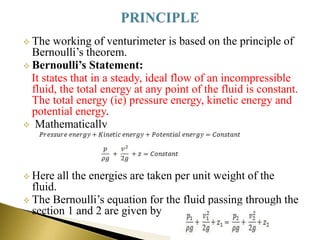
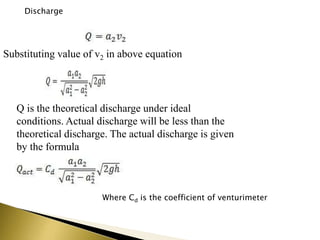
This document discusses the working principle and components of a venturimeter, which is a device used to measure fluid flow rate based on Bernoulli's principle. The main parts of a venturimeter are the converging section, throat, and diverging section. As fluid flows through the converging section into the throat, where the cross-sectional area is smallest, its velocity increases and pressure decreases. The pressure difference between two points in the venturimeter, such as at the inlet and throat, can be measured with a manometer and used to calculate flow rate according to Bernoulli's equation. The actual discharge rate is slightly less than the theoretical value due to losses and is determined using a discharge coefficient.