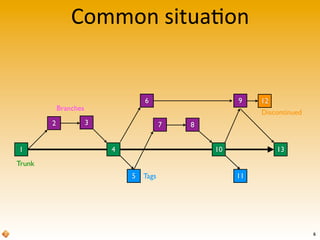
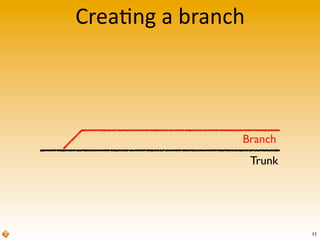
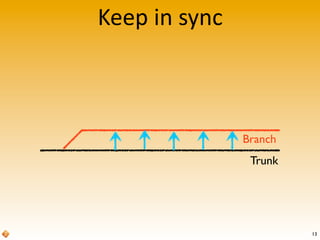
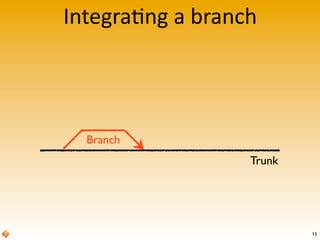
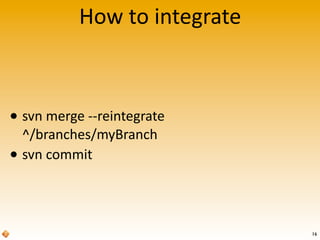
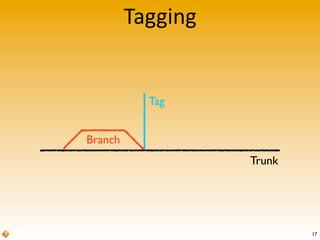
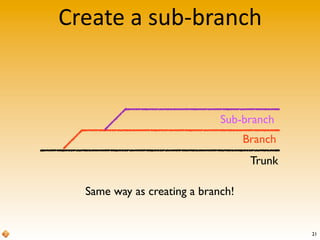
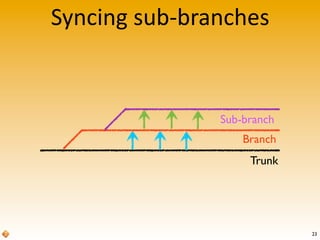
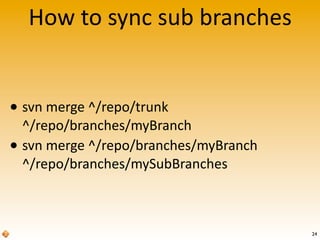
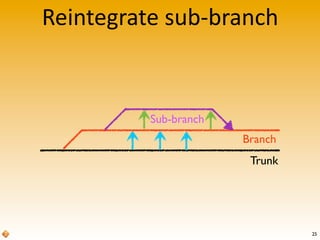
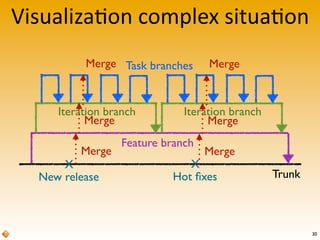
The document provides an introduction to version control using Subversion (SVN), explaining basic concepts such as repositories, branches, and tags. It outlines the reasons for using version control, common practices for branching, merging, and tagging, and also addresses handling complex projects with multiple tasks and developers. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of keeping branches in sync, resolving conflicts through collaboration, and the best practices for committing changes.