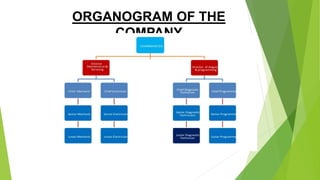
This document outlines a presentation on a student's industrial work experience at Hephzibah Autocare Limited, an automotive repair shop in Akure, Nigeria. The presentation covers the background of the organization, activities undertaken like vehicle diagnostics and maintenance, and an explanation of key diagnostic concepts like OBD-II scanners, diagnostic trouble codes, and common codes. It provides a practical example of interpreting a code and concludes with the student gaining valuable experience in diagnostics and recommending improvements to support the student training scheme.