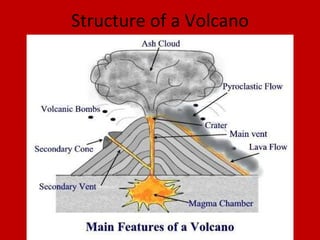
This document defines key volcanic terms and provides an overview of different types of volcanoes. It begins by defining terms like viscosity, magma, lava and ash. It then describes the basic structure of volcanoes and explains that volcanoes are openings in the Earth's crust that allow hot material to escape. The document classifies volcanoes as active, dormant or extinct and describes common types of volcanoes like shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes and supervolcanoes. It provides examples like Mt. St. Helens and highlights some benefits and hazards of volcanoes.