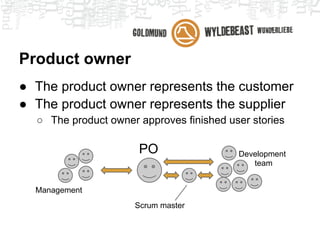
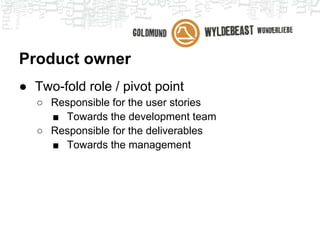
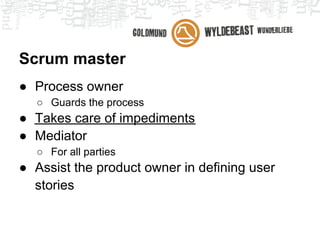
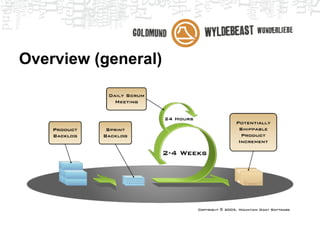
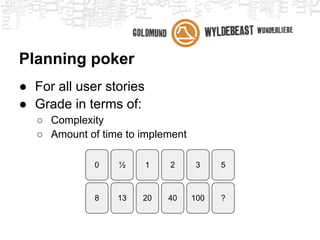
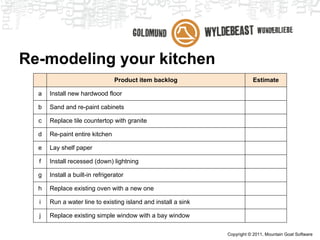
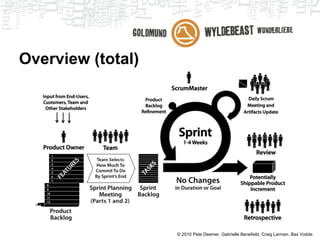
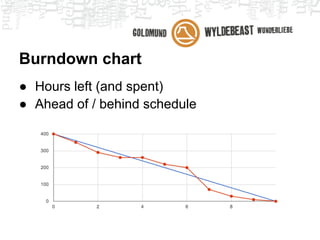
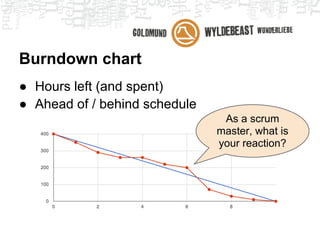
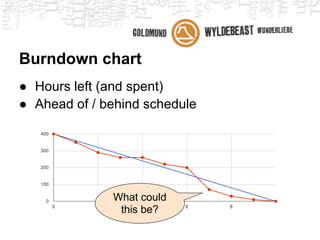
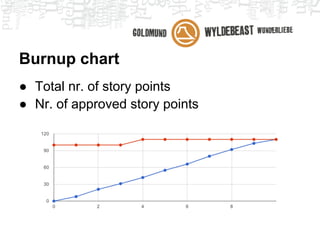
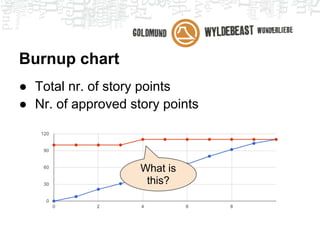
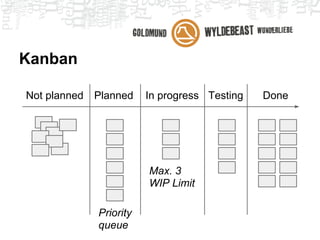
Scrum is an agile framework for managing product development. Key roles include the Product Owner, who represents stakeholders and priorities work. The Development Team works in iterations (sprints) to implement user stories, while the Scrum Master helps remove impediments. Ceremonies like planning poker, daily standups, and retrospectives provide transparency and opportunities to inspect and adapt the process sprint-over-sprint. Metrics like velocity and burndown charts are used for planning and monitoring progress. Tools like Jira help automate workflows and provide visibility.