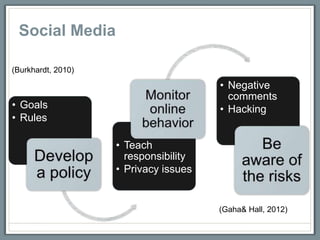
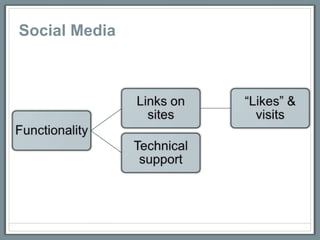
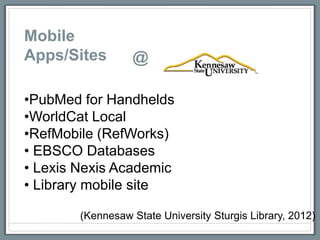
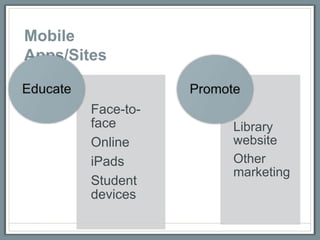
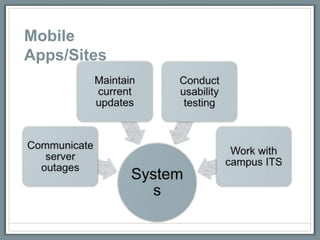
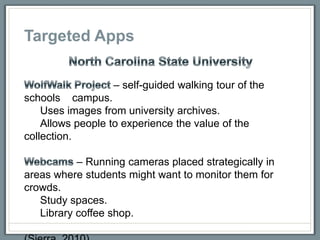
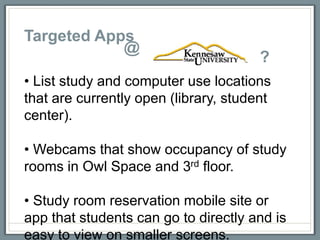
This document discusses how libraries must constantly adapt to changing user demands and technologies. It begins by comparing adapting to changing technologies to a runner encountering hills - some libraries can speed through changes, some maintain their pace, and others fall behind. Whether a library adapts well depends on its energy level and training through budget and preparation. The document then summarizes several technology trends libraries must address, including information technology, social media, mobile devices, and user expectations of convenience. It provides examples of how libraries can meet these changing demands.









![Mobile Devices
“Mobile devices are changing the way
information is delivered and accessed.” (ACRL
Research Planning and Review Committee,
2012, “Mobile environments,” para. 1)
“More than two-third of [students who own mobile devices]
use the devices for academic purposes” (ACRL Research
Planning and Review Committee, 2012, “Mobile
environments,” para. 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualsystems-121219184354-phpapp02/85/Virtual-systems-12-320.jpg)





![References
ACRL Research Planning and Review Committee. (2012). 2012 top trends in
academic libraries: A review of the trends and issues affecting academic libraries in
higher education. American Library Association. Retrieved from:
http://crln.acrl.org/content/73/6/311.full
Armstrong, Kristin. (2011). Mile markers: The 26.2 most important reasons why
women run. Emmaus, PA: Rodale Books.
Burkhardt, A. (2010). Social media: A guide for college and university libraries.
College & Research Libraries News, 71(2), 10-24. Retrieved from:
http://crln.acrl.org/content/71/1/10.short
Gaha, U., & Hall, S. (2012, October). Sustainable use of social media and electronic
resources in libraries. [PowerPoint slides]. Slides presented at the Georgia Council of
Media Organizations conference, Macon, GA.
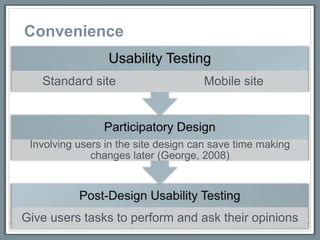
George, C. A. (2008). Designing the website – participatory design. User-centered
library websites: Usability evaluation methods (pp. 97-108). Oxford: Chandos
Publishing. Retrieved from:
http://works.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1009&context=carole_george](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualsystems-121219184354-phpapp02/85/Virtual-systems-28-320.jpg)
![References, cont.
Jasek, C. (2004). How to design library Web sites to maximize usability.
[Pamphlet]. San Diego, CA: Elsevier. Retrieved from:
http://www.elsevier.com/framework_librarians/LibraryConnect/lcpamphlet5.pdf
Kennesaw State University Sturgis Library. (2012). Mobile & software. Retrieved
from: http://kennesaw.edu/library/services/widgetsAppsSoftware.html#
Sierra, T. (2010). Opportunities for mobile-enhanced library services and
collections. [PowerPoint slides]. Retrieved from SlideShare website:
http://www.slideshare.net/tsierra/opportunities-for-mobile-enhanced-library-
services-and-collections#btnNext
Swanson, T. A., & Green, J. (2011). Why we are not Google: Lessons from a
library Web site usability study. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, 37(3), 222-
229. Retrieved from: https://www.evernote.com/shard/s7/sh/450c865e-83ad-40bb-
9f4e-4f0e8d187872/9056a4a4877a8647823d1de9a2c402ac/res/f0431bd8-c160-
432f-9f02-c749a3b9cb15/sdarticle.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualsystems-121219184354-phpapp02/85/Virtual-systems-29-320.jpg)