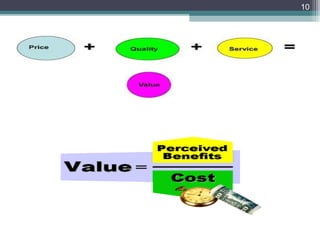
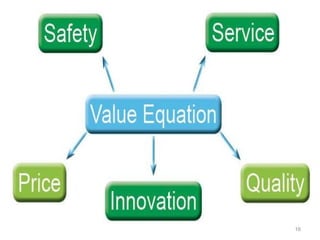
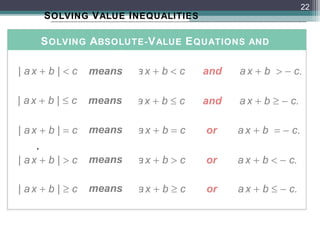
Value analysis is a technique to examine the functions of an item or product to determine if costs can be reduced while maintaining or improving functionality. The value equation defines value as benefits received divided by price paid. For example, the value of healthcare services can be calculated as the magnitude of patient improvement divided by the cost of care. Solving value equations and inequalities involves determining if the expression inside the absolute value is positive or negative.