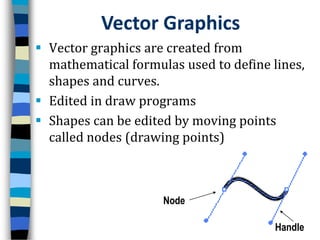
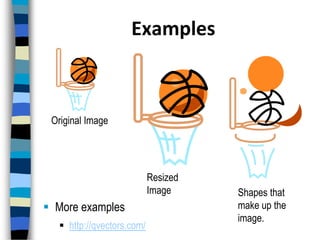
Vector graphics are created using mathematical formulas to define lines, shapes, and curves. They can be edited by moving nodes and have advantages like resolution independence and small file sizes. Popular vector graphic software includes Adobe Illustrator, CorelDraw, and Inkscape. Common file formats are AI, EPS, and SVG.