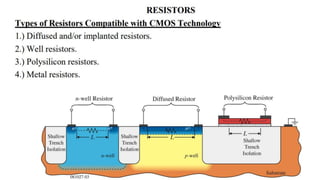
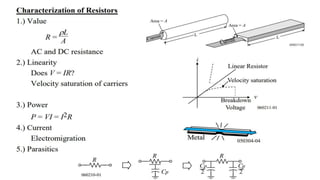
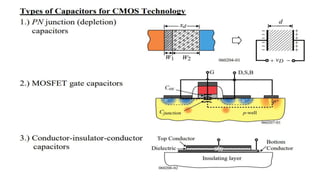
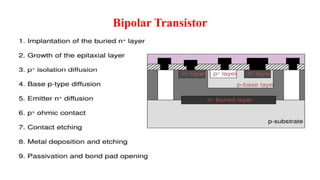
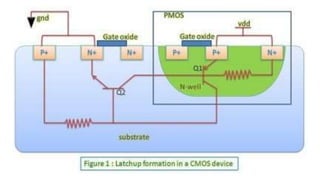
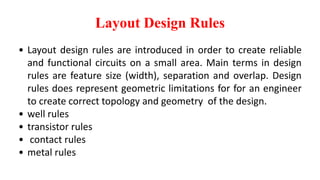
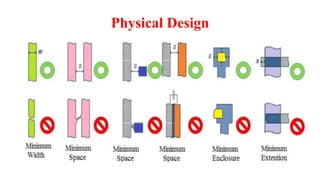
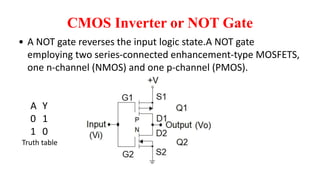
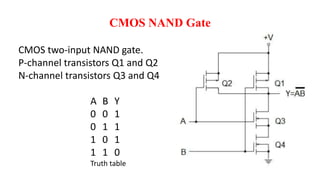
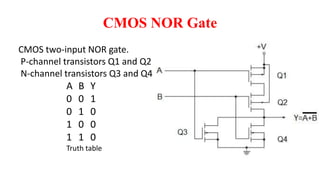
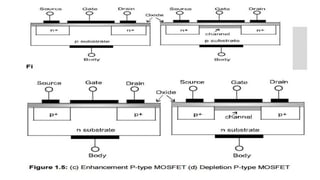
This document provides information on CMOS technology and embedded systems. It discusses latch-up, which refers to a short circuit formed between power and ground rails that can damage an IC. It is caused by parasitic bipolar transistors forming a SCR structure. Methods to prevent latch-up include adding resistance to limit current, surrounding transistors with oxide to break the SCR structure, and latchup protection circuitry. The document also covers layout design rules, physical design, CMOS logic gates like inverters, NAND and NOR gates, and MOS transistor operation.