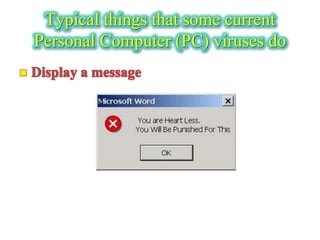
The document discusses the history of computer worms and viruses. It describes how the first widely known worm, the Morris worm, was created by a graduate student in 1988 and how he was later convicted. It defines worms as software that replicates itself across a network by exploiting security vulnerabilities. The document also provides details on typical functions of computer viruses today, how viruses spread through email, and examples like the Melissa virus. It concludes with recommendations for prevention like keeping systems updated and using antivirus software.