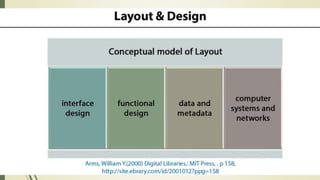
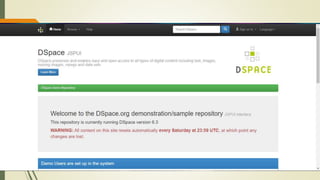
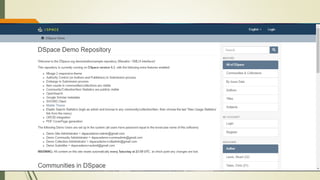
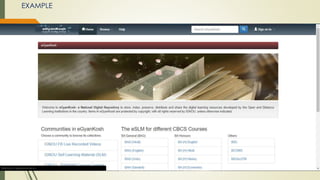
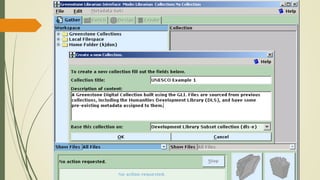
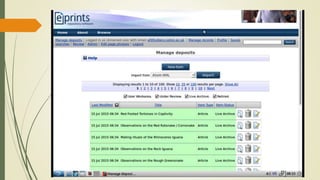
This document discusses the user interface of digital library software. It defines what a user interface is and explains that it is important for digital libraries to have an effective user interface since users can be from varied backgrounds. It describes principles for designing a good user interface, such as making it simple and familiar. It also discusses how to evaluate user interfaces, including criteria like ease of use and user satisfaction. Finally, it provides examples of the user interfaces of specific digital library software like DSpace, Greenstone, and EPrints.