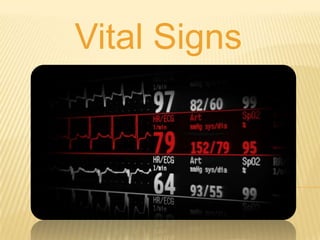
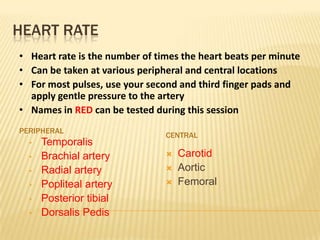
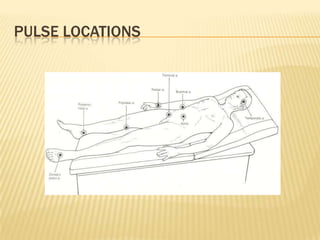
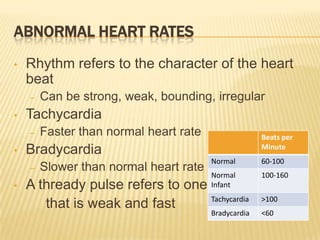
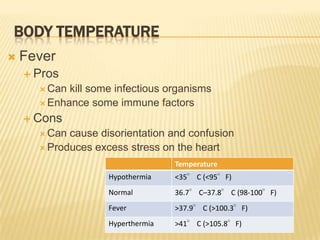
Vital signs include blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, BMI, and body temperature. Blood pressure is measured by the force of blood in the arteries and is written with the systolic pressure over the diastolic pressure. Normal blood pressure is below 120/80 mmHg, while hypertension is 140/90 mmHg or higher. Heart rate is the number of heart beats per minute and can be measured at different pulse points. Respiratory rate is the number of breaths per minute and is normally between 12-20 breaths per minute. BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight, and normal BMI is between 18.5-24.9. Body temperature is normally around 98-100°F, with