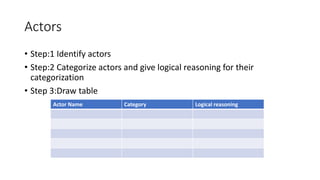
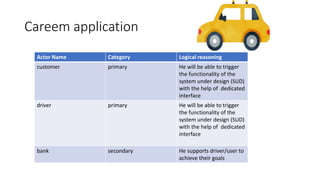
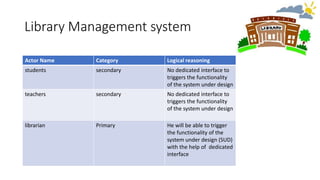
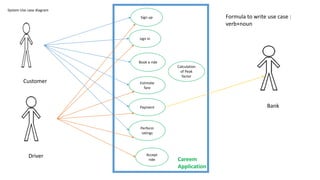
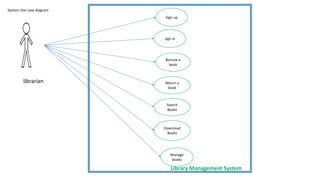
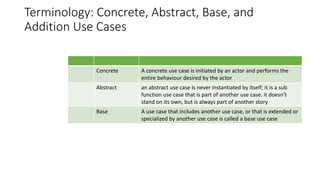
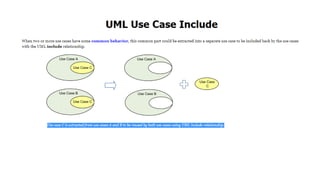
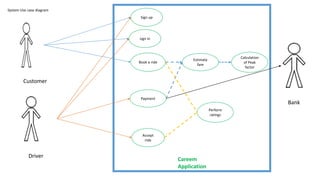
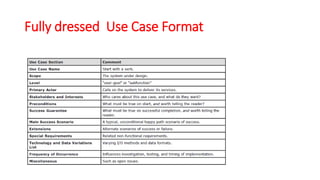
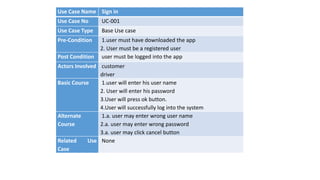
The document discusses use case analysis in software engineering. It defines what a use case is, including that it specifies system requirements and describes scenarios of how actors will use the system. It also defines actors, scenarios, different use case formats (brief, casual, fully dressed), and relationships between use cases like include and extend. The document then provides examples of identifying actors and writing use cases for a ridesharing and library management system.




![Actor Definition
• An actor specifies a role played by a user or any other system that
interacts with the subject." [UML spec. v2.0]
• We use the term "actor" to represent the role of someone or
something that interacts with the system.
• Actors exist outside of the scope of a use case and are responsible for
initiating use cases.
• an actor is something with behavior, such as a person (identified by
role),computer system, or organization; for example, a cashier.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usecaseusecasedescription-240121124300-fc063b0c/85/use_case-use_case-description-pptx-5-320.jpg)