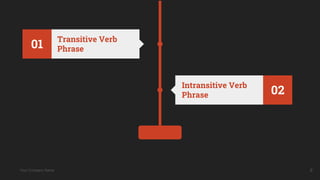
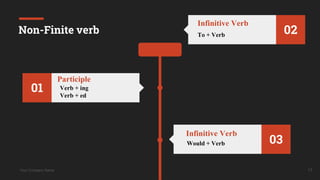
The document discusses verb phrases, detailing the two main types: finite and non-finite verb phrases, and their characteristics. Finite verbs convey tense and number, while non-finite verbs do not indicate time and can function in various grammatical roles. It also touches on transitive and intransitive verbs, as well as active and passive voice constructions.


![Introduction:
• Verb Phrase consist of an obligatory main verb and at times is aided by
an auxiliary verb, negative particle or an adverb.
VP= Obligatory [main Verb] + Optional [Auxiliary verb +negative particle+ Adverb]
Examples:
• He writes a letter.
VP= Main verb [writes]
• She does not really believe her own claims .
VP= Auxiliary verb [does] + Negative particle [not] + Adverb [really]
+ Main Verb [believe]
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/verbphraseinstylistics-230112141154-d3a00475/85/Verb-Phrase-in-Stylistics-pptx-3-320.jpg)