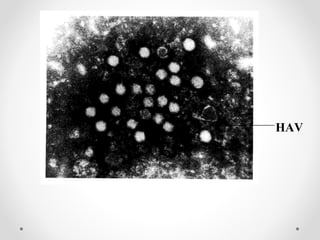
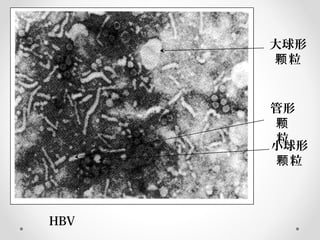
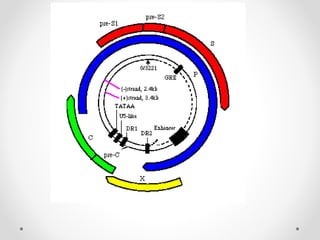
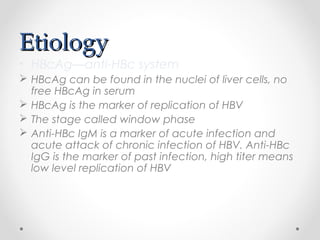
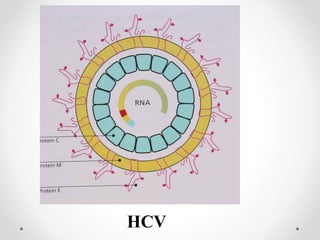
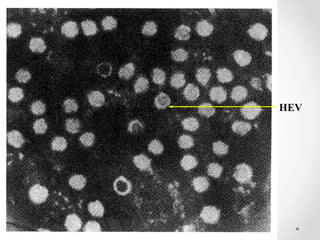
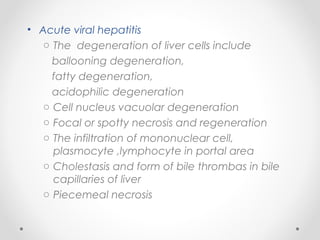
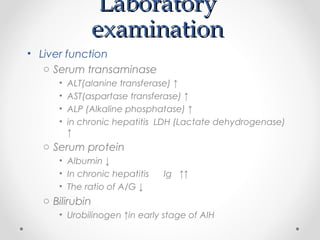
Viral hepatitis can be caused by five main viruses - hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. While the clinical symptoms are often similar, the viruses differ in their modes of transmission and tendencies to cause acute or chronic infection. Hepatitis A and E typically cause acute infection transmitted through the fecal-oral route, while hepatitis B, C, and D can establish chronic infections transmitted through blood or other bodily fluids. Understanding the differences between the hepatitis viruses is important for preventing and treating viral hepatitis.