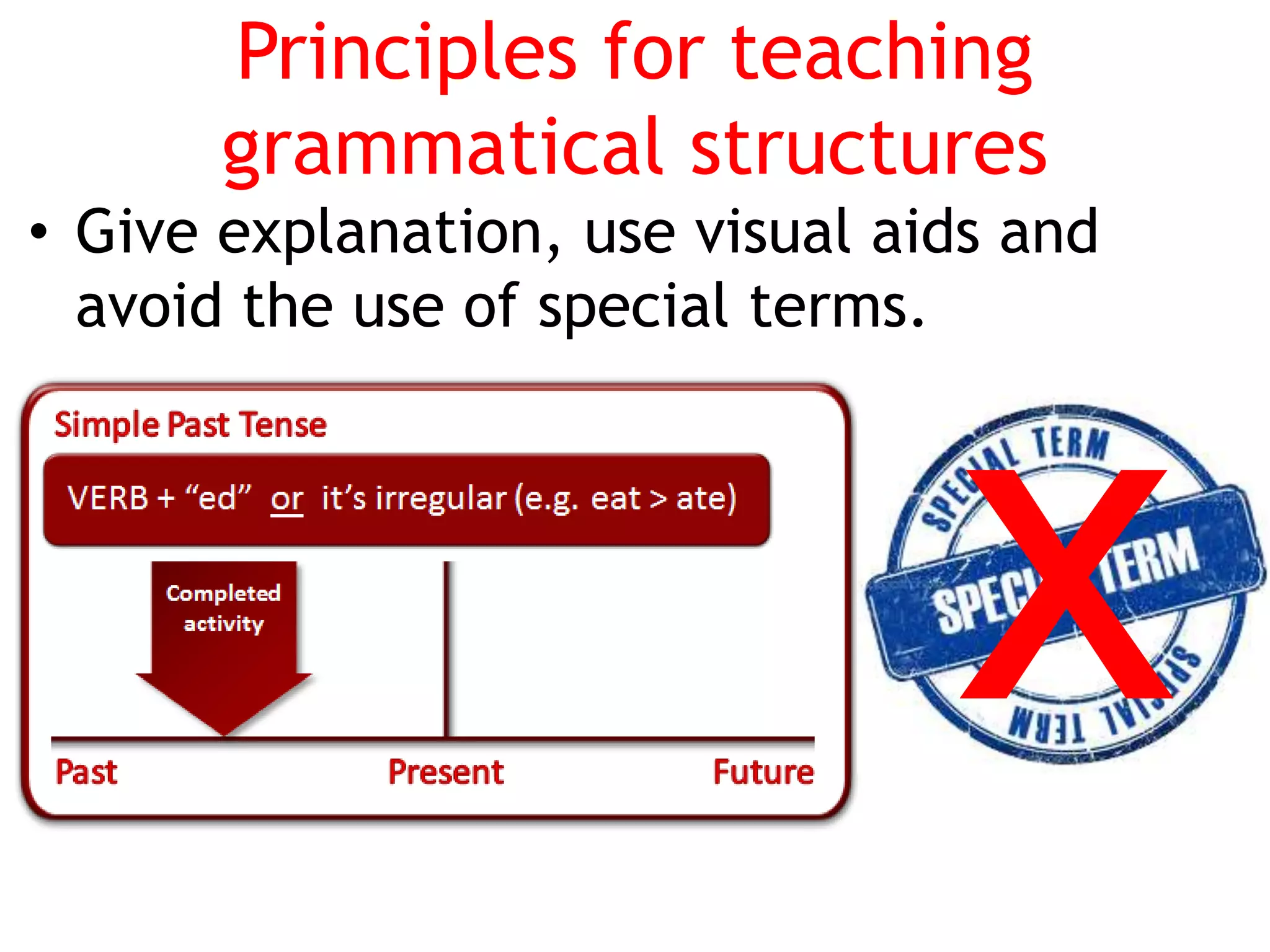
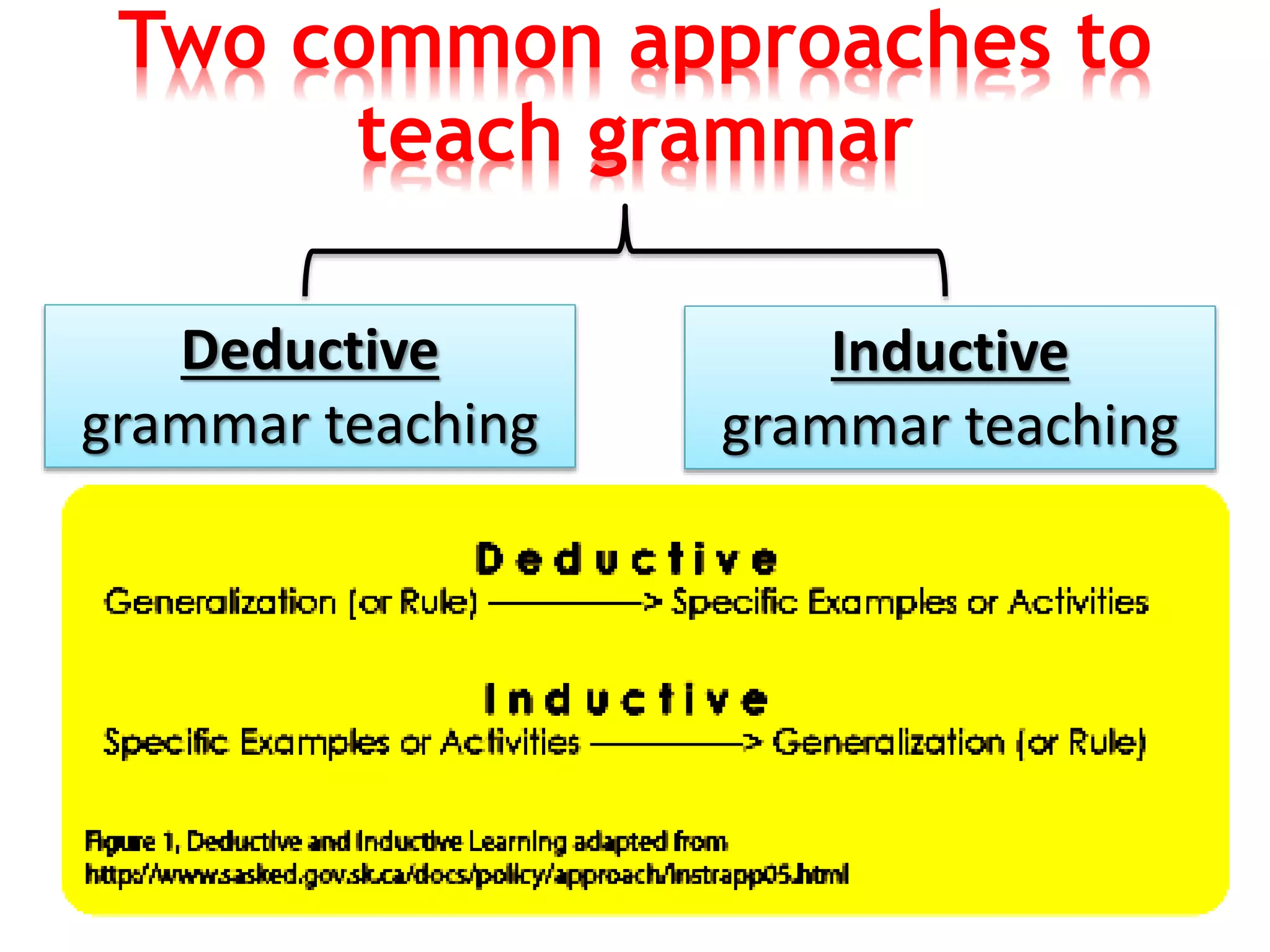
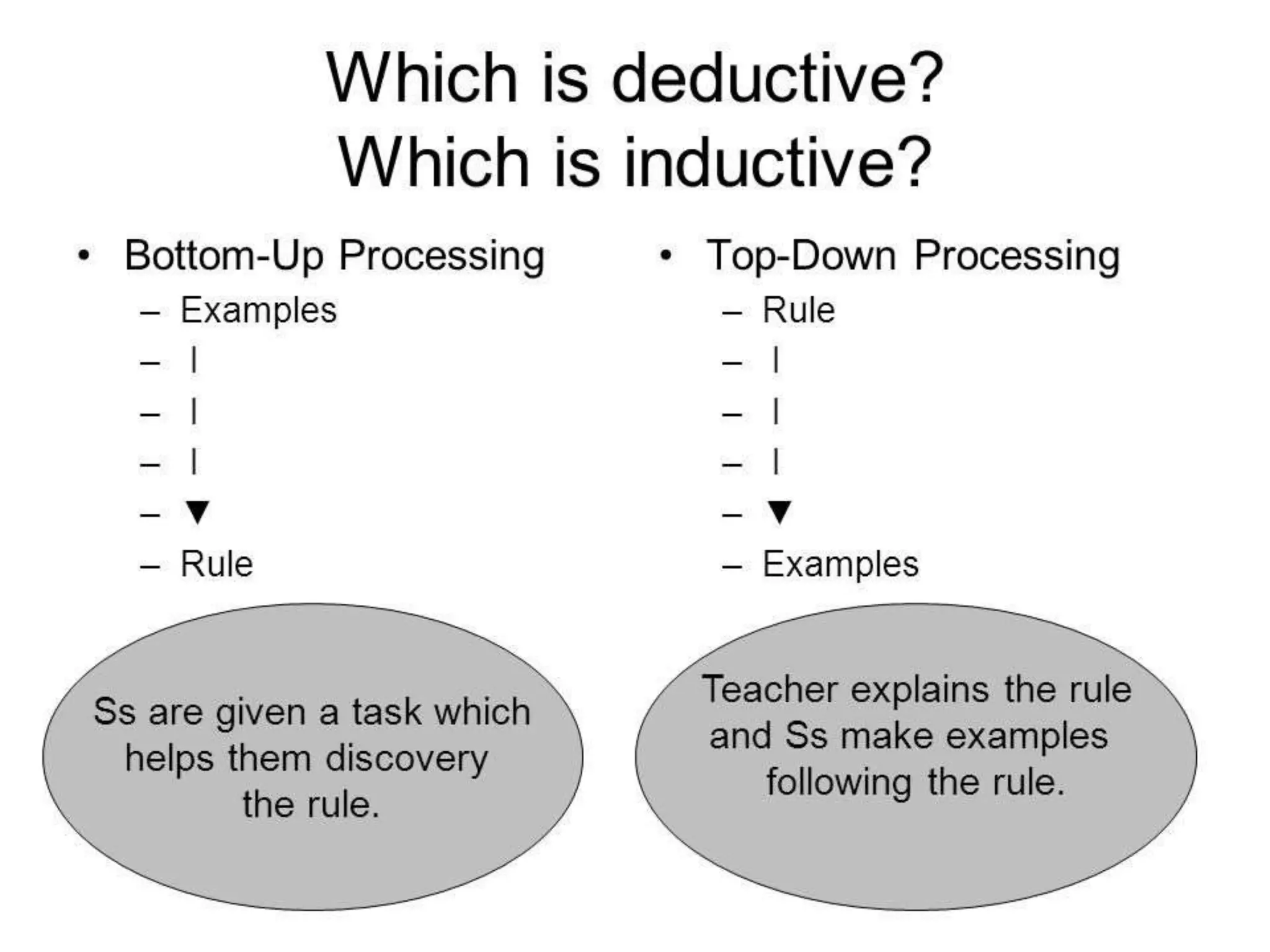
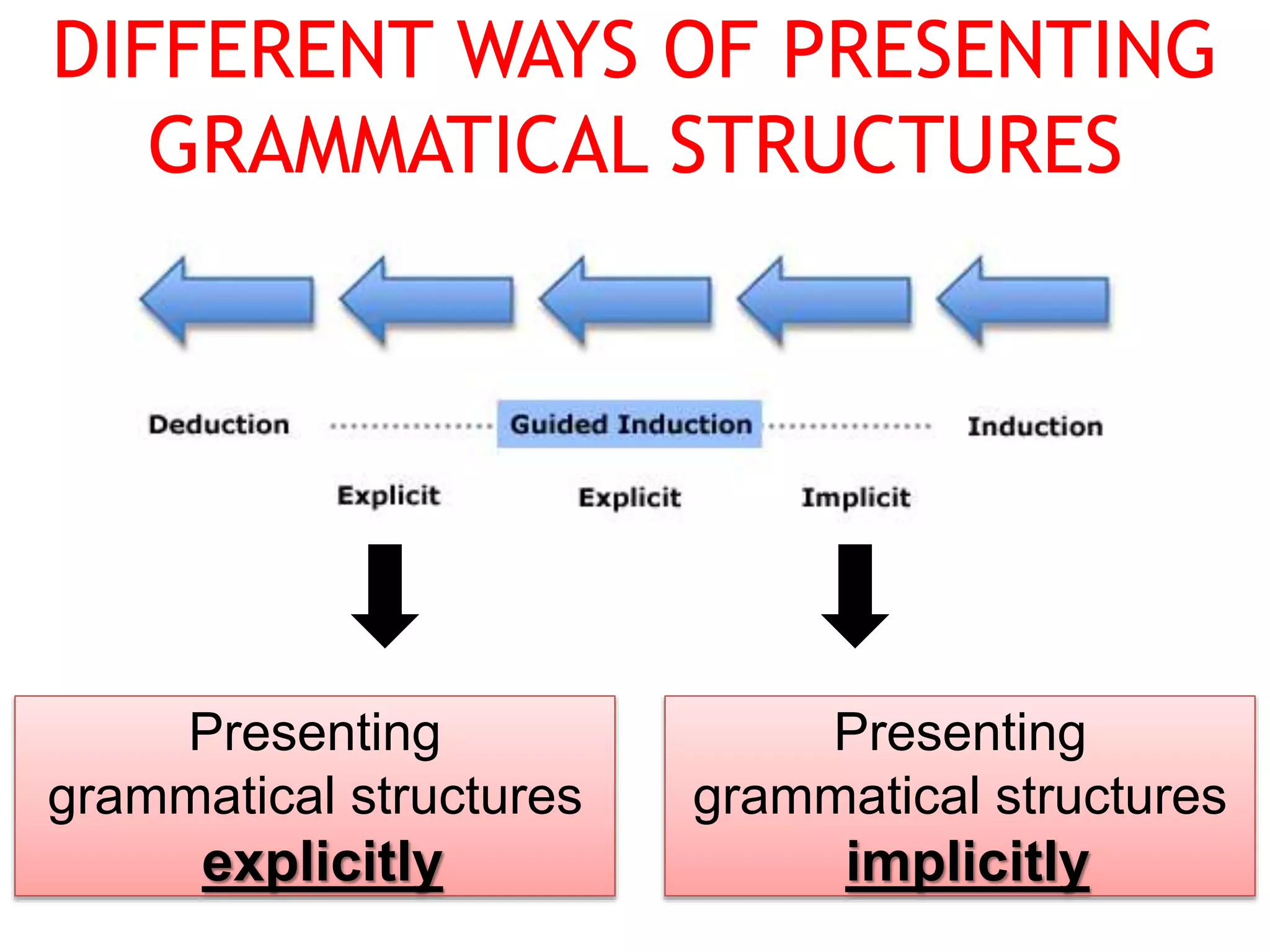
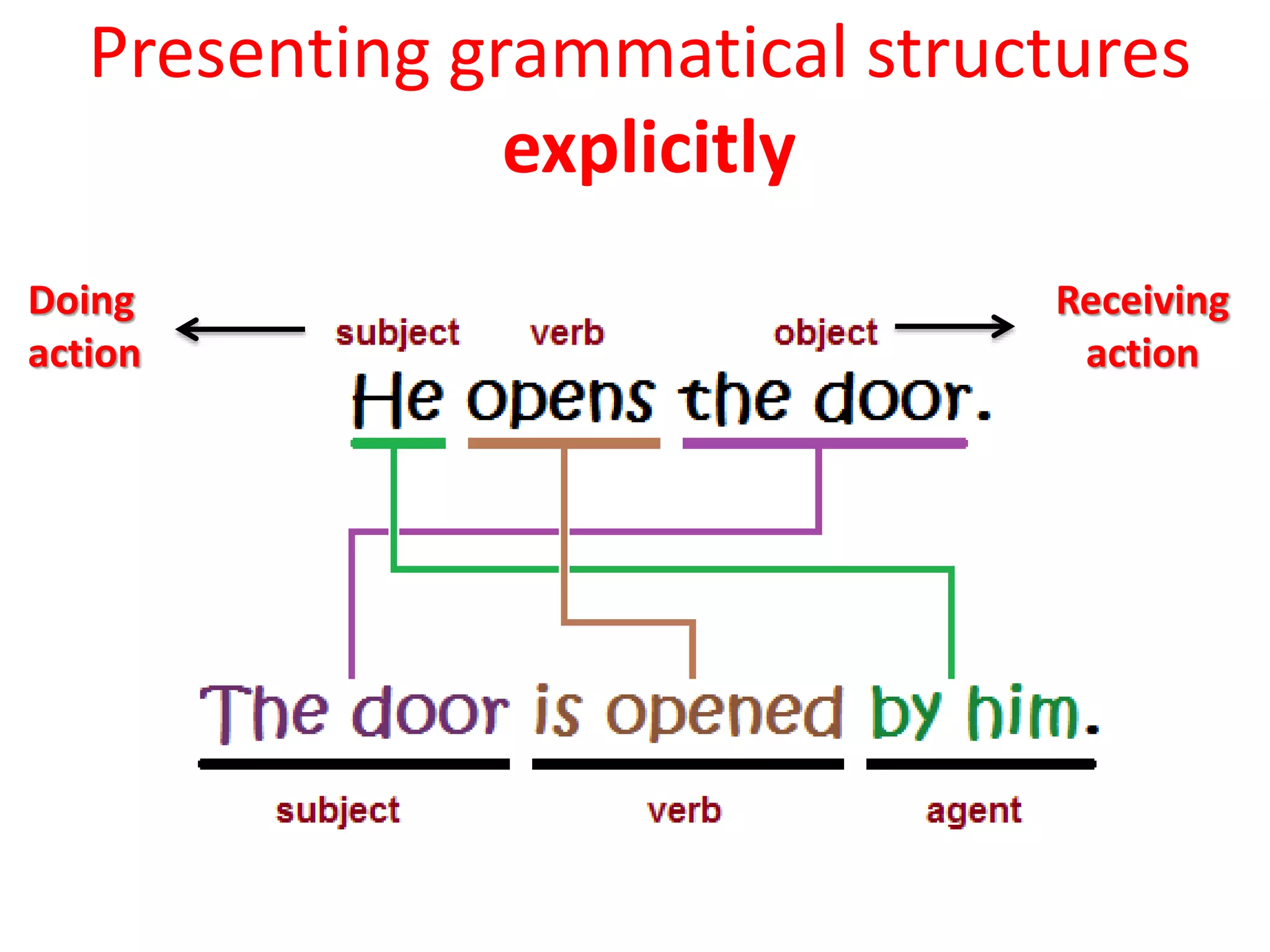
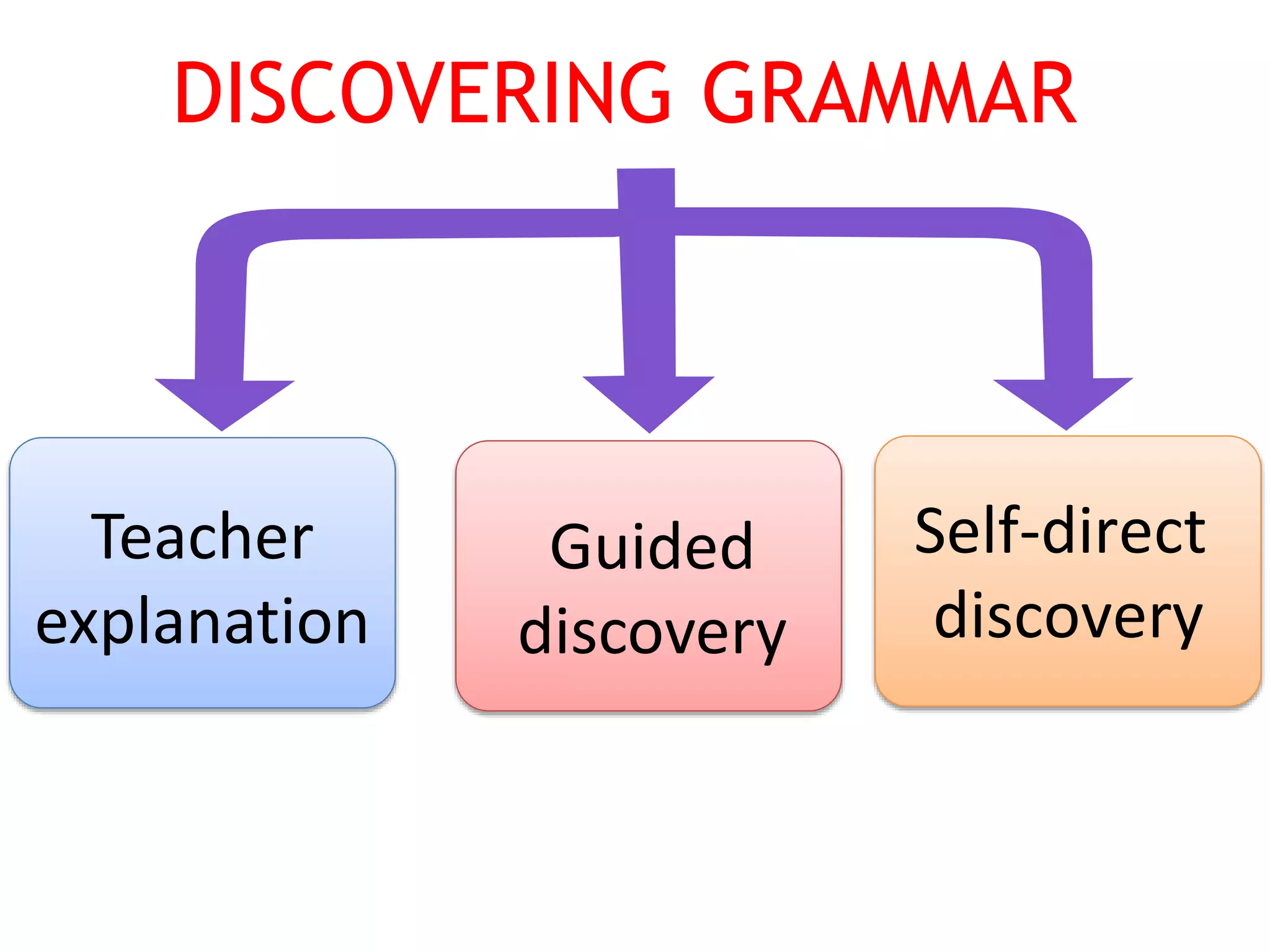
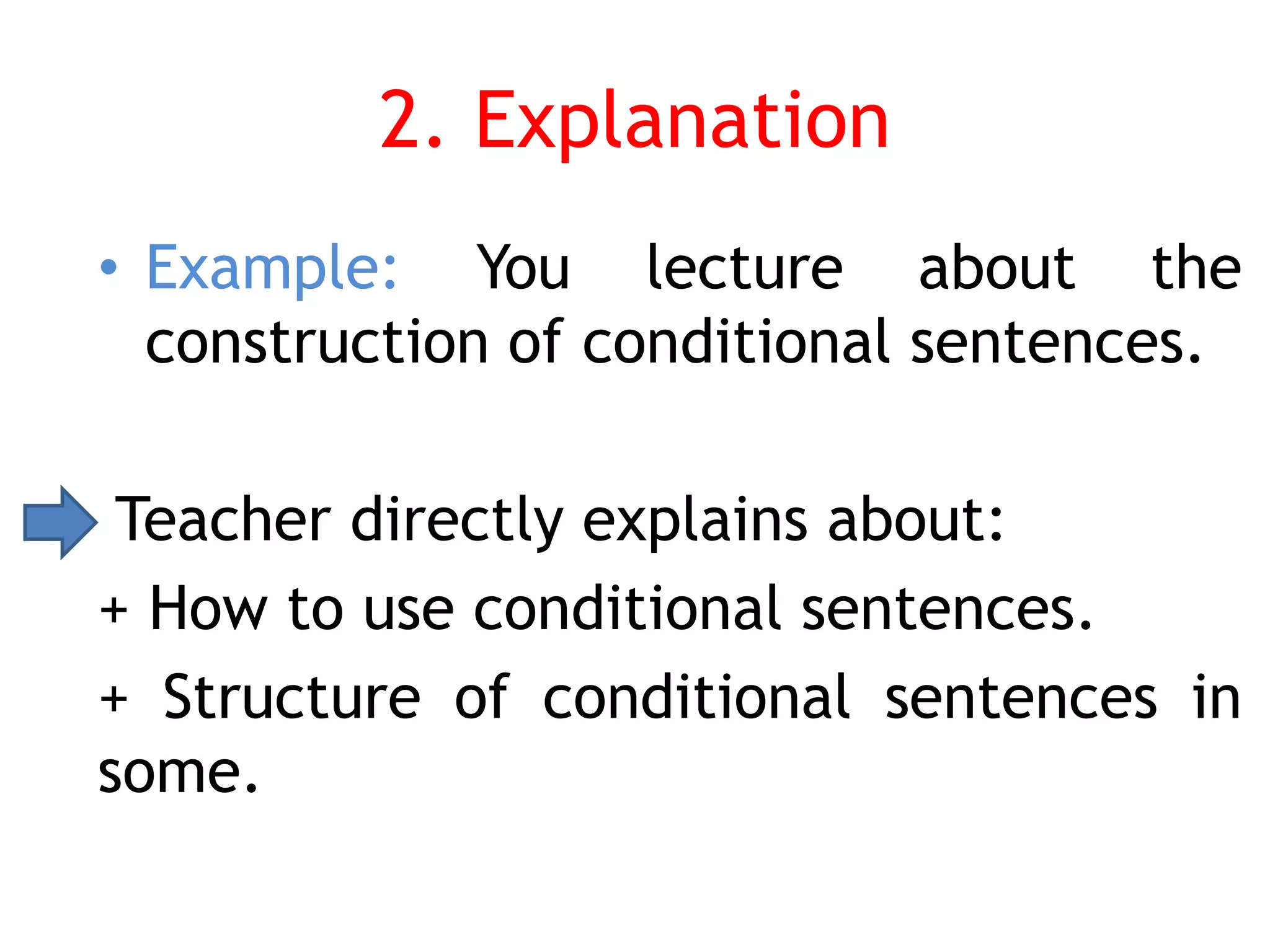
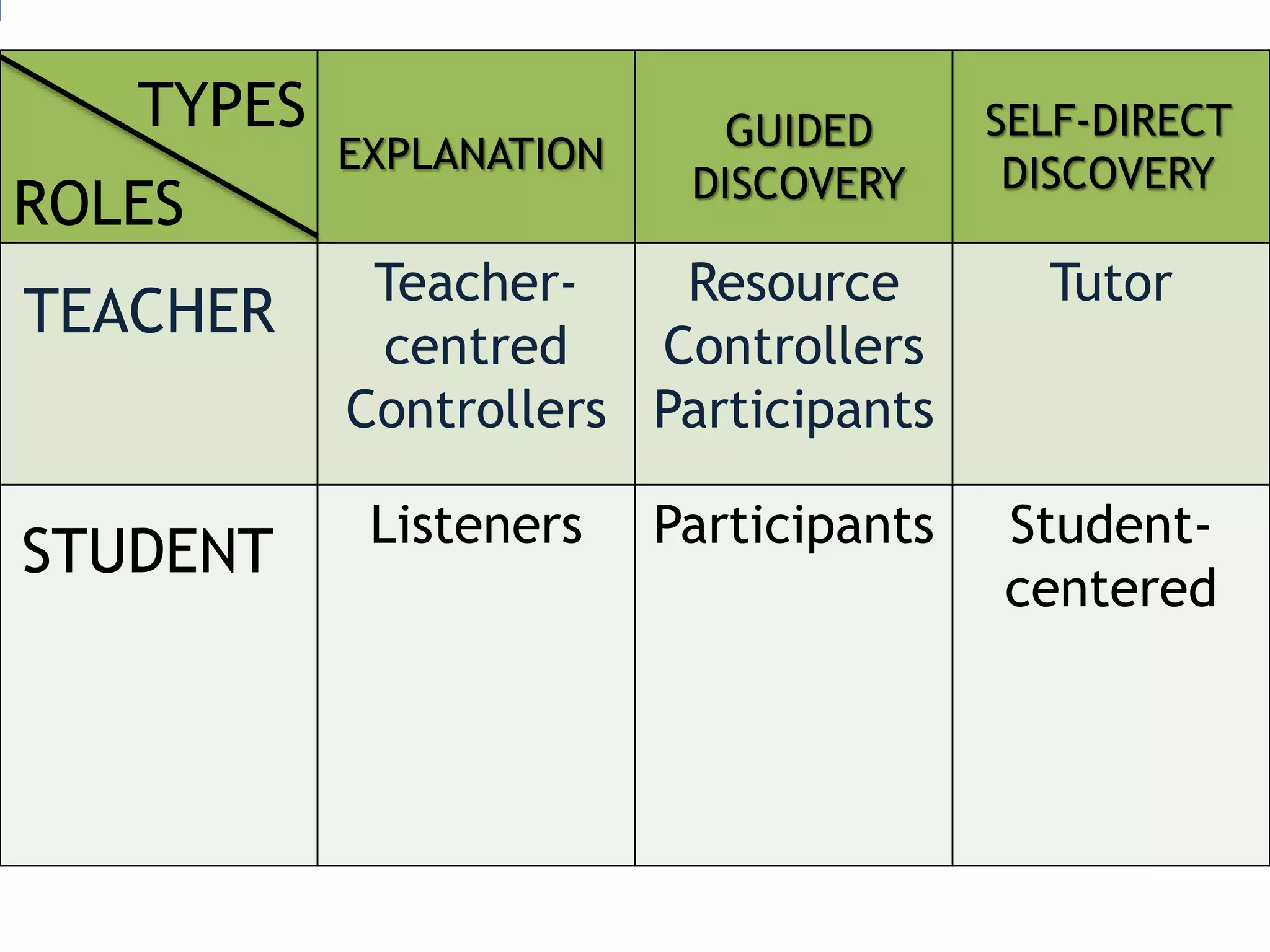
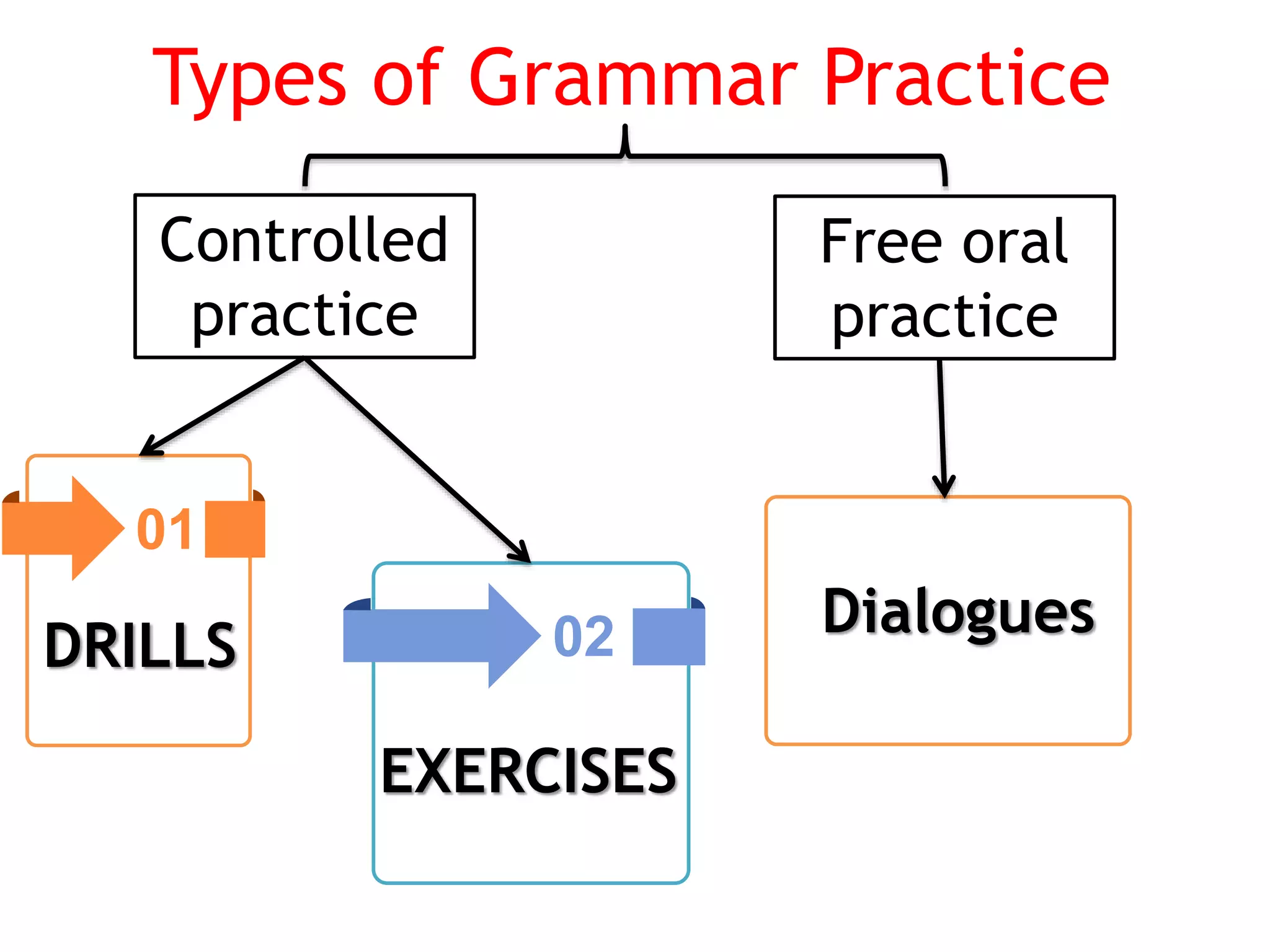
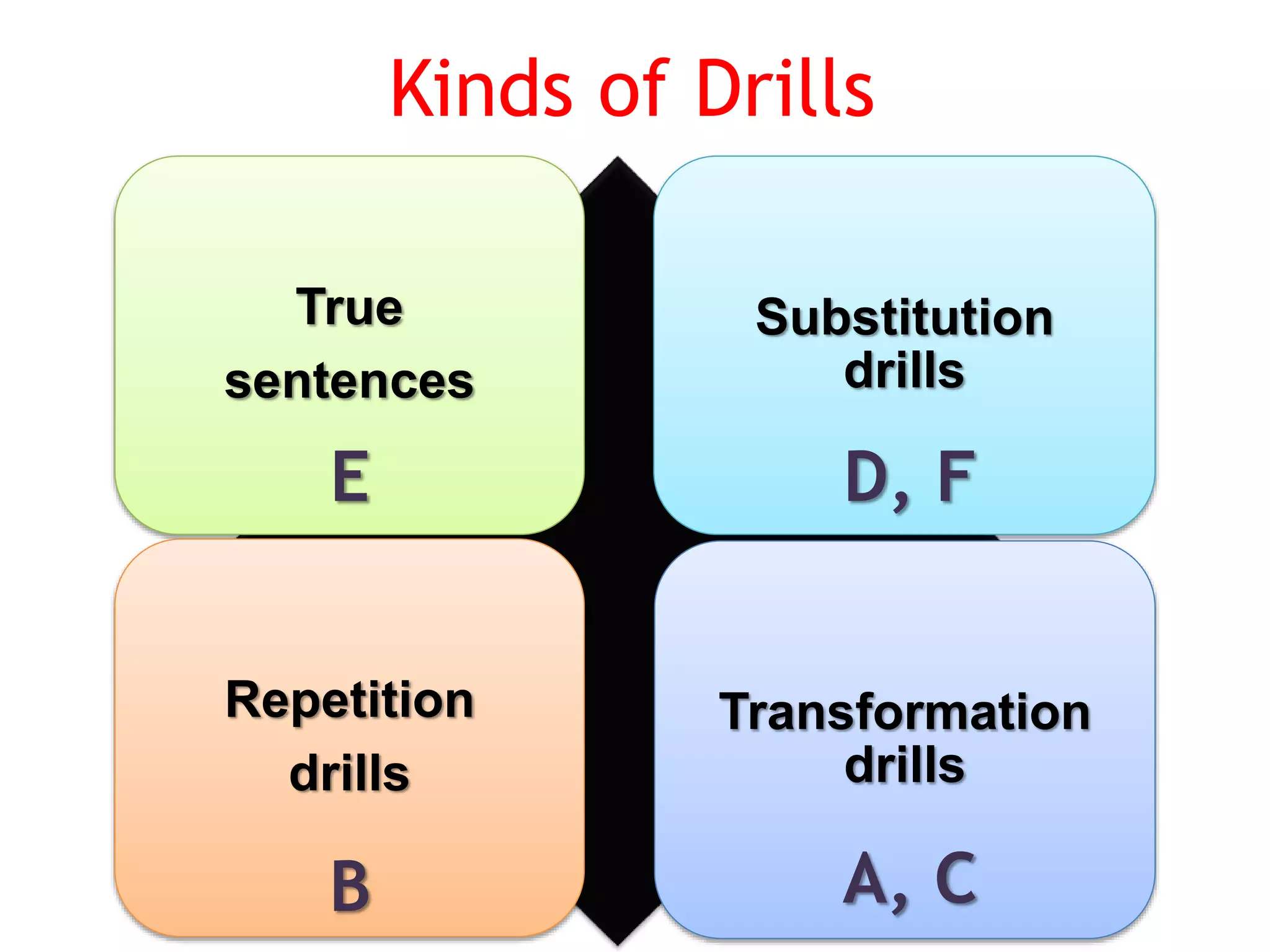
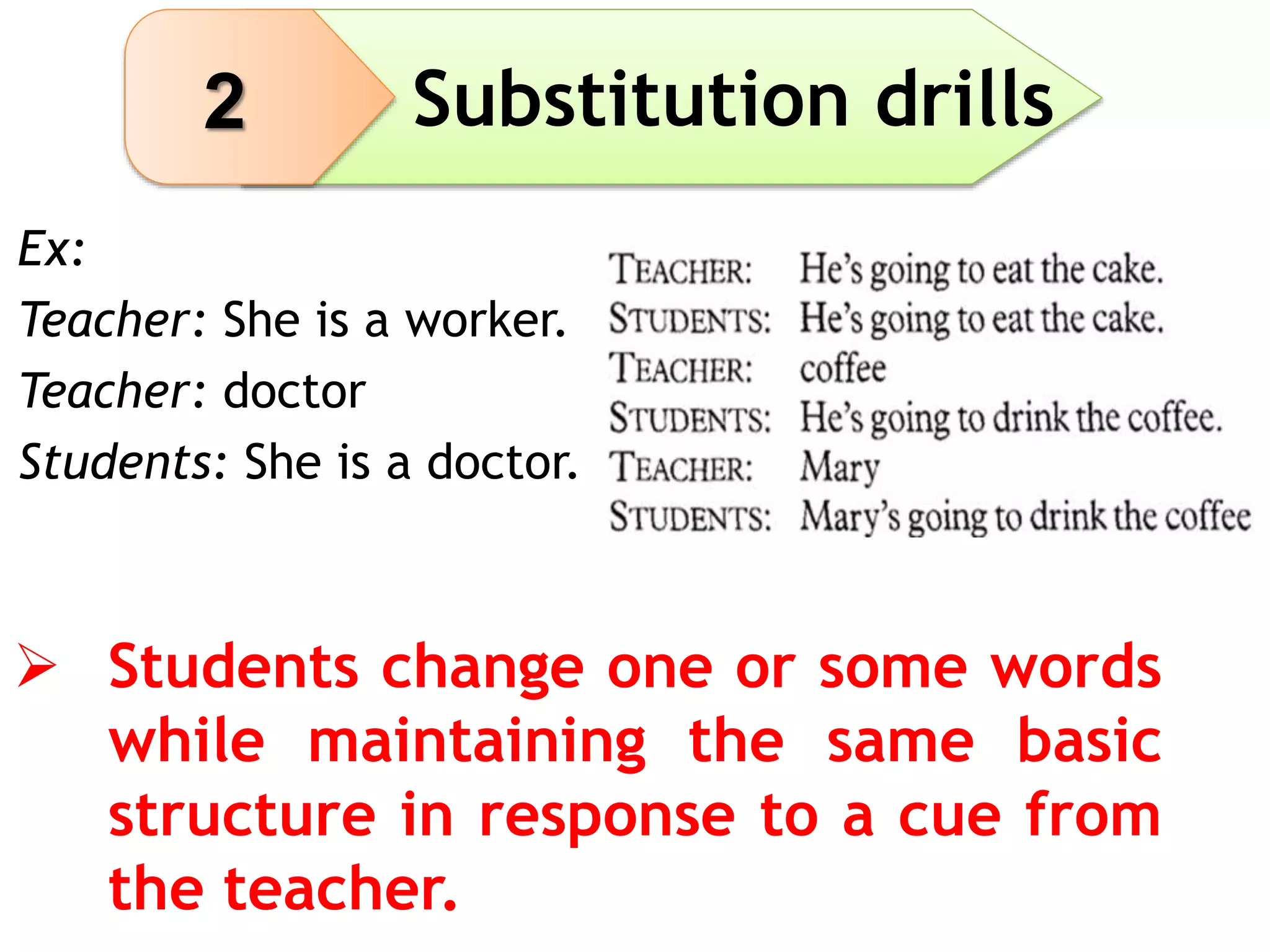
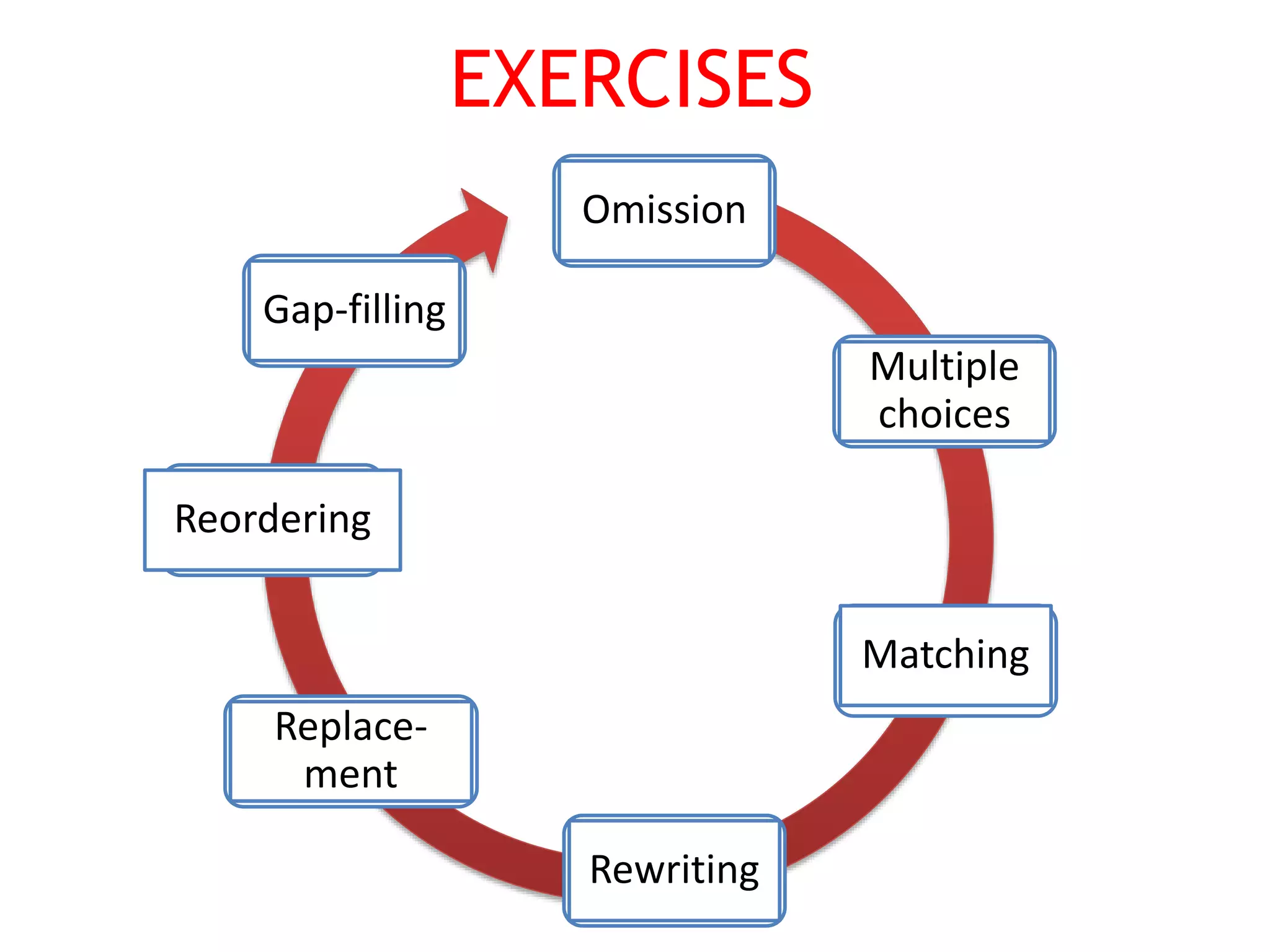
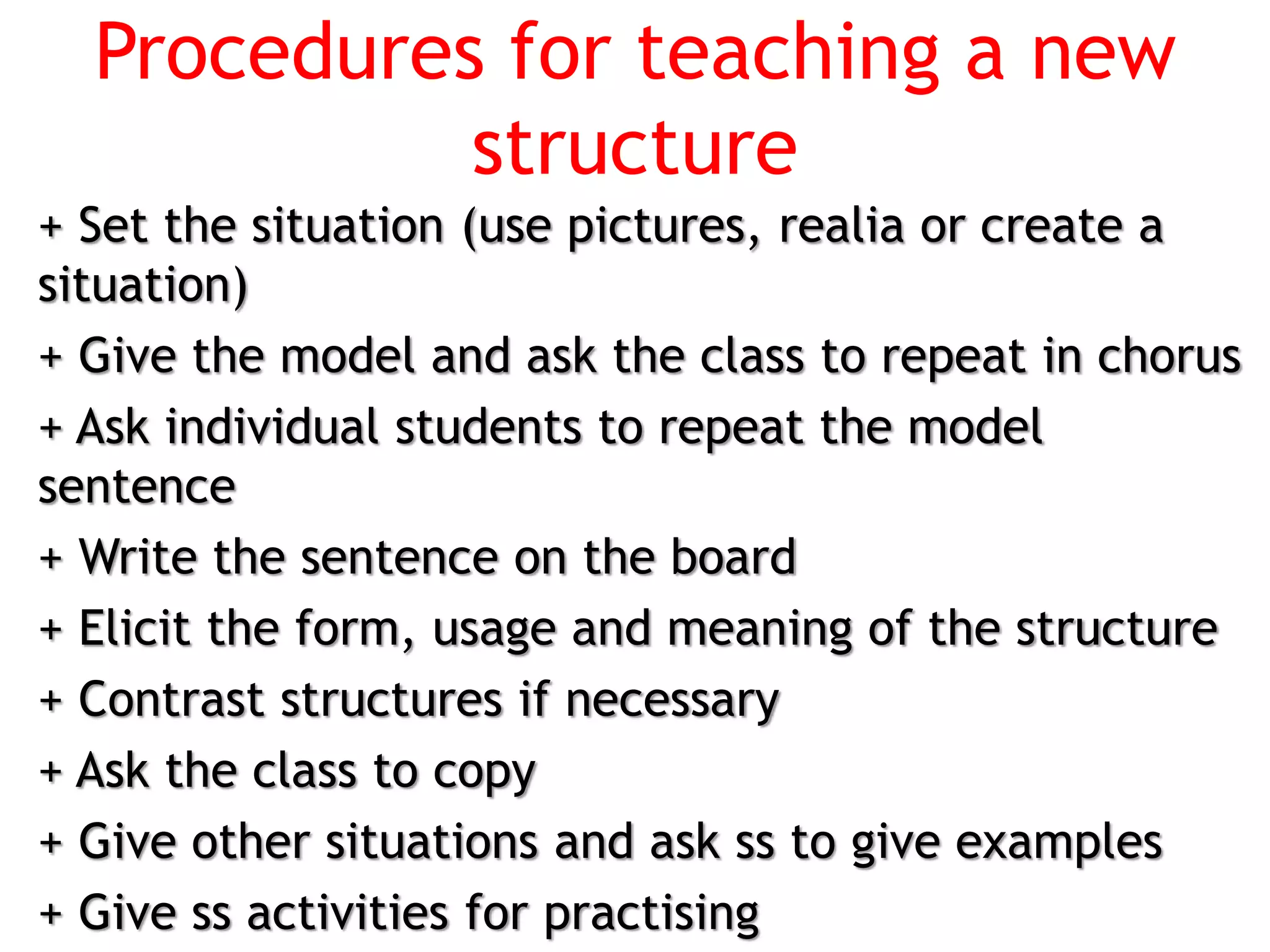
This document provides an overview of teaching grammar. It begins by defining grammar and discussing the key principles for presenting grammatical structures. These principles include teaching structures implicitly through examples, using oral and written forms with explanations, linking form to meaning, and emphasizing communication. The document also discusses different approaches for grammar practice, including drills, exercises, and games. It notes that drills focus on repeating structures while exercises make students more familiar with grammar points. Finally, the document provides recommendations for choosing good grammar books and outlines the typical procedures for teaching a new grammatical structure.