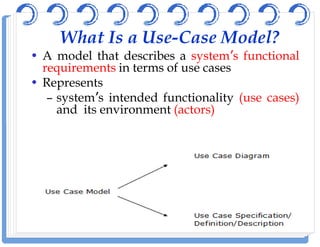
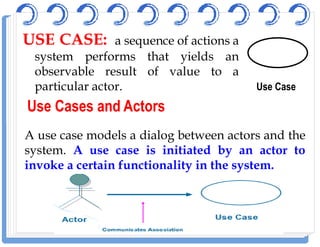
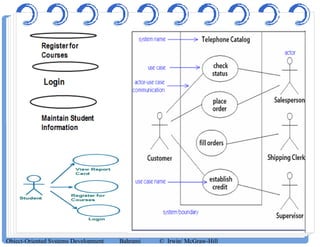
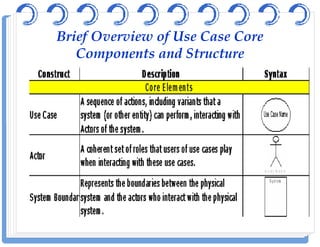
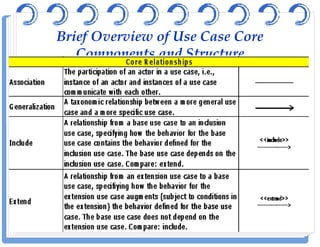
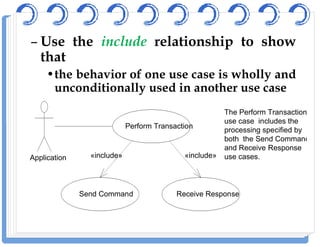
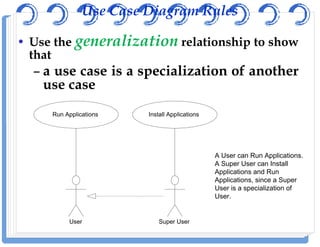
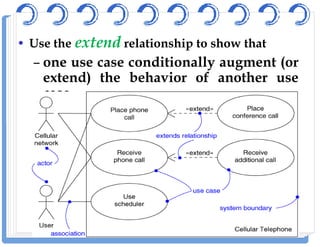
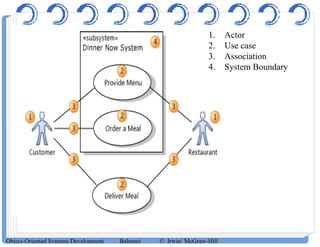
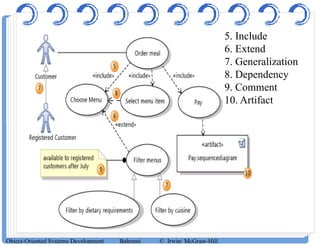
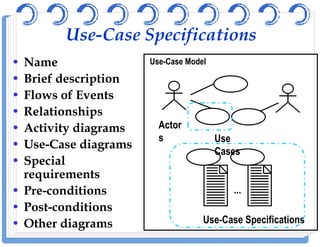
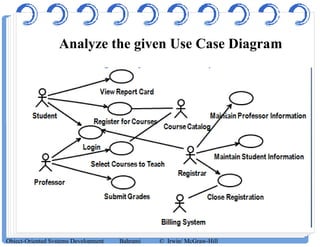
The document discusses use case diagrams and their components. It defines key terms like actors, use cases, and relationships between use cases. It explains that use case diagrams model interactions between actors and a system, and capture the system's functional requirements. Diagrams show actors outside the system boundary and use cases inside it. Relationships like "include", "extend", and "generalization" define relationships between use cases. The document provides examples and guidelines for creating use case specifications that describe use case scenarios in detail.