Embed presentation
Downloaded 111 times






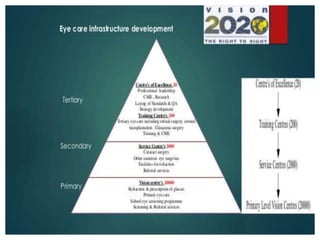

The Vision 2020 initiative aims to eliminate preventable blindness globally by 2020. Launched by the WHO in 1999, India has committed to developing a national plan of action to target the major causes of blindness like cataracts, refractive errors, and more. The plan focuses on preventative interventions, human resource development, and building infrastructure like vision centers, service centers, training centers and centers of excellence to provide eye care services and increase access at the primary, secondary and tertiary levels.






