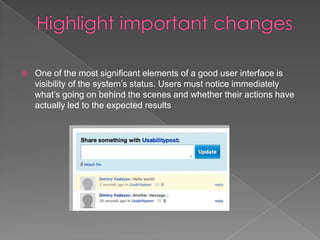
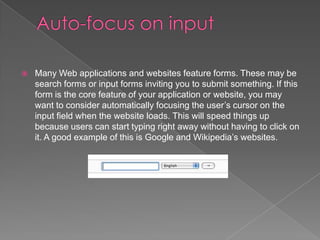
User interface design aims to create systems that are usable and adaptable to changing user needs. Good UI design considers principles of layout, color theory, and negative space while ensuring visibility of system status and directing attention to important elements. Forms and input fields should be automatically focused to improve usability. Error messages should be polite, consistent, and constructive based on the user's background and experience.