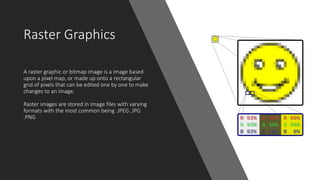
This document summarizes raster and vector graphics. Raster graphics use a grid of pixels that can be edited individually, while vector graphics use points and paths defined by coordinates. Common raster formats are JPEG and PNG, while common vector formats are SVG, EPS and PDF. Raster graphics generally have more file format support and are better for photos due to storing pixel data, while vector graphics can be scaled without quality loss and allow flexible editing but are less suitable for complex photos.