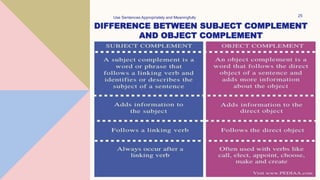
This document provides an overview of the key parts of a sentence including the subject, predicate, object, complement, and modifiers. It defines each part and provides examples. The subject refers to who or what the sentence is about. The predicate includes the verb and everything that follows it. Objects are things acted upon by the verb. Complements modify the subject or object. There are different types of each part such as direct/indirect objects and subject/object complements. Exercises are included to identify each part in sample sentences.