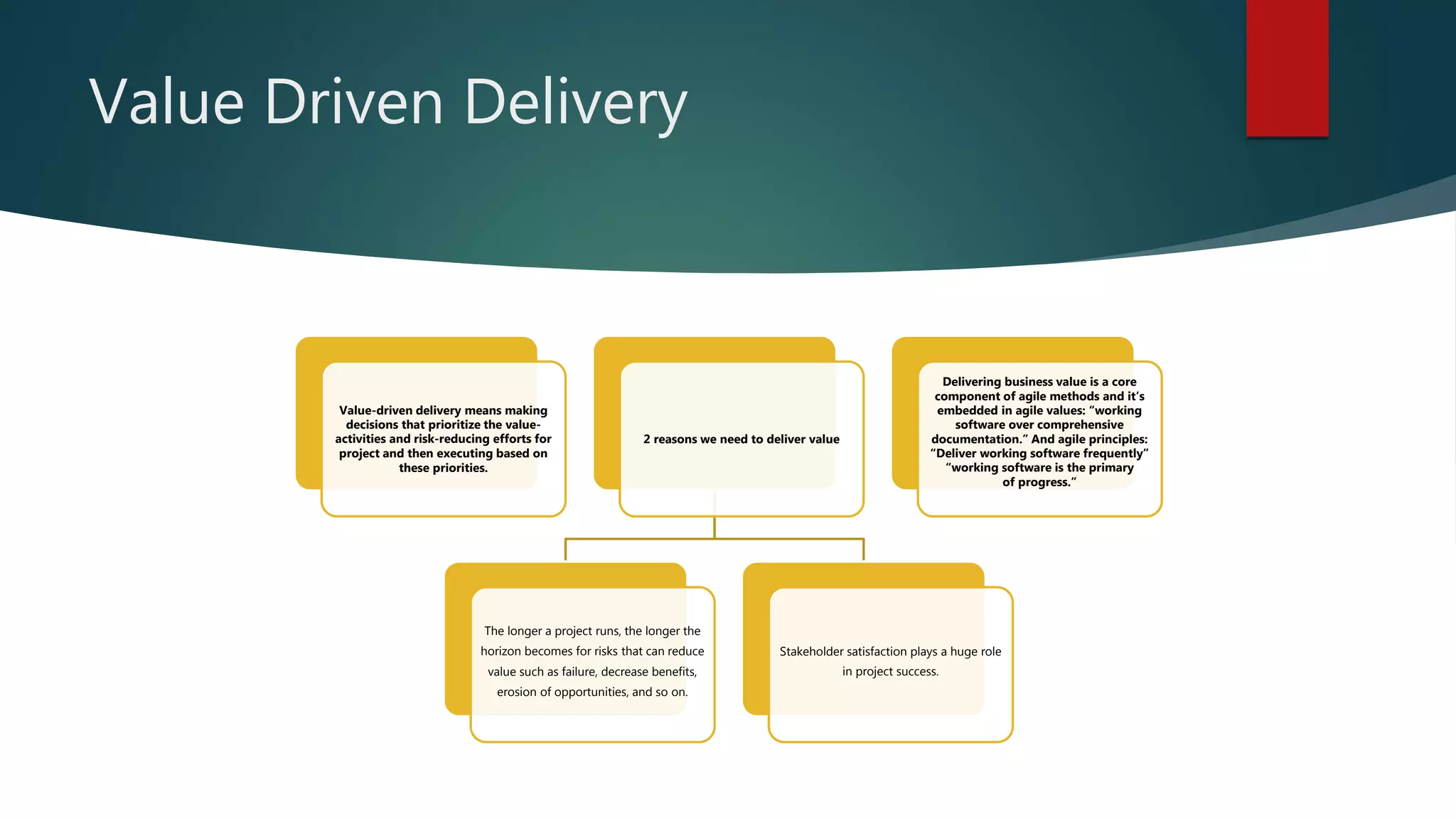
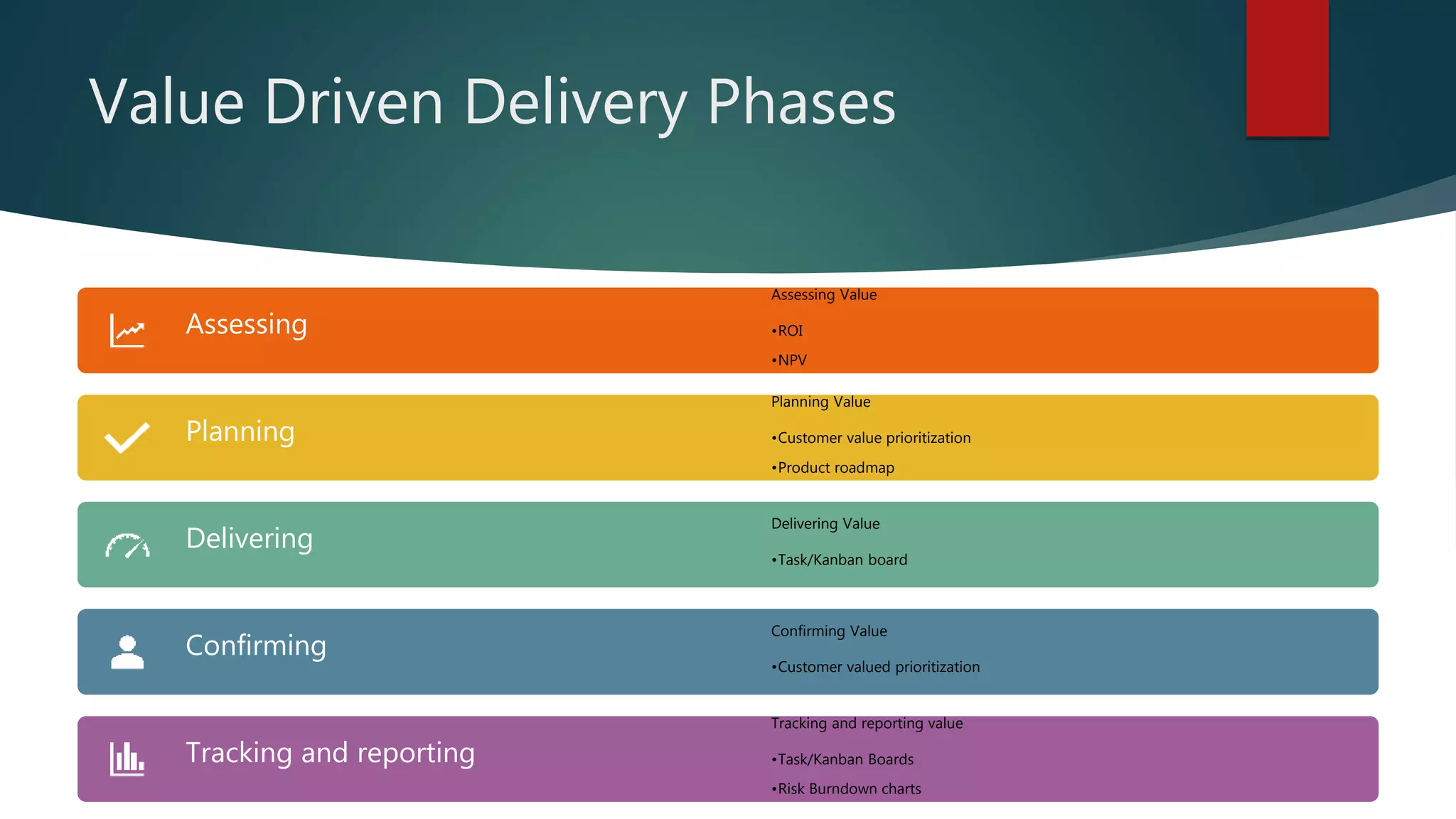
Value-driven delivery focuses on prioritizing project activities to maximize customer value, as defined by factors like monetary benefit and satisfaction. The approach emphasizes reducing risks and minimizing waste, leveraging metrics such as ROI and prioritization techniques to inform decisions throughout the project lifecycle. Best practices include iterative delivery, stakeholder collaboration, and responsiveness to changing requirements to ensure the highest value is consistently provided to customers.