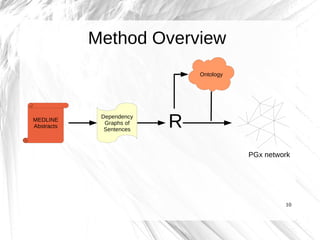
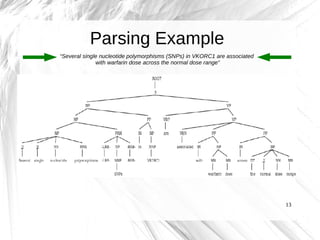
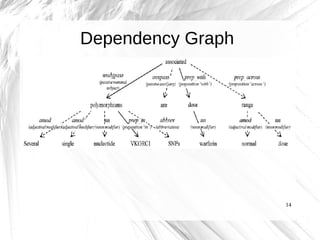
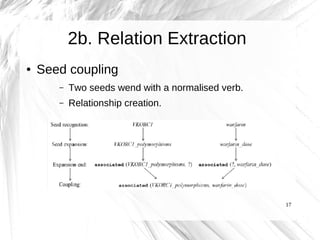
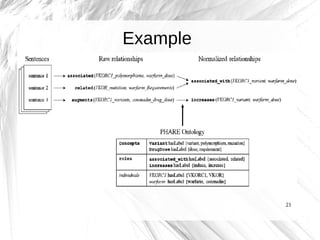
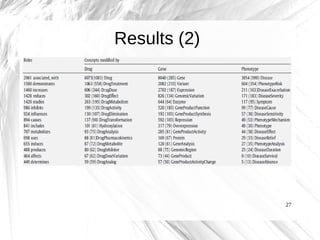
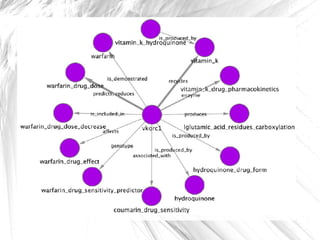
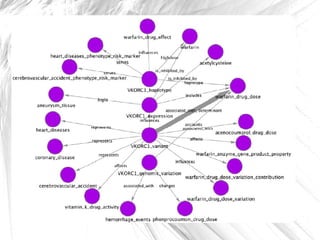
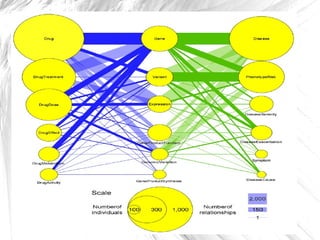
This document presents a method for automatically extracting relationships from biomedical literature and constructing a semantic network for pharmacogenomics knowledge. The method uses natural language processing techniques to parse sentences from abstracts, extract raw relationships between entities, and normalize relationships into an ontology. It was tested on over 17 million MEDLINE abstracts, extracting over 41,000 raw relationships. An ontology of 237 concepts and 76 roles was created to label the most frequent relationship types between genes, drugs and phenotypes. The results demonstrate an effective new approach for pharmacogenomics text mining and knowledge base construction.