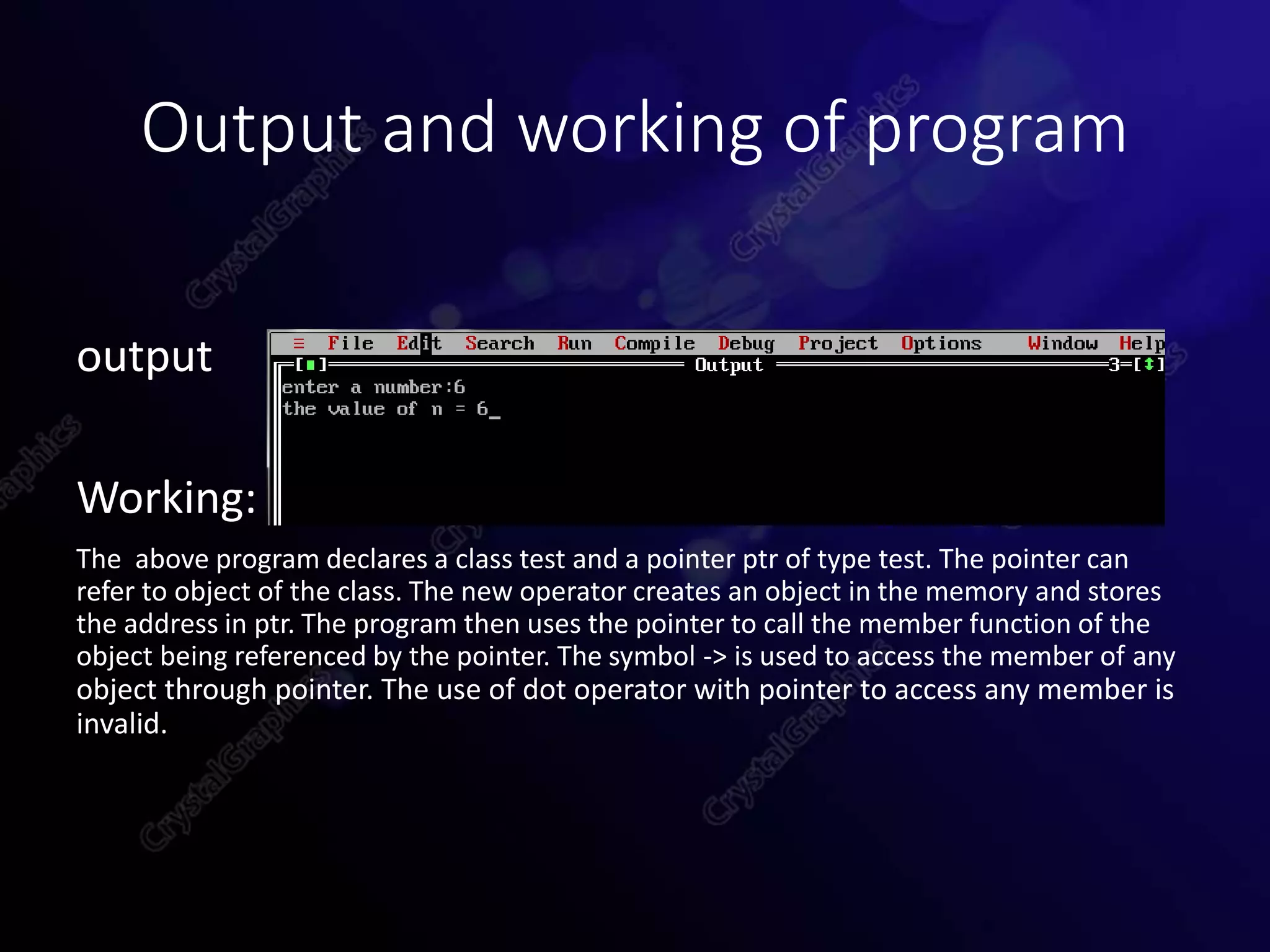
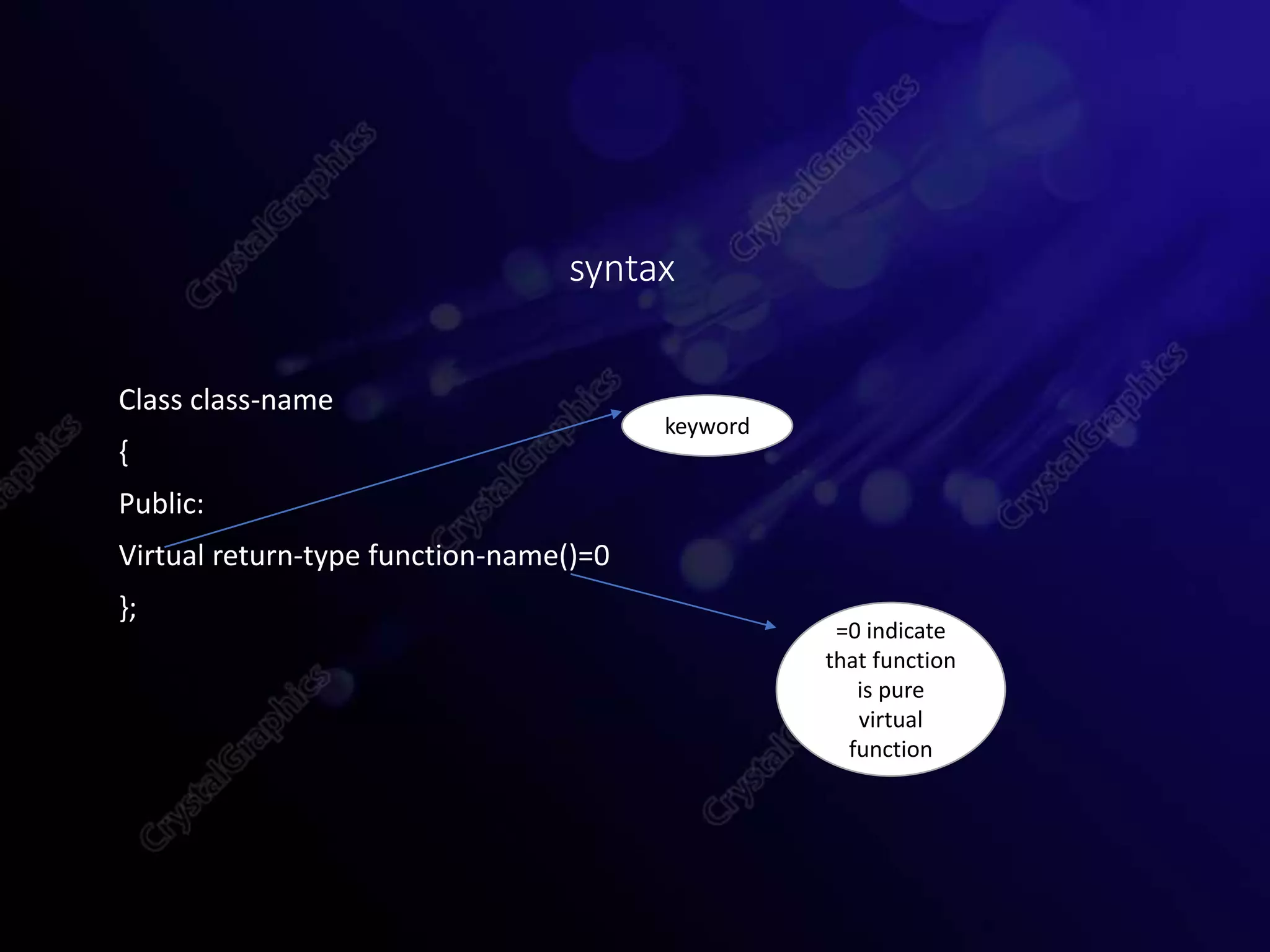
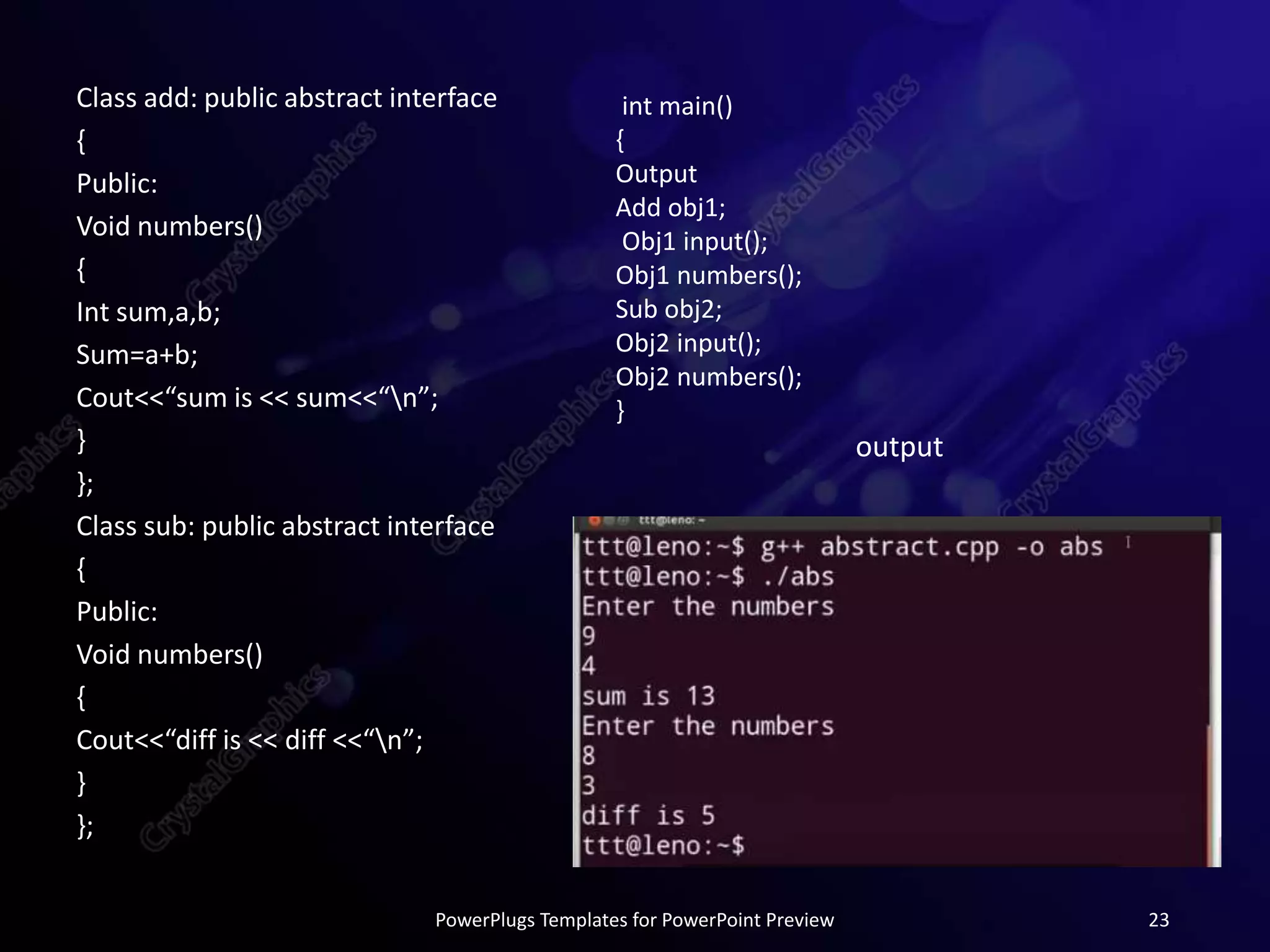
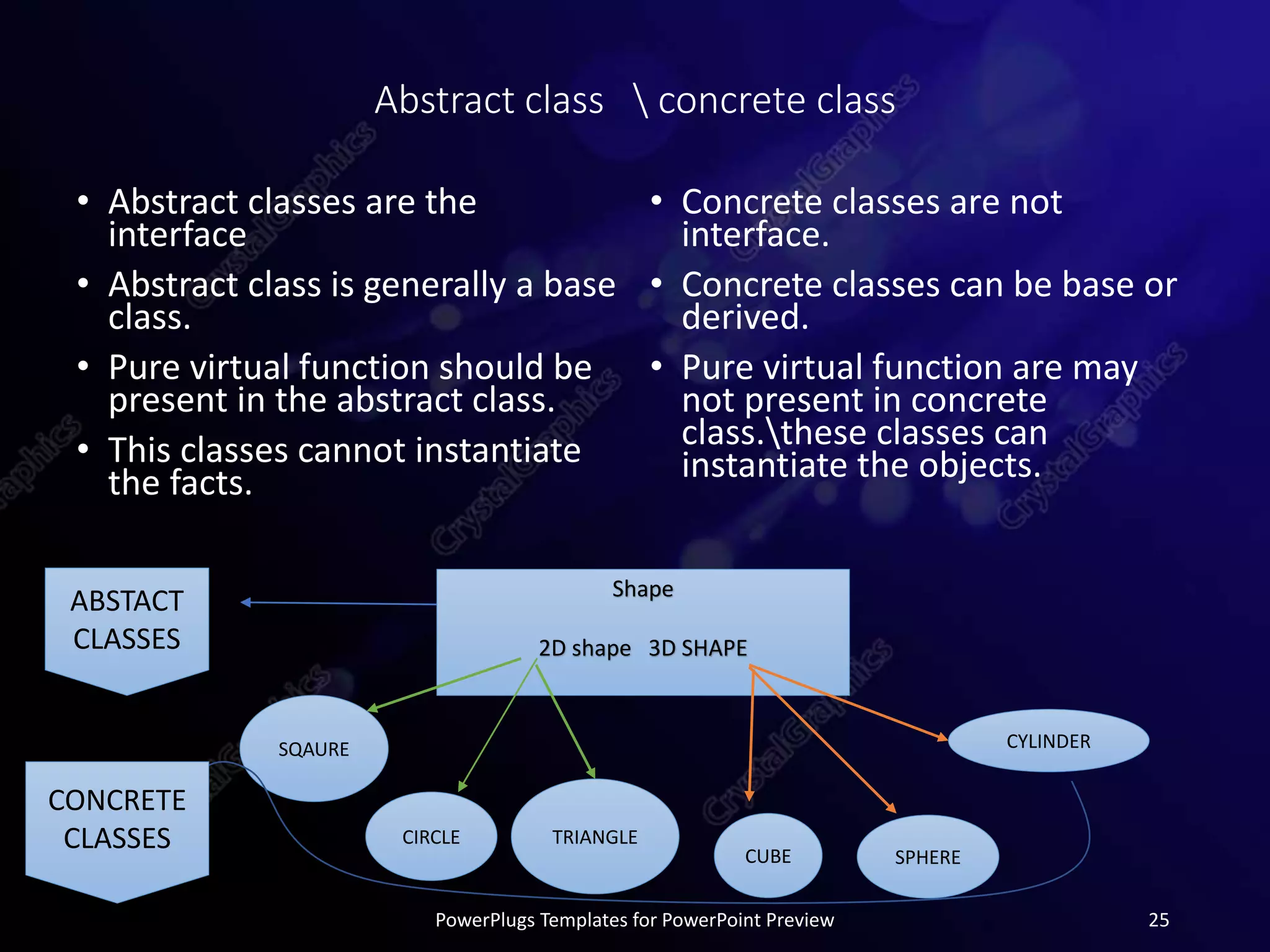
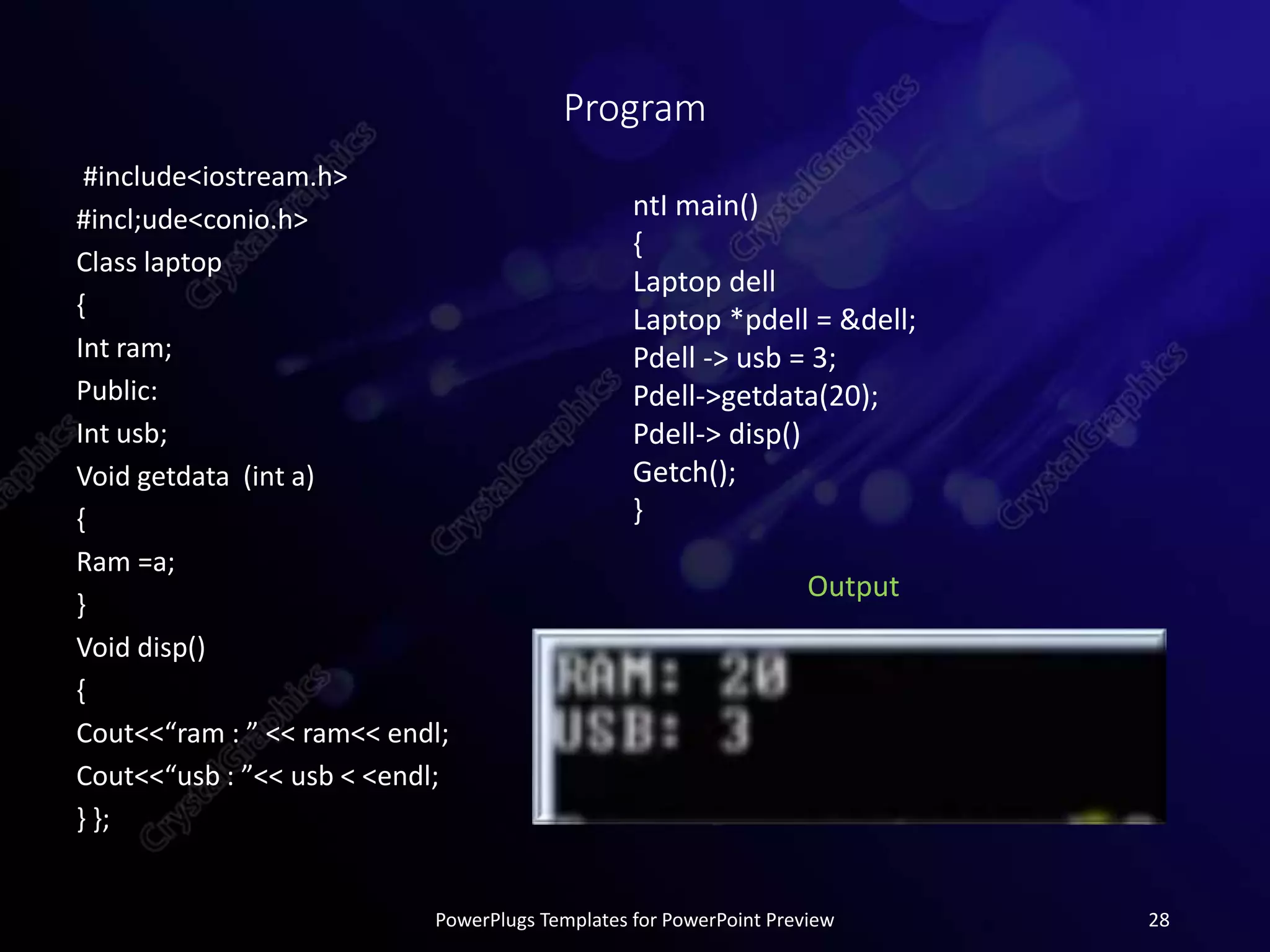
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in C++ including polymorphism, virtual functions, pure virtual functions, abstract classes, and pointers to objects. It defines each concept, provides syntax examples, and short programs to demonstrate how each concept works in practice. The document is submitted as part of a programming fundamentals course by Sidra Tahir to her instructor at COVT Post Graduate College for Women in Lahore, Pakistan.