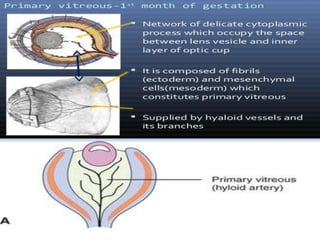
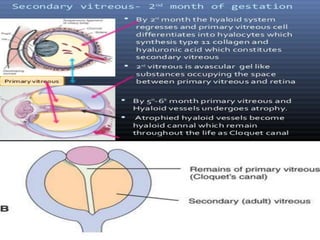
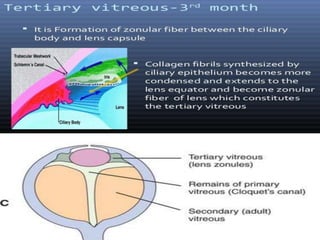
The document discusses the three stages of vitreous development: primitive or primary vitreous, definitive or secondary vitreous, and tertiary vitreous. Primitive vitreous originates partly from mesenchymal and surface ectoderm tissues and contains a vascular system that supplies nutrition to the developing lens. This primitive vitreous regresses by the second month of gestation. Definitive vitreous is secreted by the optic cup and contains type II collagen fibrils and hyalocytes. Tertiary vitreous develops later in gestation and forms the vitreous base and ciliary zonules.