The document discusses functions and function components in C++. It introduces key concepts such as:
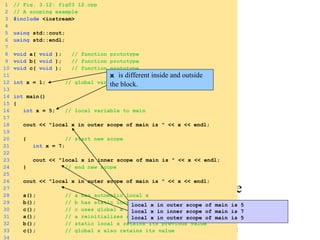
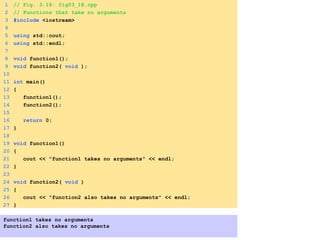
- Functions allow programmers to divide programs into modular and reusable pieces.
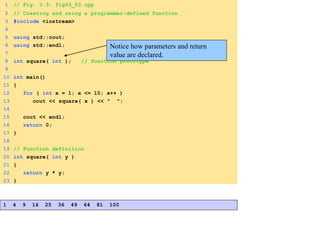
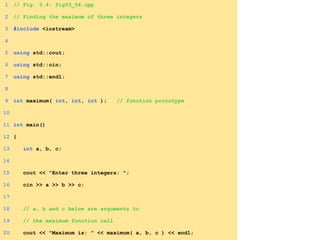
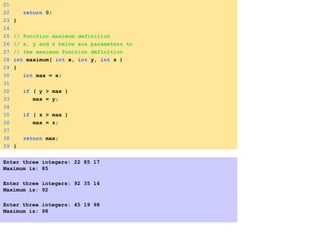
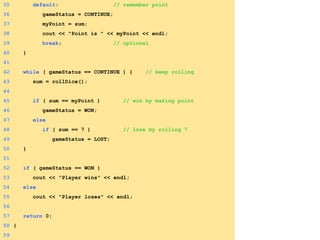
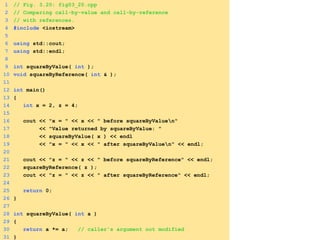
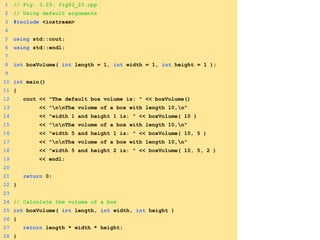
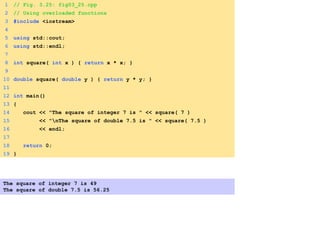
- Functions are defined once and can be called multiple times from different parts of a program. They take in parameters and return values.
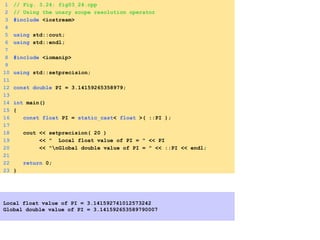
- The standard library provides many commonly used functions for tasks like math operations.
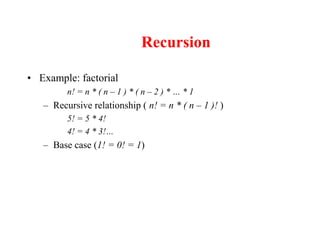
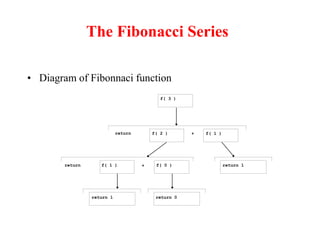
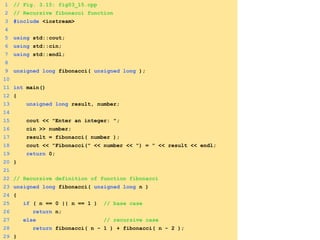
- Functions can be used to encapsulate and reuse code through prototypes and definitions.
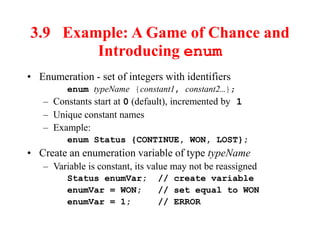
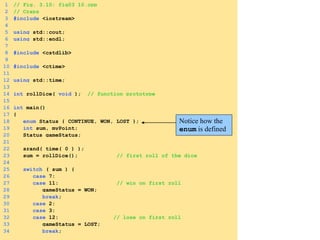
- Enumerations allow defining a set of integer constants with unique names for use as variable types.
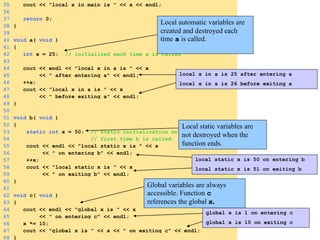
- Storage classes like static and auto determine where variables are stored in memory and their scope within a program.