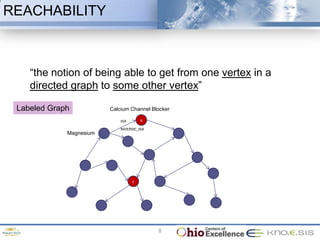
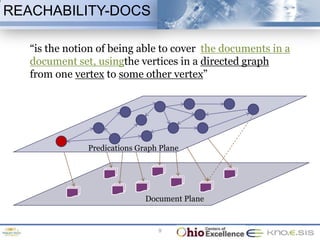
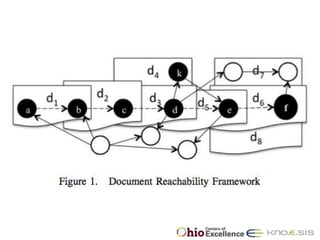
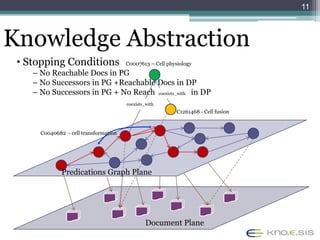
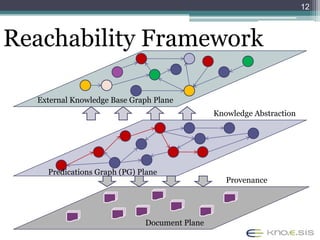
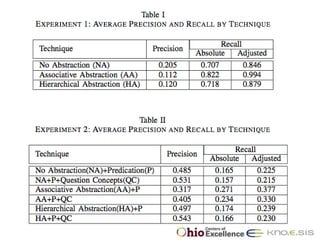
The document discusses the 48th ACM Southeast Conference and the presentation on semantic predications for complex information retrieval in biomedical literature. It highlights challenges in querying and document navigation, and introduces a framework utilizing semantic predications for knowledge-driven retrieval, enhancing the effectiveness of information discovery in the biomedical domain. Future work includes improving path/predication ranking and addressing computational complexity.


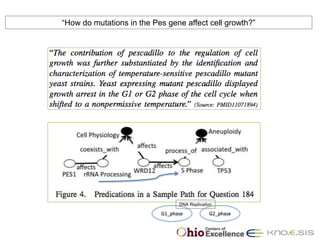
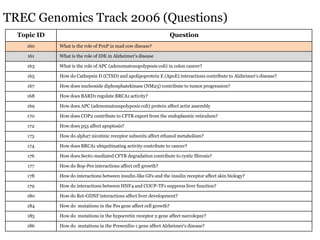
![“How do mutations in the Presenilin-1 (PS1) gene affect Alzheimer’s disease (AD)?”
PS1 associated_withAlzheimer’s Disease
. . . mutations in PS1 lead to Alzheimer’s disease by increasing the
extracellular levels of [amyloid peptide 42] A42. (Source: PMID10652366)
Semantic Predications
. . . familial early onset Alzheimer’s disease is caused by point mutations in
the amyloid precursor protein gene on chromosome 21, in the presenilin
2(PS2)1 gene on chromosome 1, or, most frequently, in the presenilin
chromosome14 finding_site_ofpresenilin1
1(PS1) gene on chromosome14. . . (Source:PMID9013610)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cameron-bibm2011-120217122640-phpapp02/85/Cameron-bibm2011-3-320.jpg)