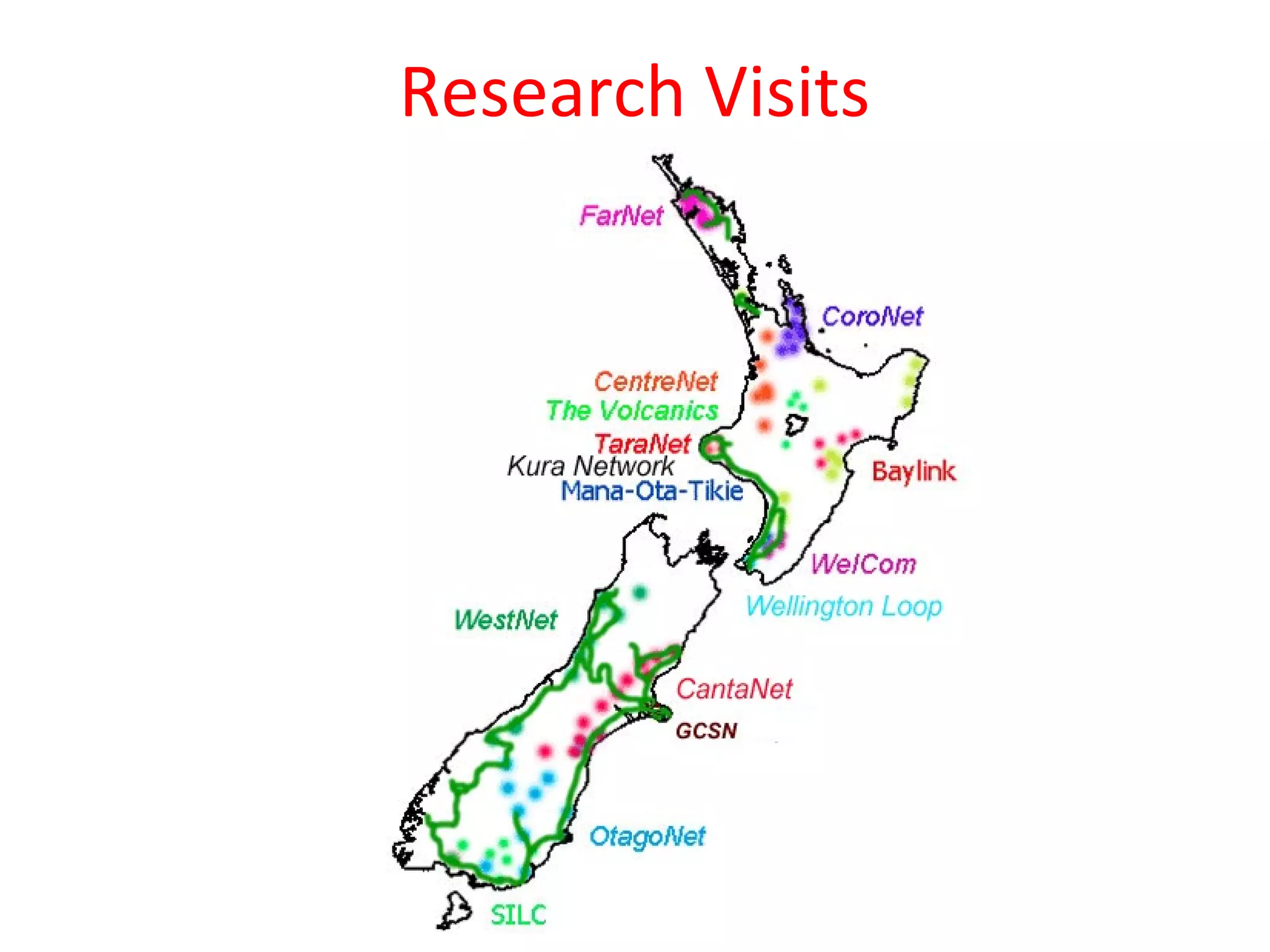
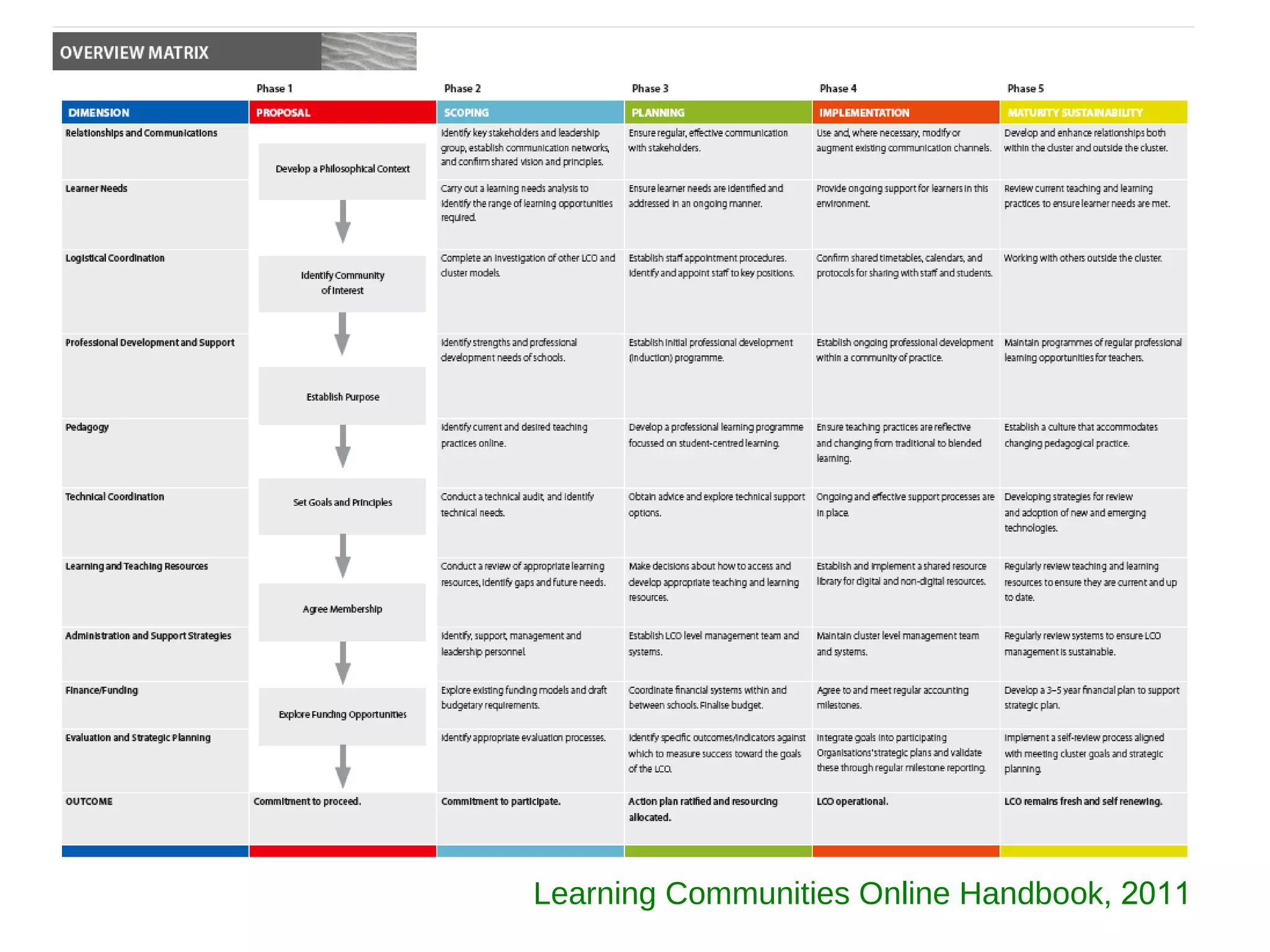
The document examines the development of e-learning clusters in New Zealand, focusing on barriers to maturity and sustainability, as well as the roles of leadership and resources. It highlights common obstacles such as lack of vision and inter-cluster cooperation, and discusses the importance of articulated visions for successful e-learning initiatives. It also outlines the research conducted through interviews, observations, and document analysis to inform future developments in virtual schooling.