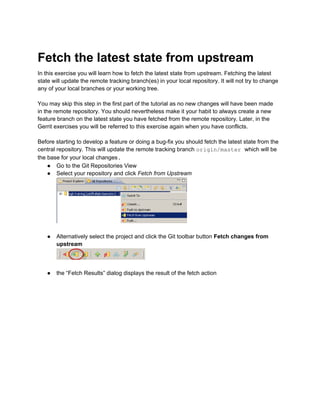
Fetching the latest state from the remote repository updates the remote tracking branches in the local repository without changing any local branches or the working tree. This allows developers to base new feature branches on the most up-to-date code from upstream. Developers should fetch changes regularly, especially before starting new features or fixes, to keep their local repositories in sync with the central repository.