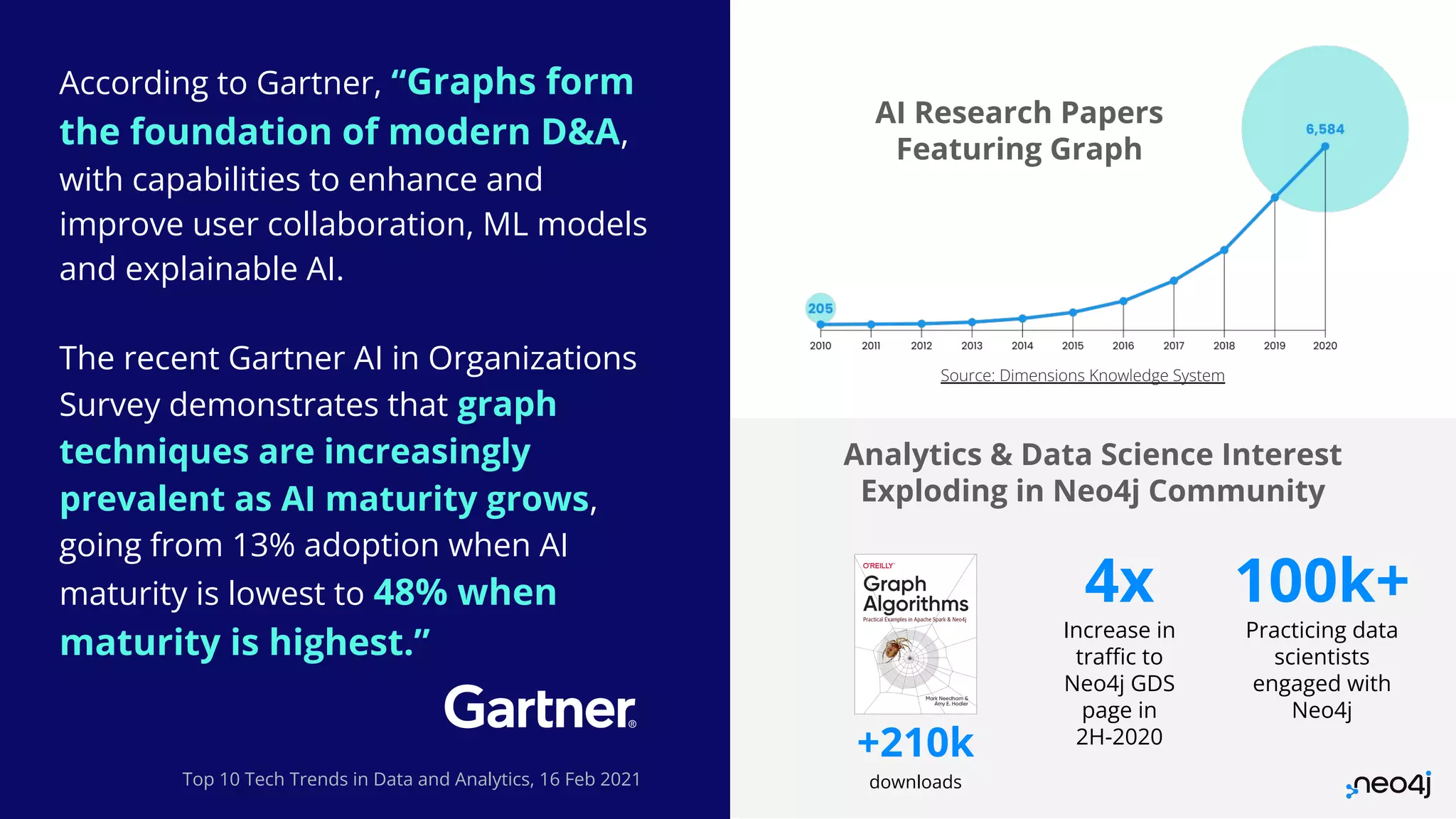
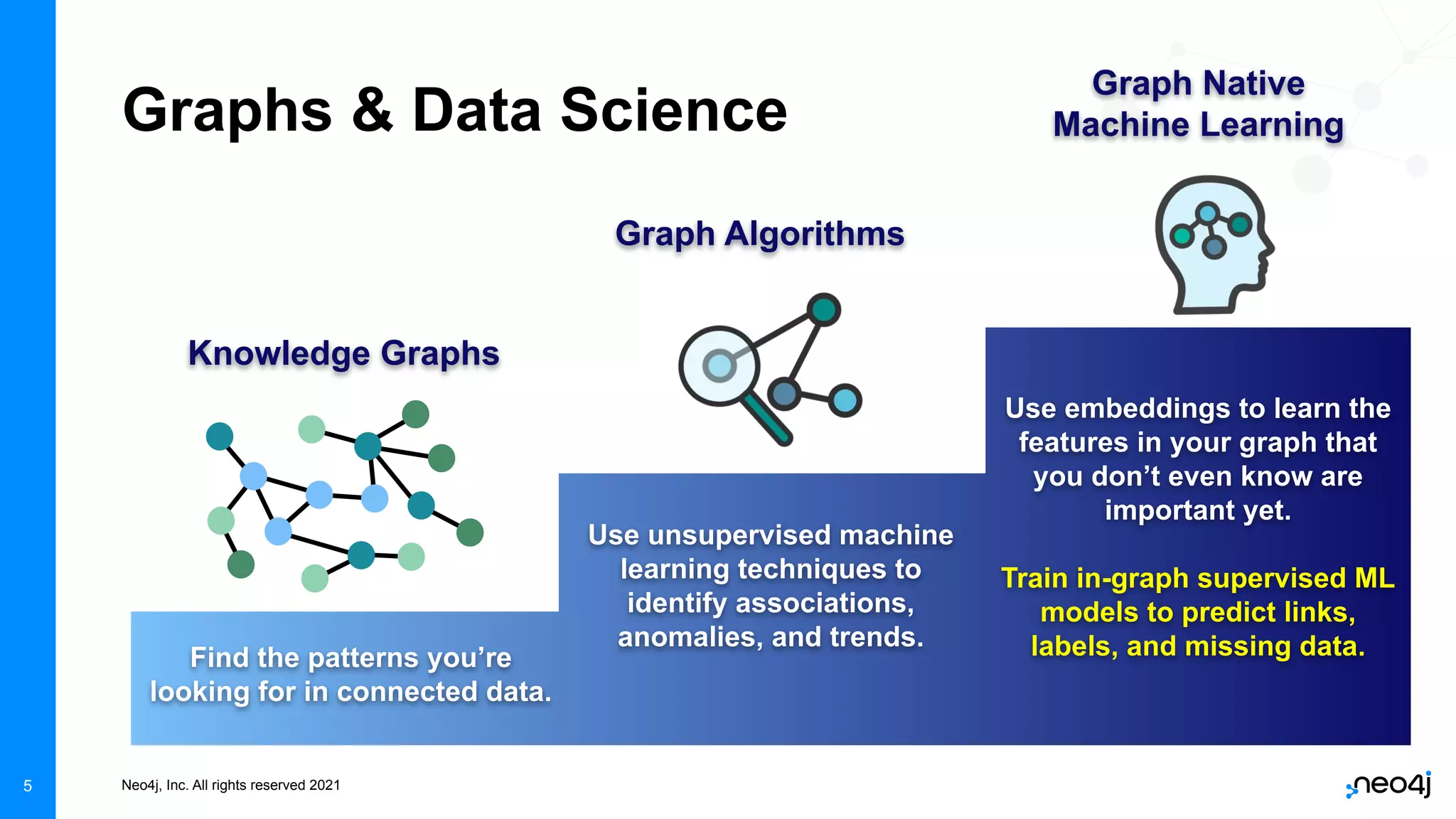
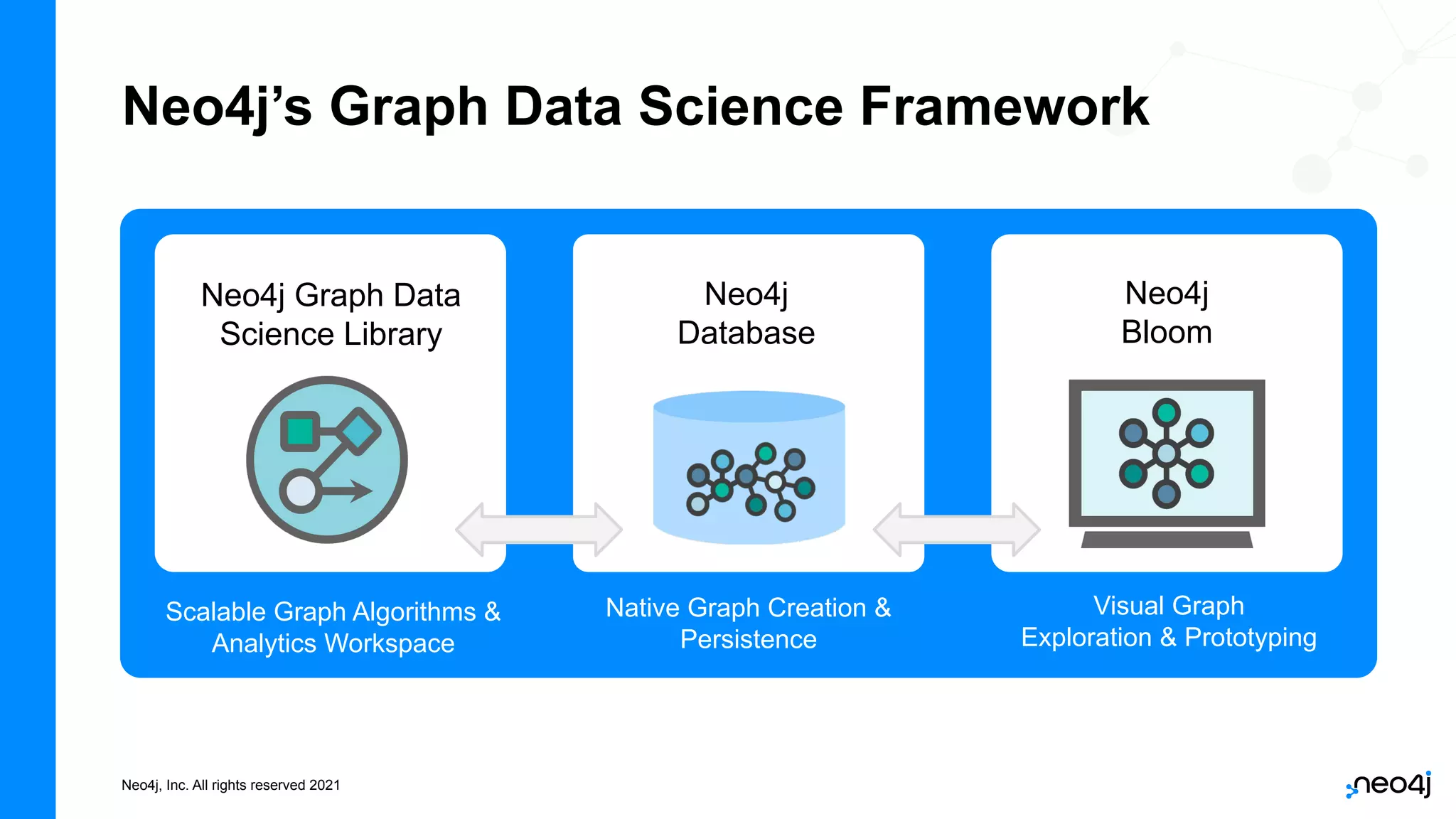
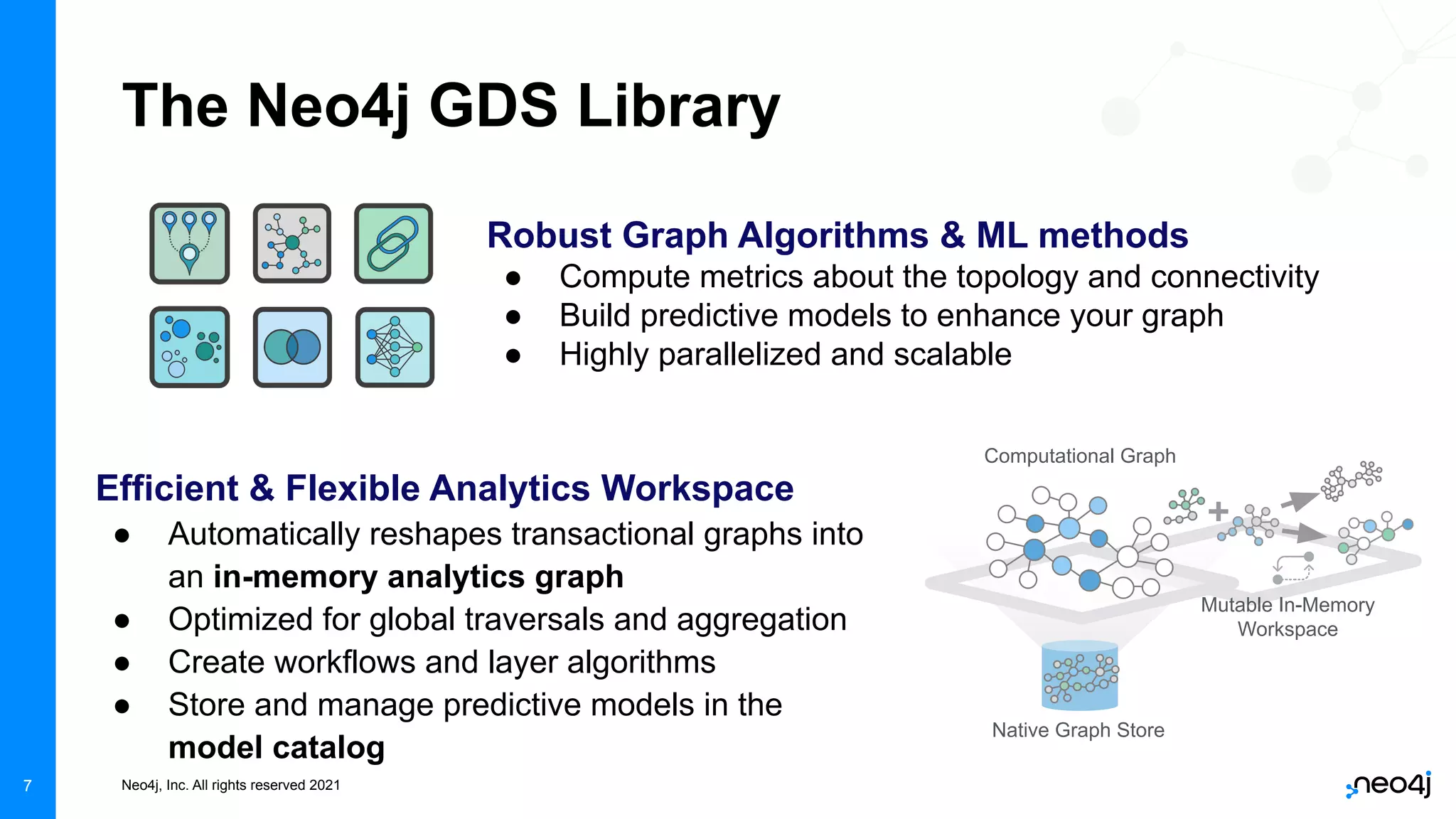
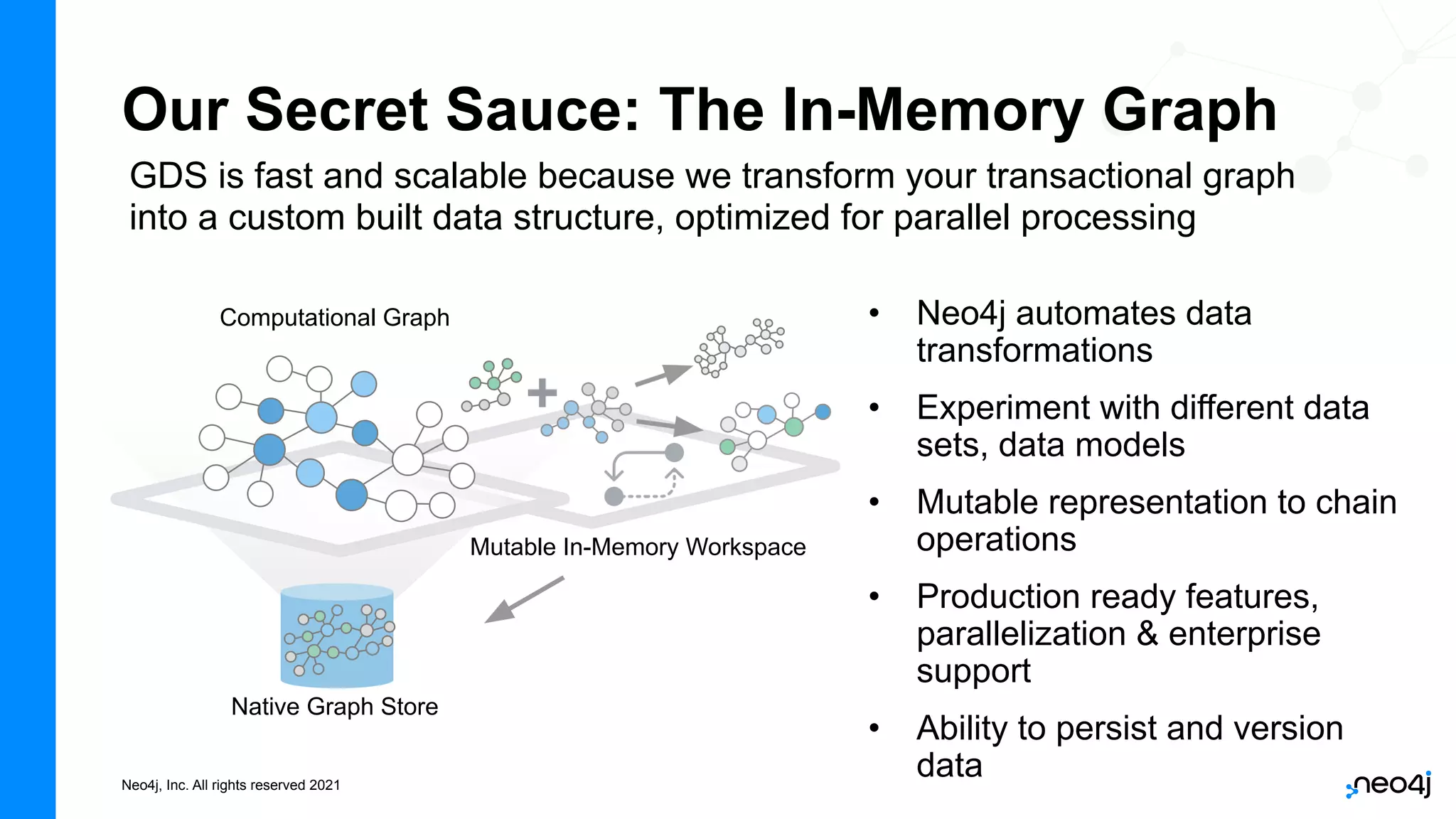
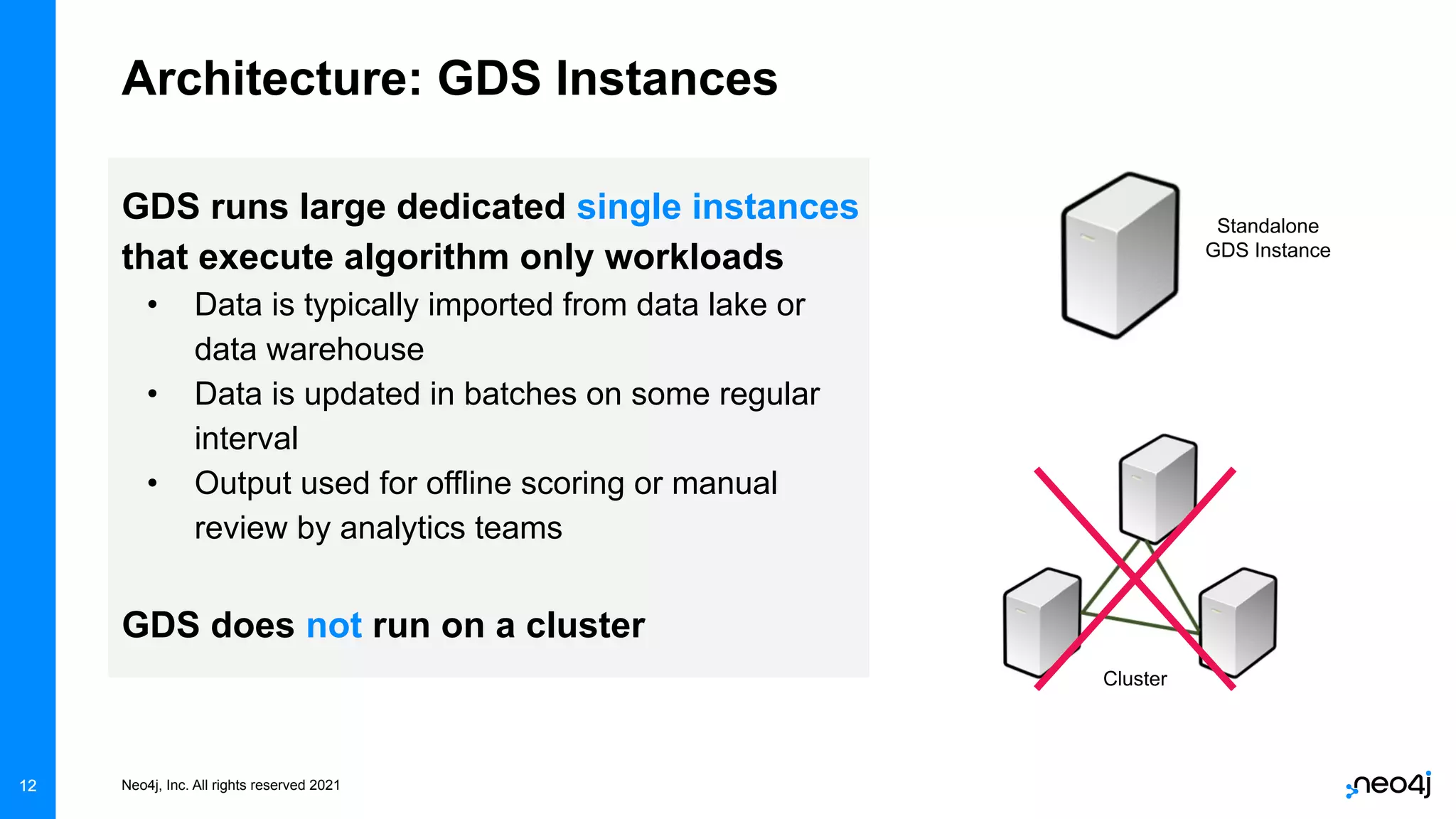
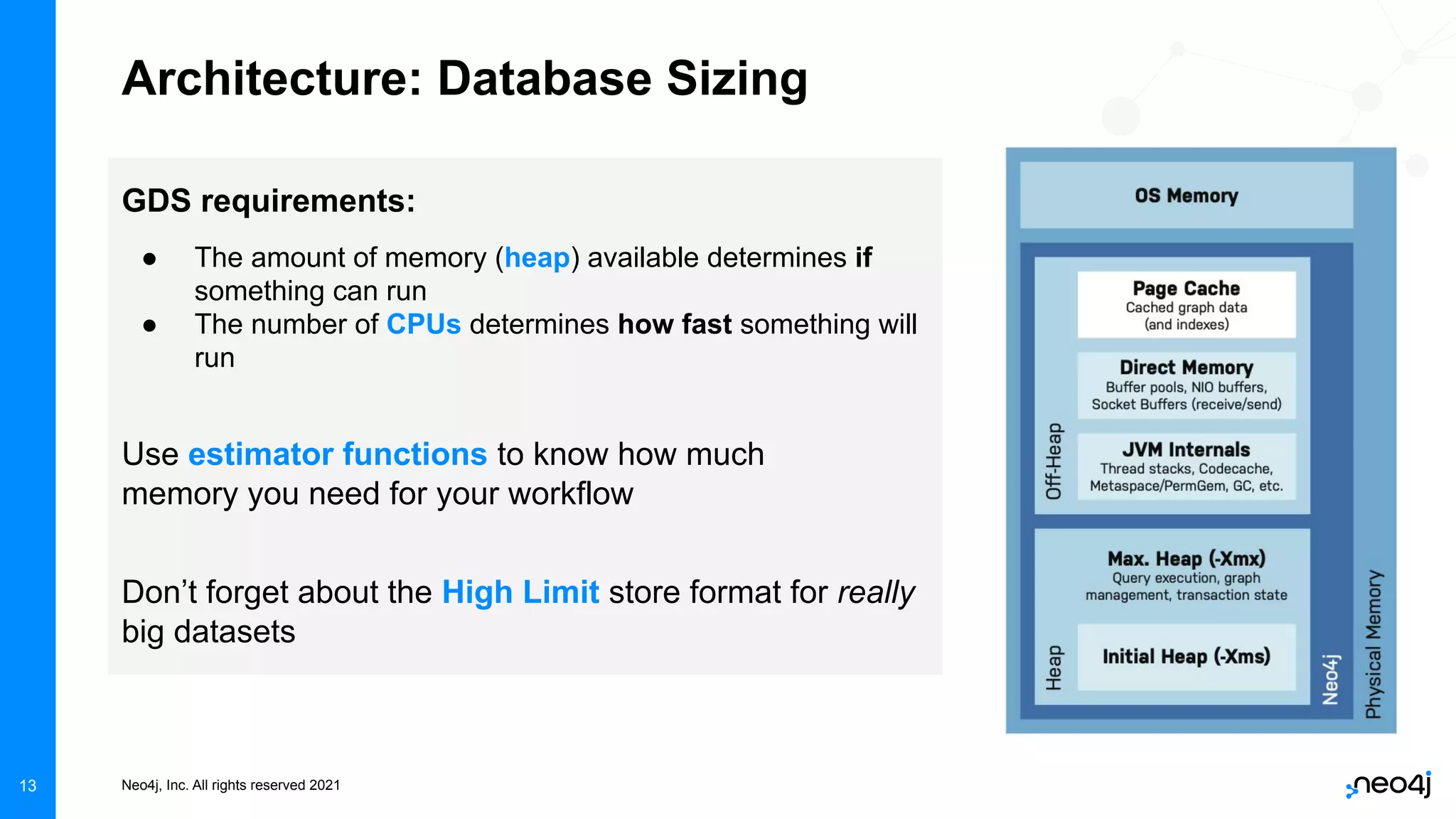
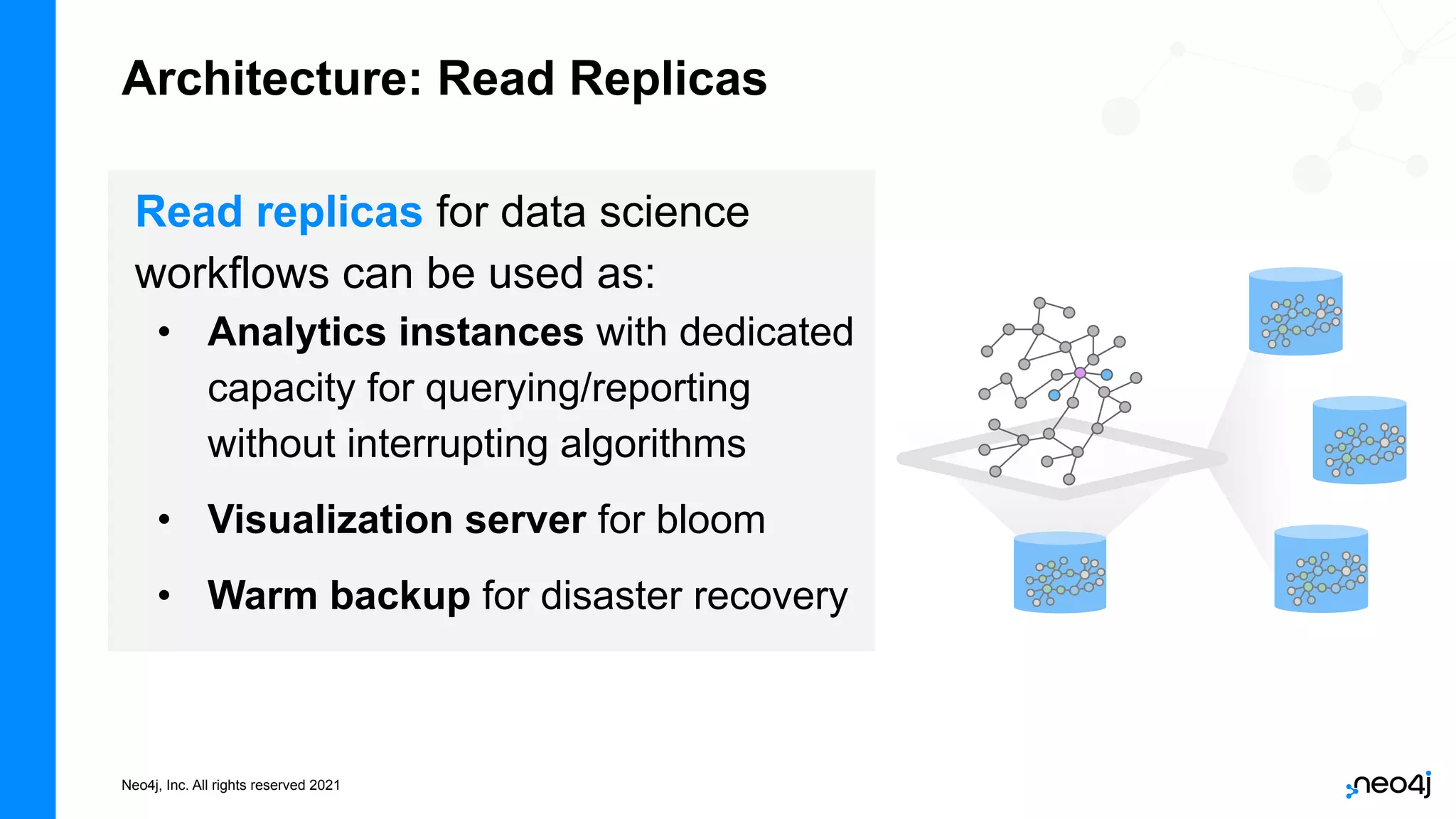
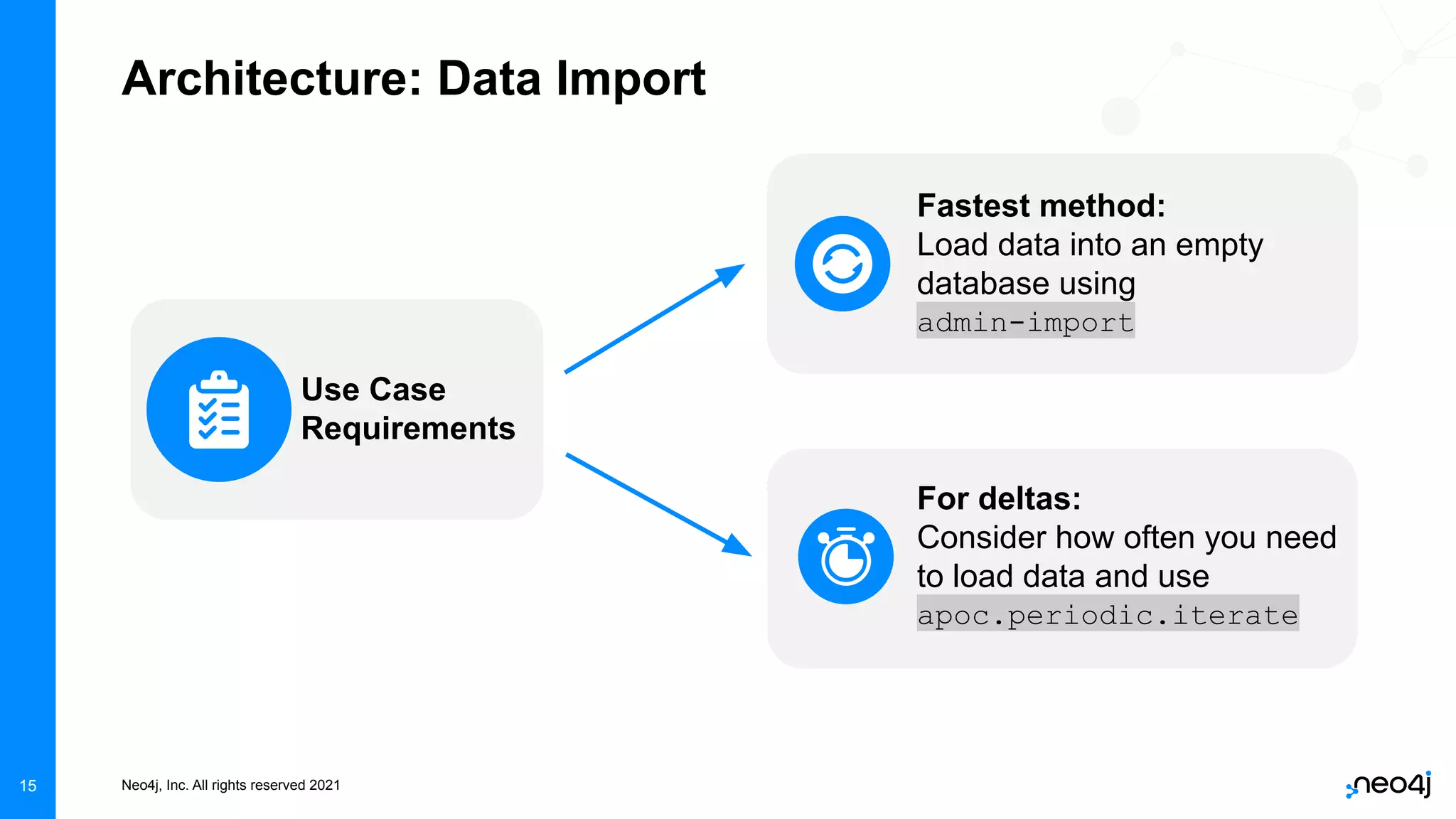
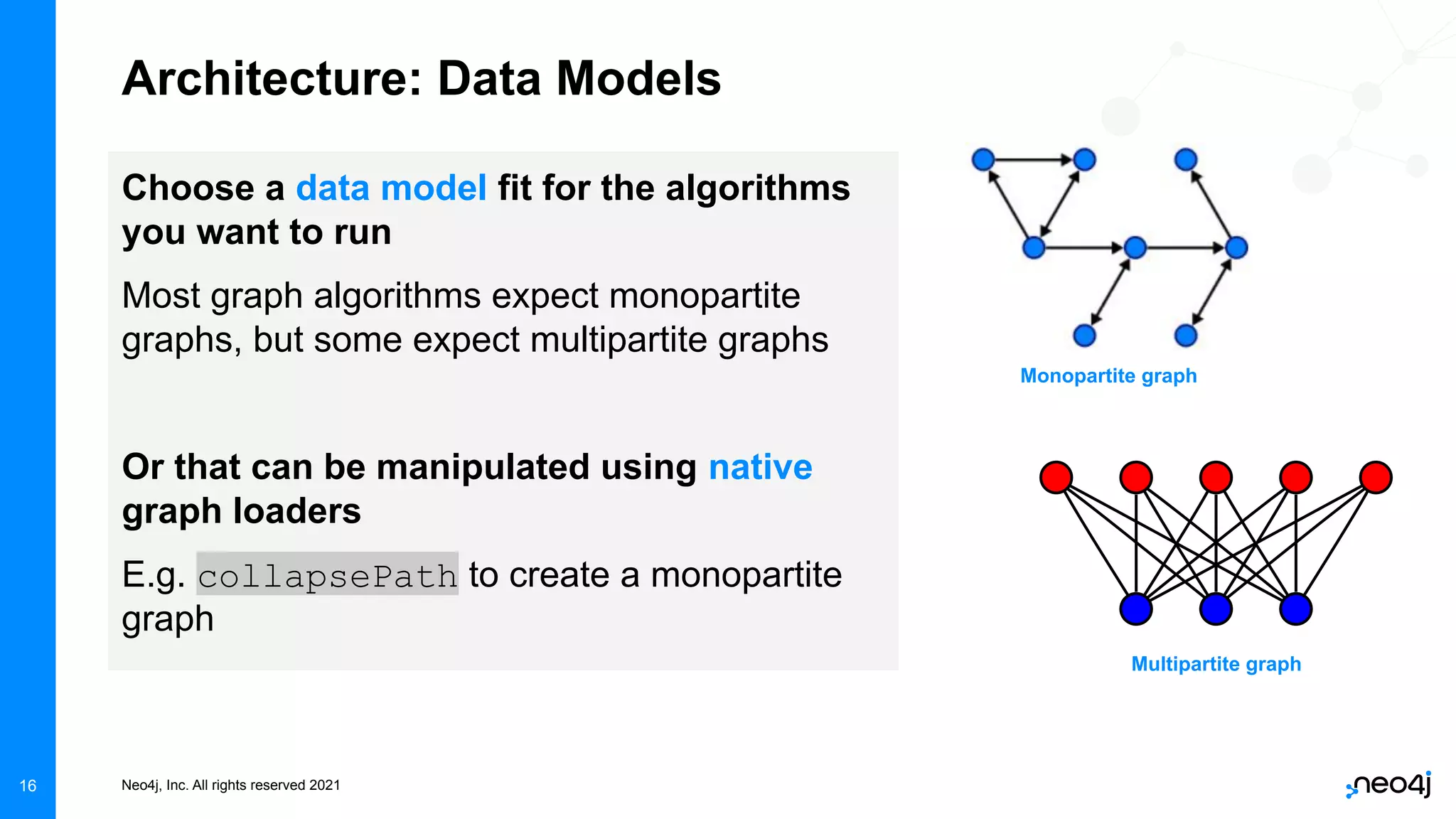
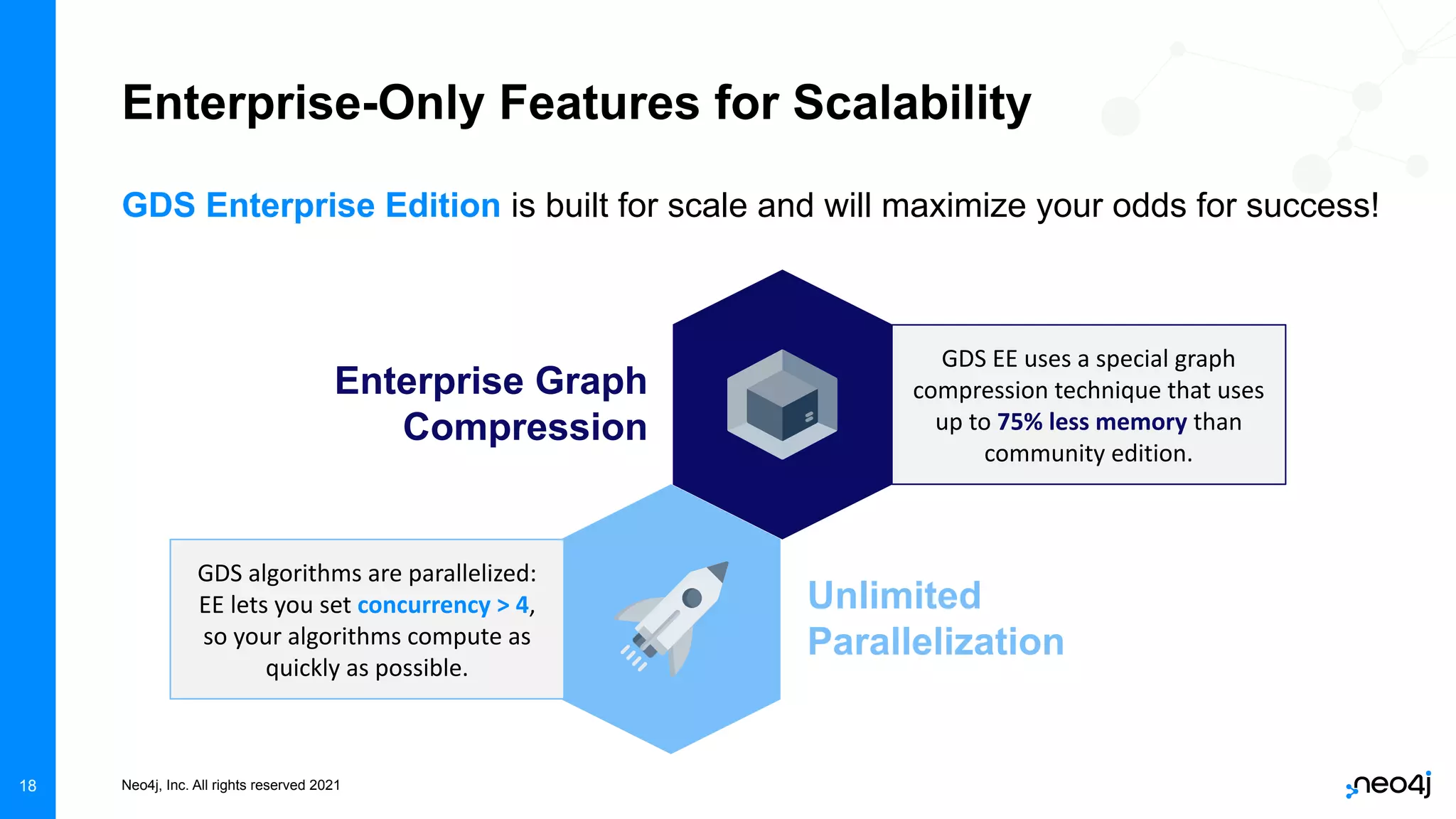
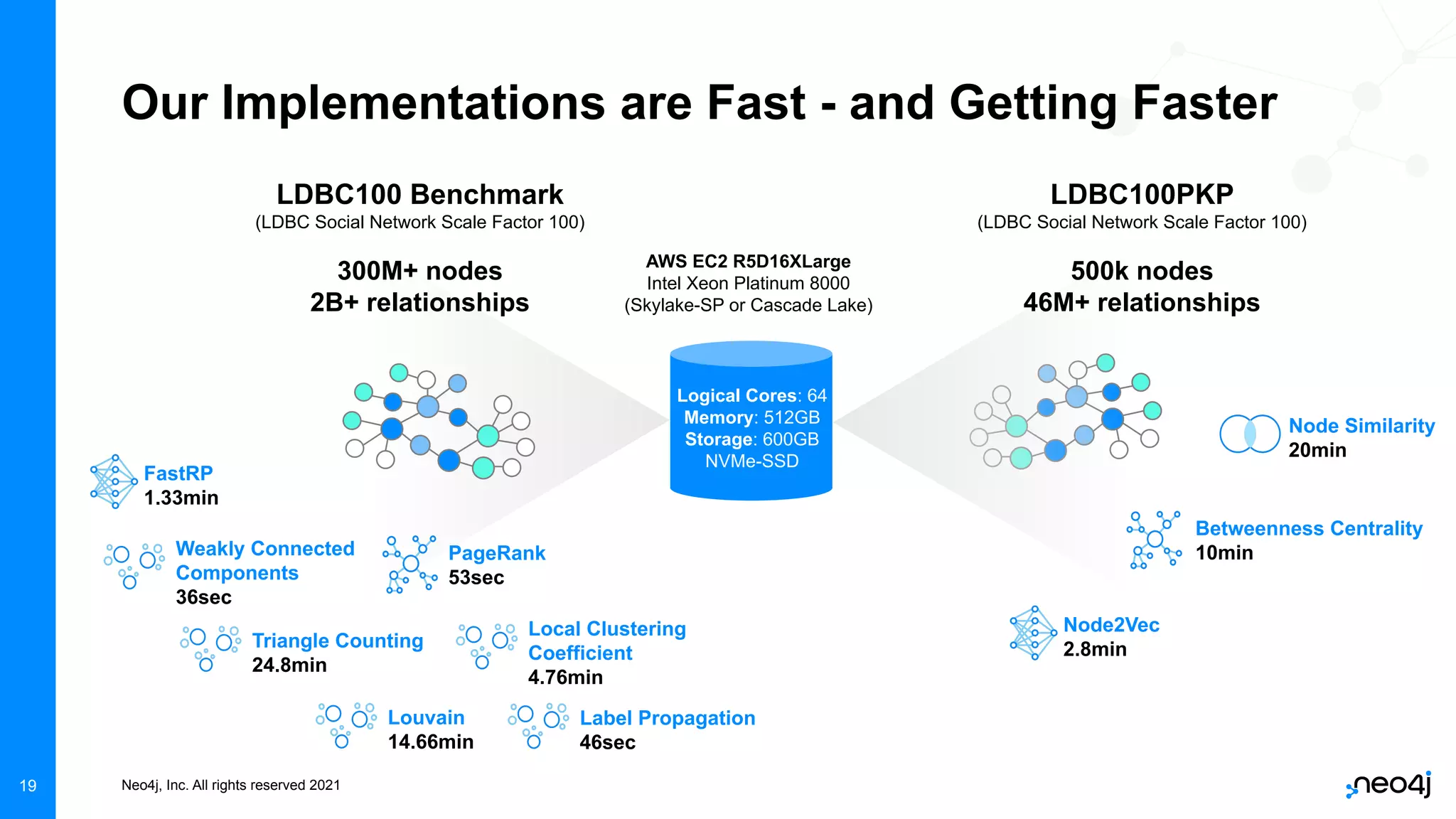
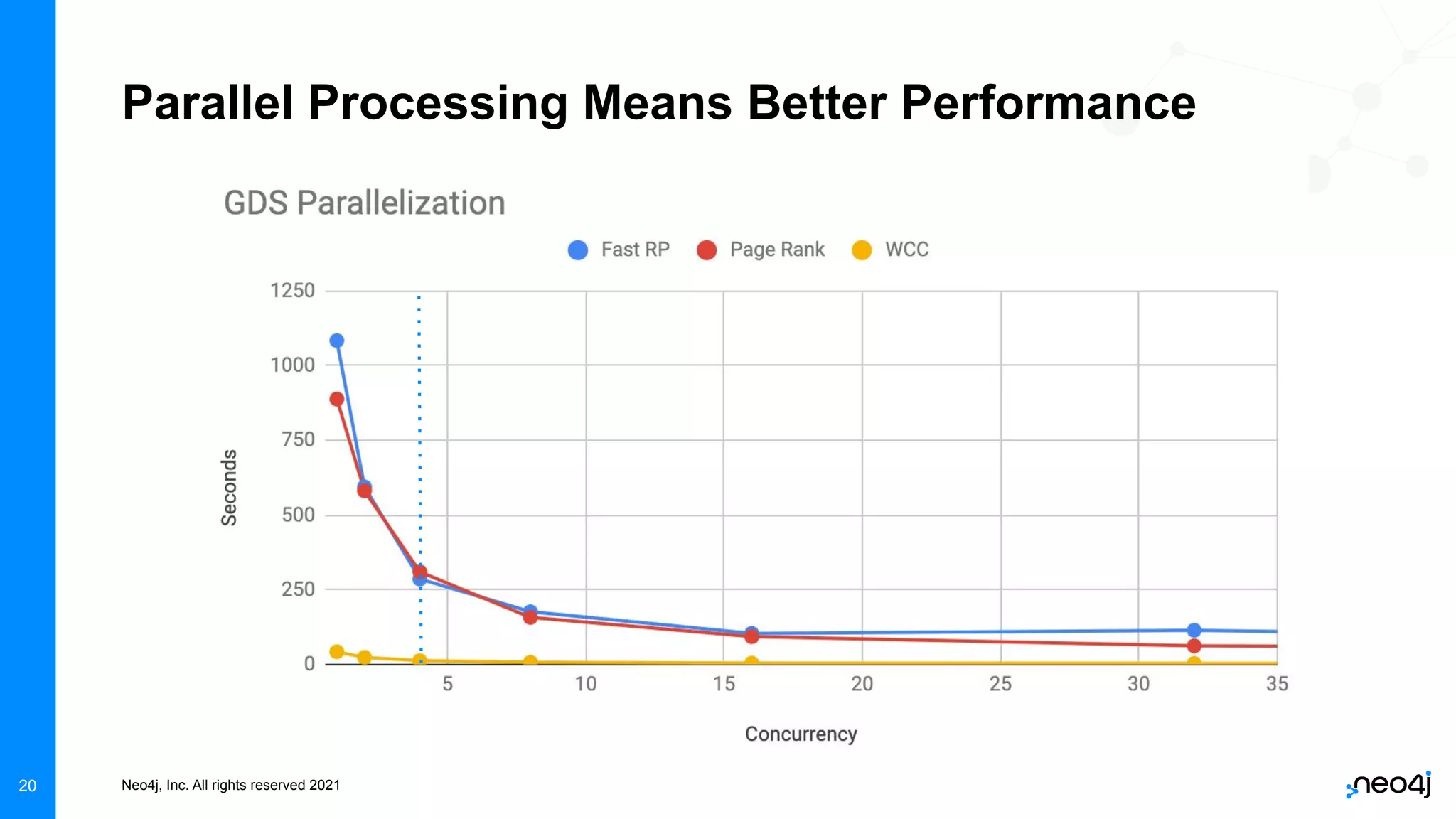
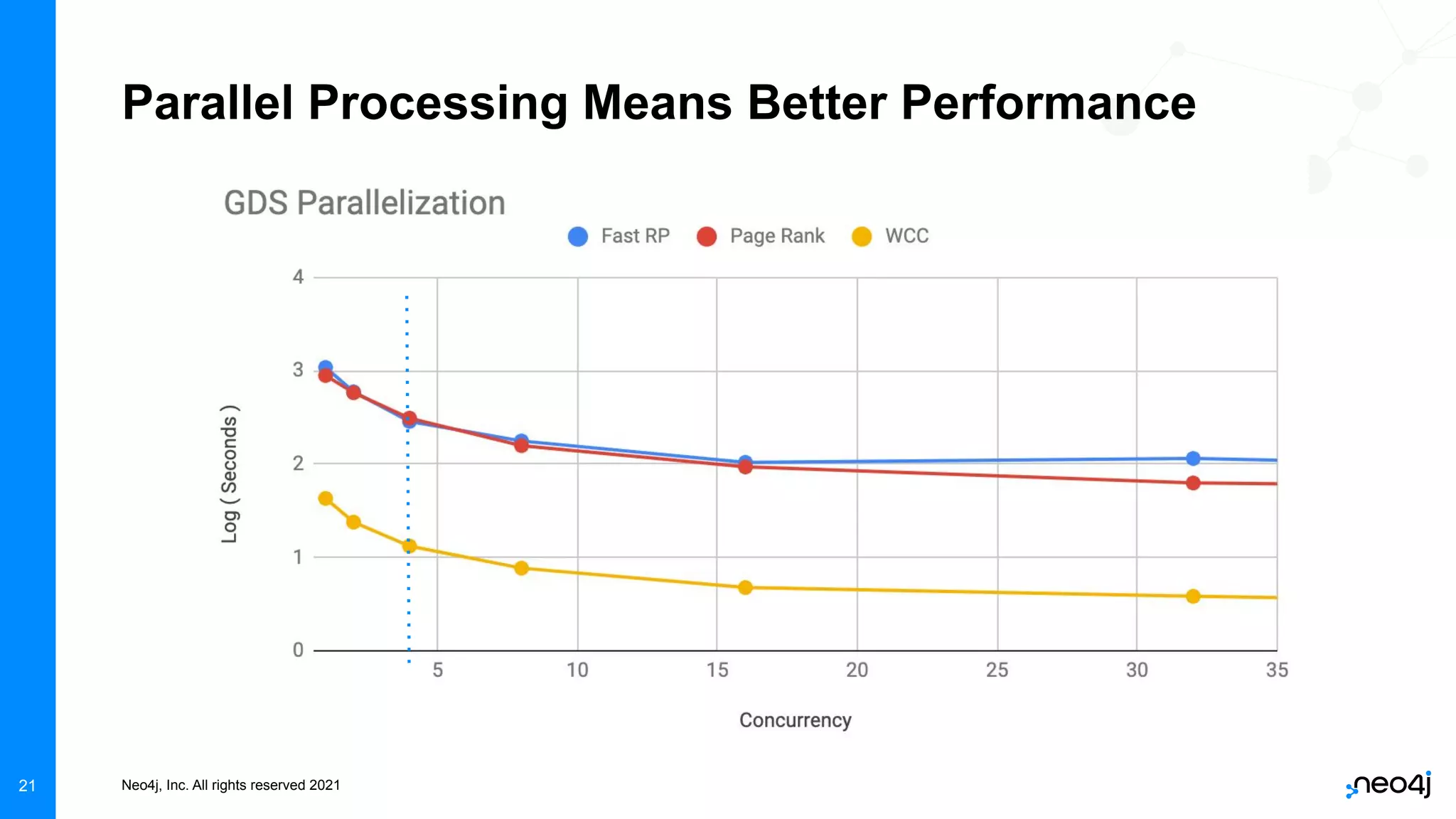
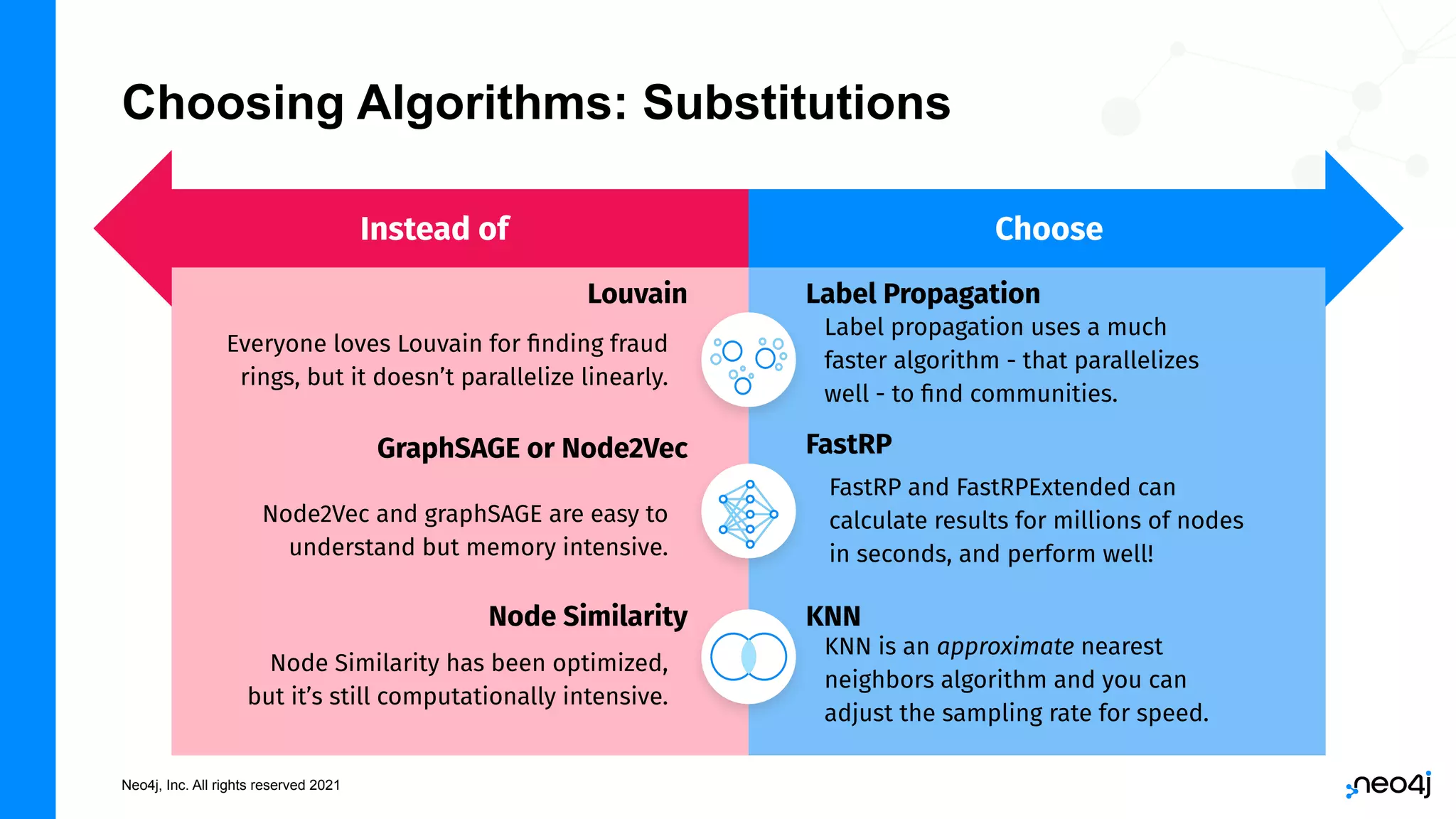
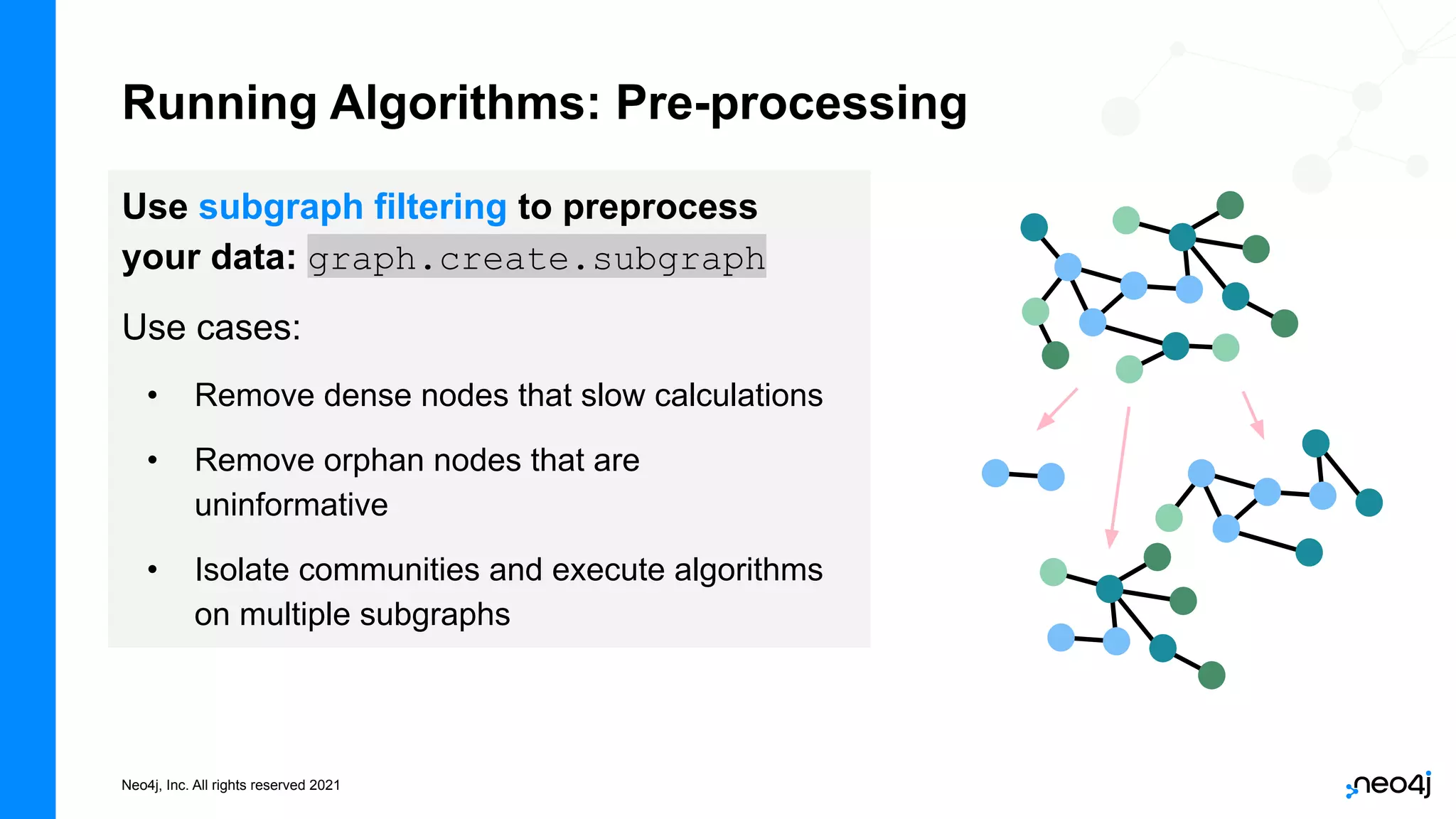
The document discusses graph data science and Neo4j's Graph Data Science (GDS) framework. GDS allows running graph algorithms and machine learning models at scale on large graph datasets. It discusses key aspects of GDS including architecture, data import, algorithm selection, and case studies of customers using GDS on graphs with billions of nodes and relationships. GDS runs on dedicated instances and supports features like enterprise graph compression, unlimited parallelization, and named graphs to optimize performance on large datasets.