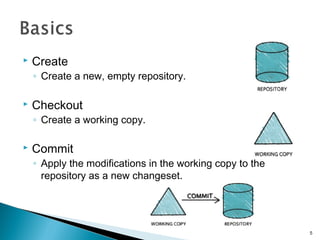
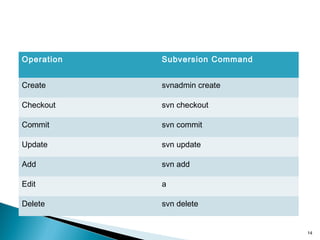
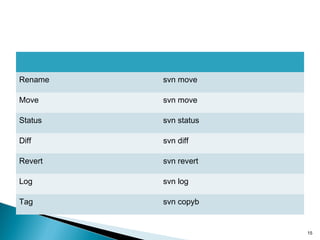
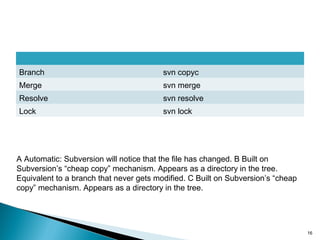
This document discusses version control systems and their goals of allowing developers to work simultaneously without conflicts while maintaining a complete history. It describes the basics of centralized and distributed version control systems. Centralized version control operations like commit, update, and log are outlined along with distributed version control operations like clone, push, and pull. Version numbering schemes are also covered.