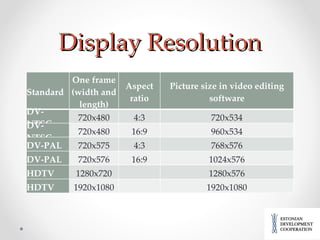
Video has educational value when used in learning. It can engage students and be used for social learning activities. There are different types of analog and digital video formats and standards. Educational videos can include lectures, demonstrations, interviews, student-created videos, and more. The video creation process involves planning, filming, editing, and publishing videos online or on physical media for sharing. Various free and commercial software can be used for video editing.
![Video in learning process Veronika Rogalevich [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/videoinlearningprocess-110802134500-phpapp01/75/Video-in-learning-process-1-2048.jpg)






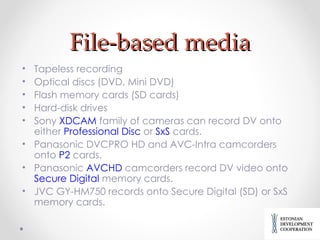

![Main raw formats DV-AVI is Microsoft's implementation of DV video file, which is wrapped into an AVI container. This container is used primarily on Windows-based computers, though Sony offers two tapeless recorders, the HDD-based HVR-DR60 [16] and the CompactFlash-based HVR-MRC1K, [17] for use with DV/HDV camcorders that can record in DV-AVI Quicktime -DV is DV video wrapped into Quicktime container. This container is used primarily on Apple computers (MOV-files). MXF -DV wraps DV video into MXF container, which is presently used on P2-based camcorders (Panasonic) and on XDCAM/XDCAM EX camcorders (Sony).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/videoinlearningprocess-110802134500-phpapp01/85/Video-in-learning-process-11-320.jpg)














![If You have some questions or comments, get in touch! Veronika Rogalevich Educational technologist Tallinn University Center of E-learning [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/videoinlearningprocess-110802134500-phpapp01/85/Video-in-learning-process-26-320.jpg)