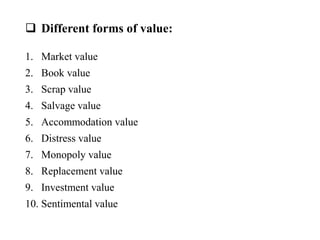
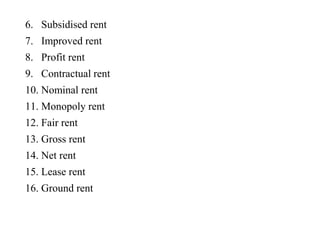
The document discusses valuation and estimation of properties. It defines valuation as determining the fair price or value of a property based on factors like structure, location, and income. Valuation is needed for buying/selling, taxation, rent fixation, loans, compensation, and more. Estimation calculates construction costs. Methods of valuation include rental, land and building, profit, and development approaches. Types of value and rent are also outlined. Standard rent is the legal rent determined from a property's value.