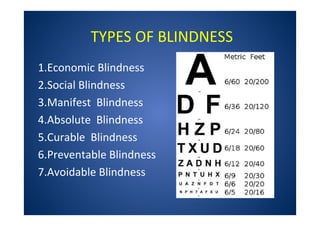
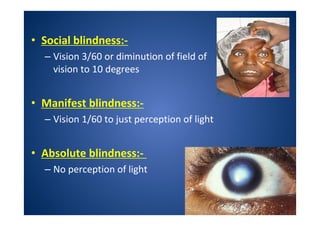
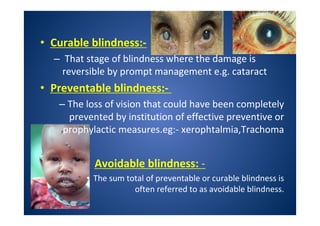
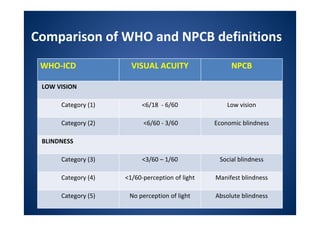
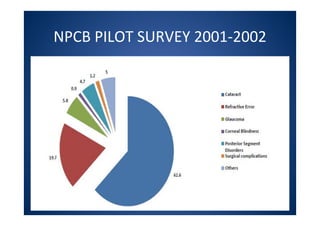
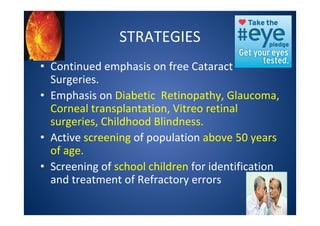
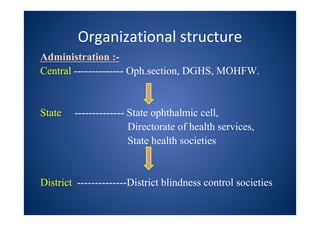
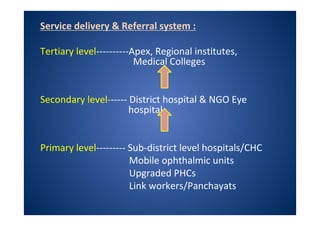
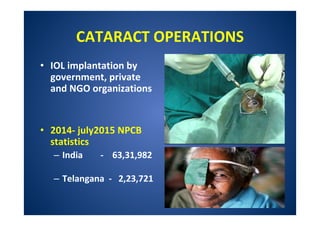
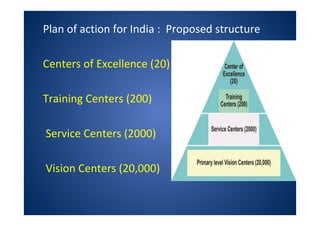
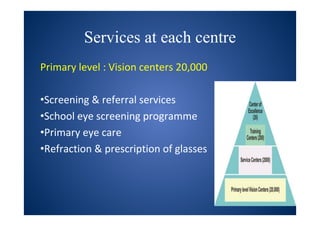
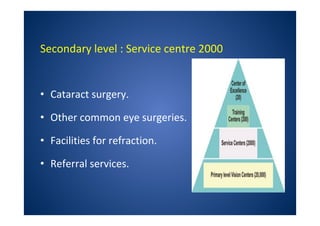
The document discusses India's National Programme for Control of Blindness (NPCB). It was launched in 1976 with the goal of reducing blindness prevalence from 1.49% to <0.3% by 2020. NPCB aims to provide eye care services through activities like cataract surgeries, school eye screening, and using mobile eye units. It is organized with district and state-level societies. The strategies involve increasing access to treatment, emphasizing conditions like glaucoma, and raising awareness. Vision 2020 aims to eliminate preventable and curable blindness globally through primary, secondary, and tertiary eye care centers across India.