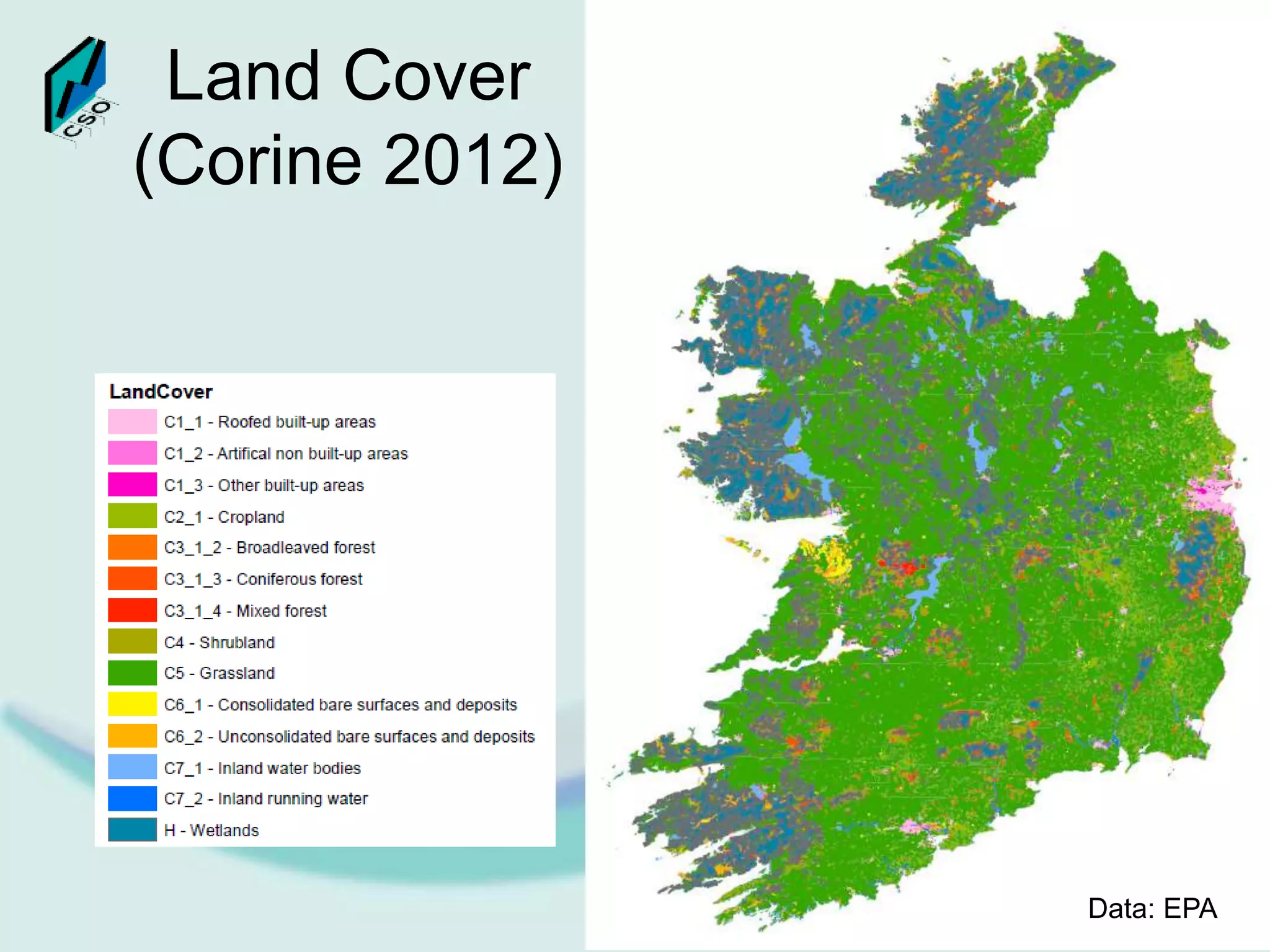
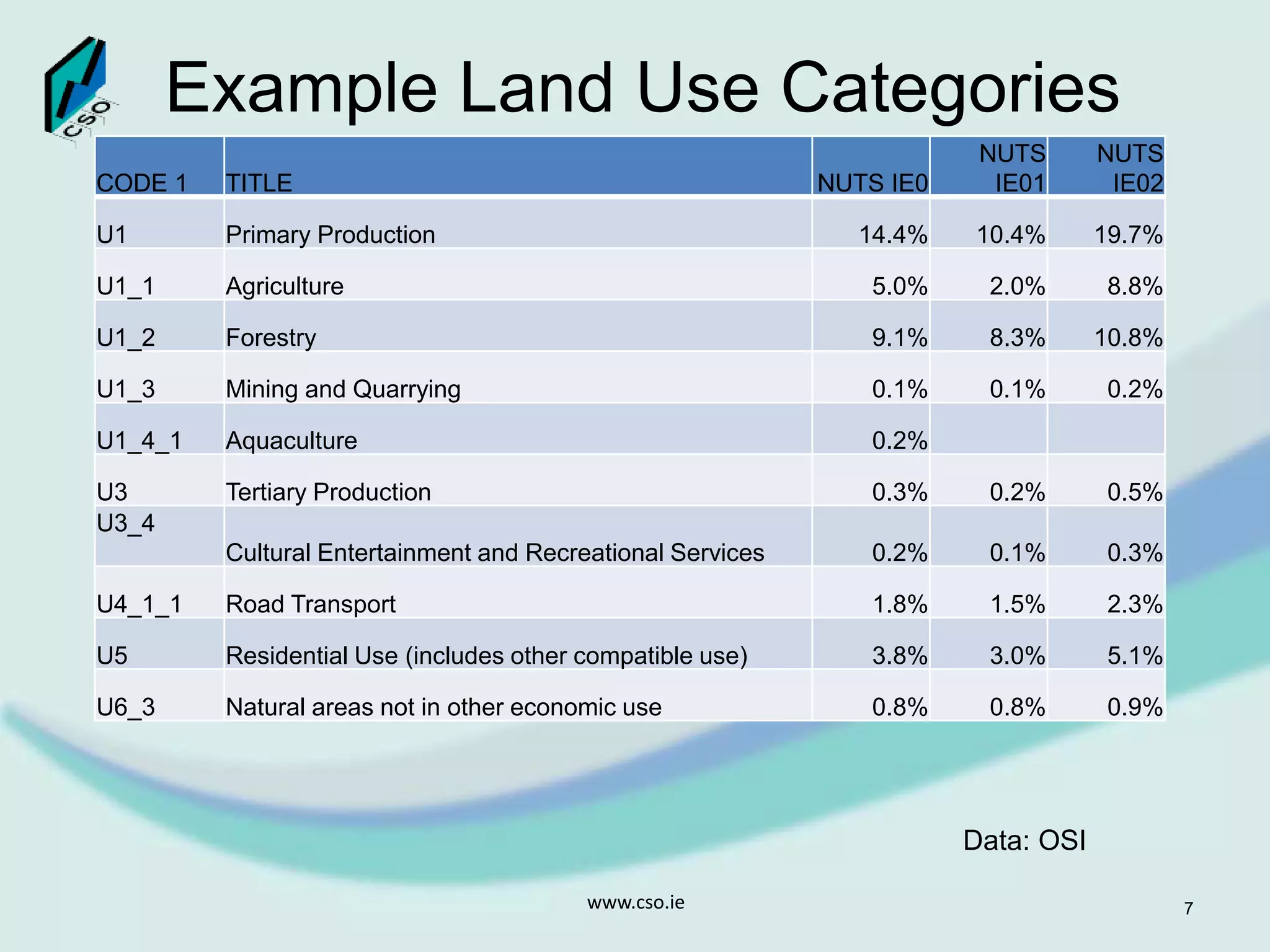
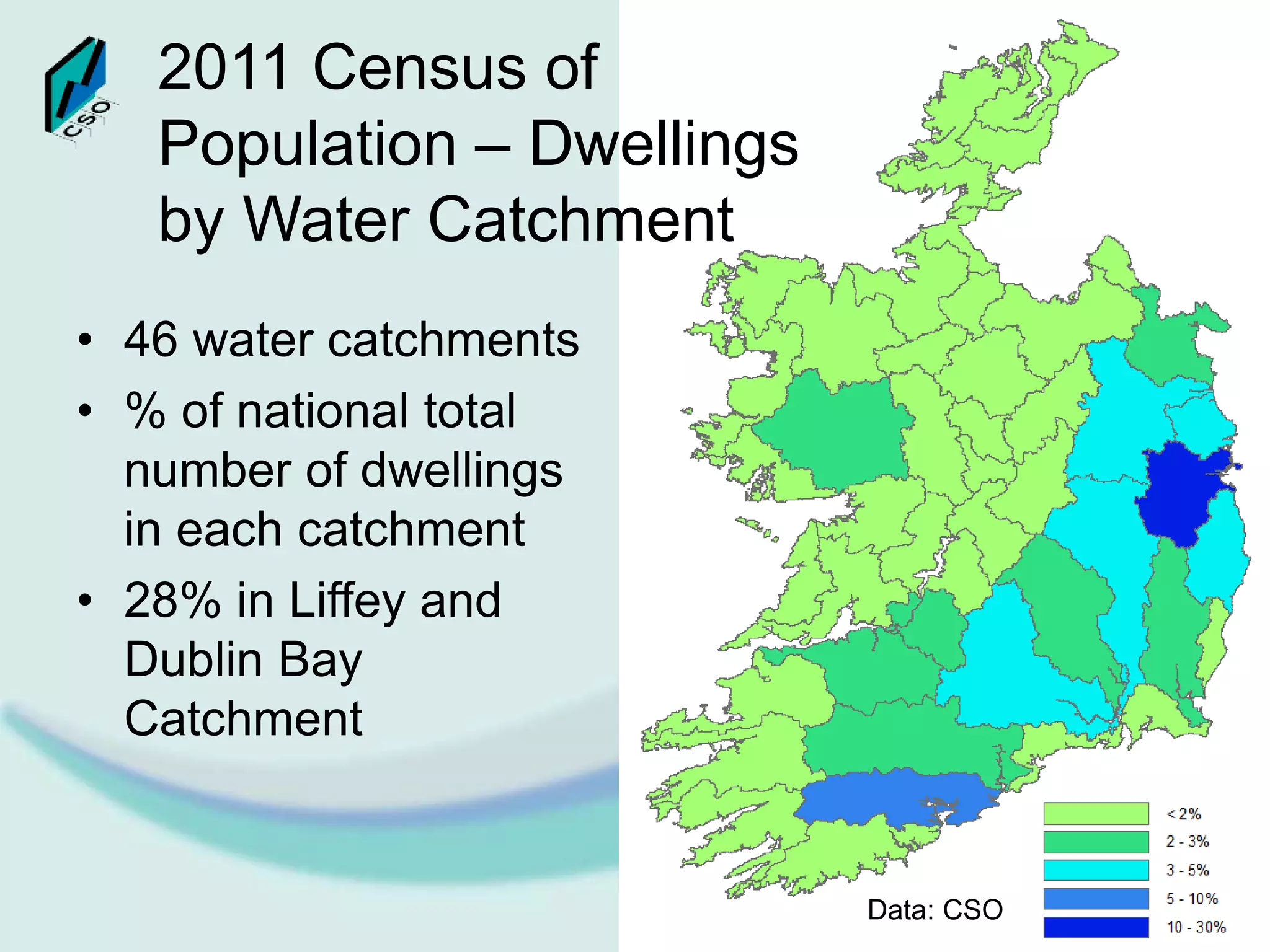
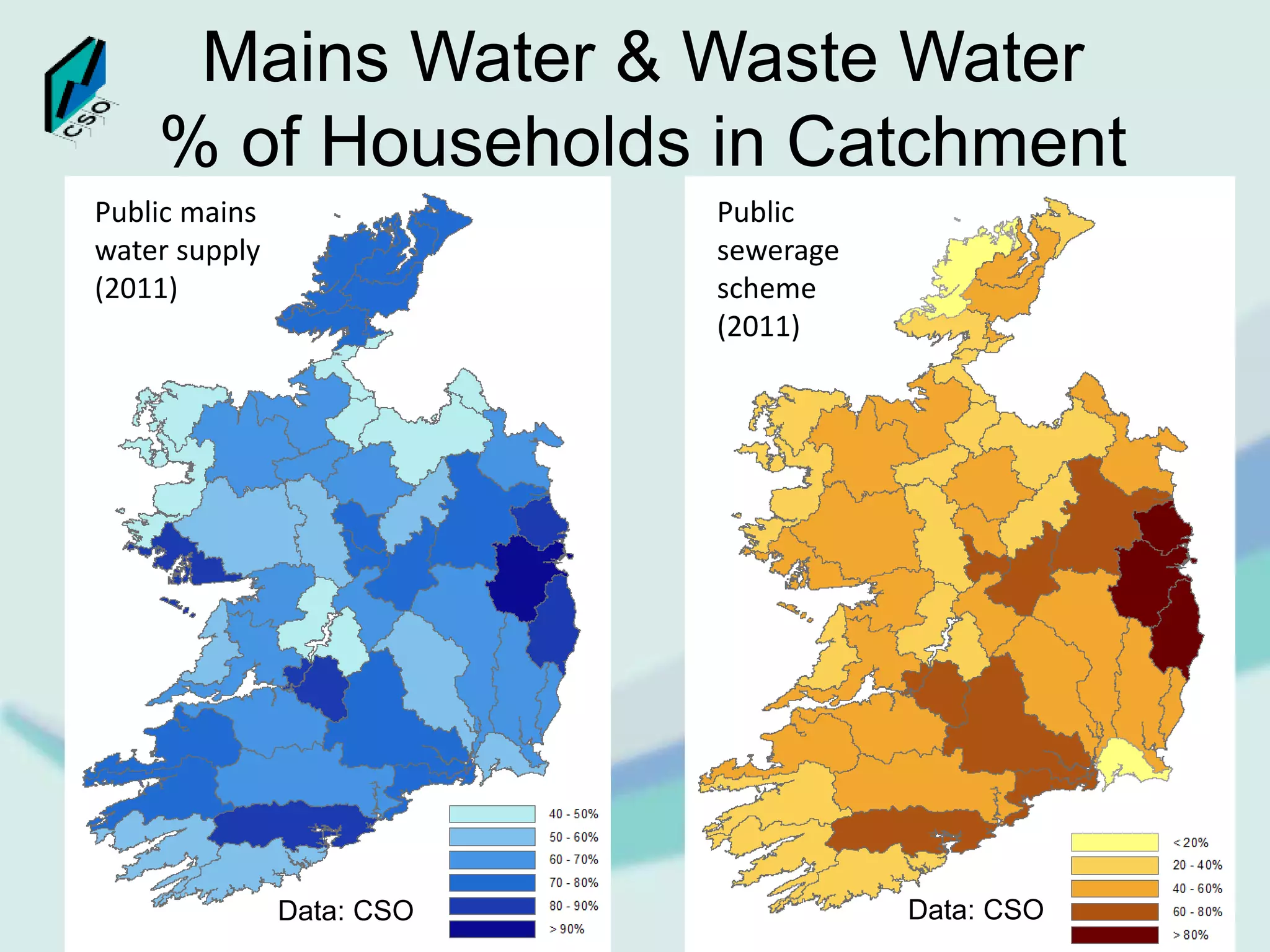
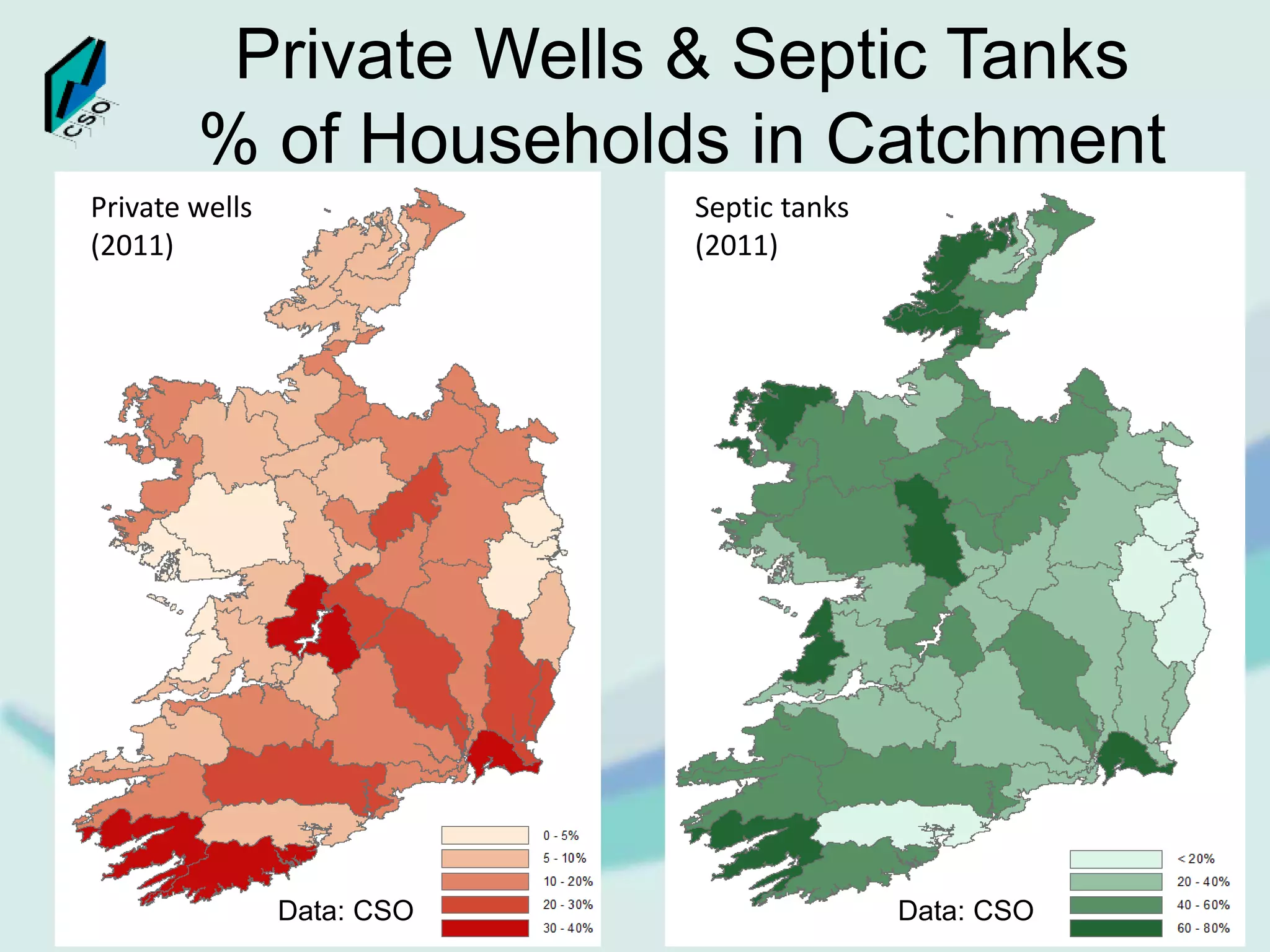
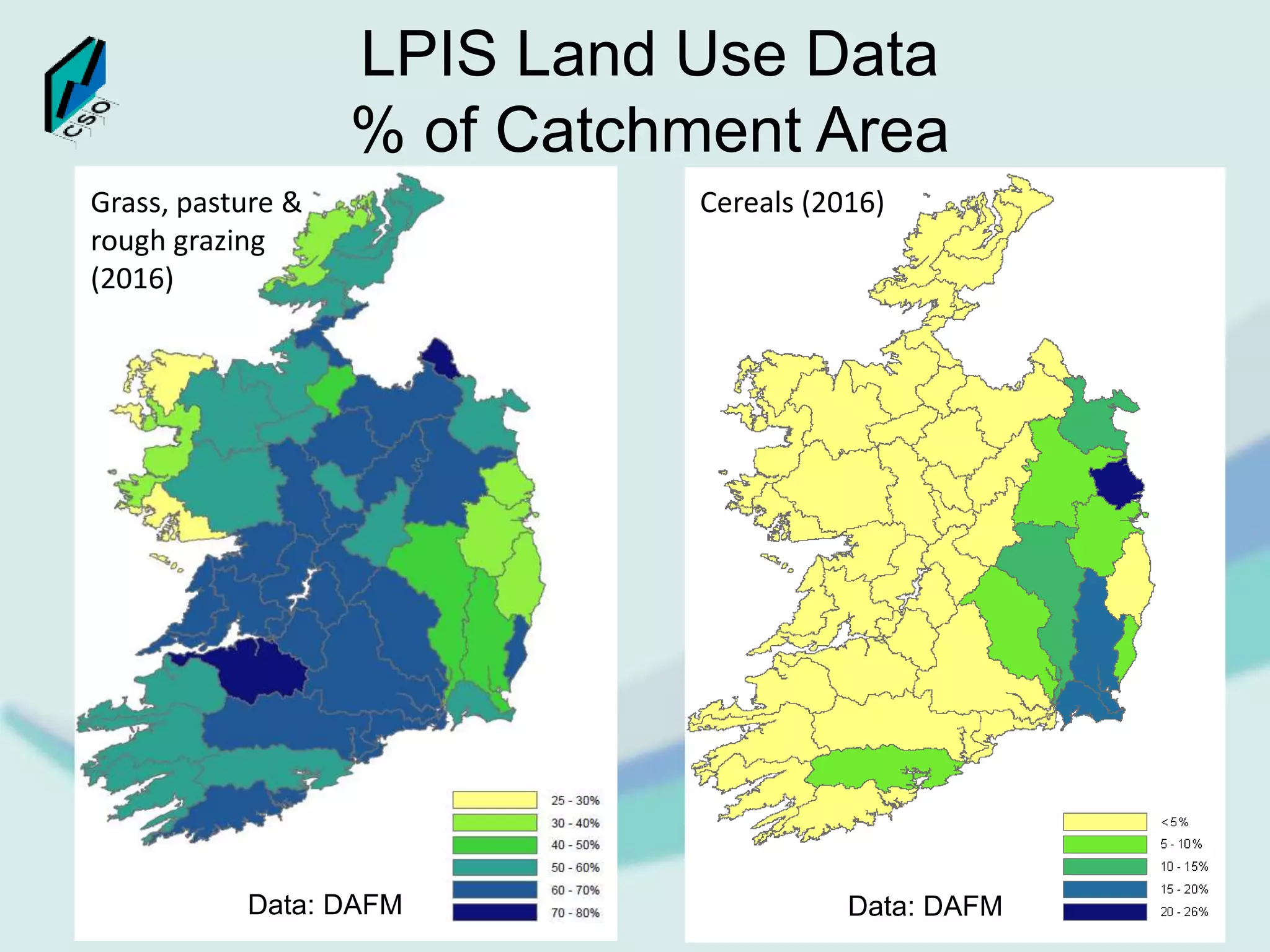
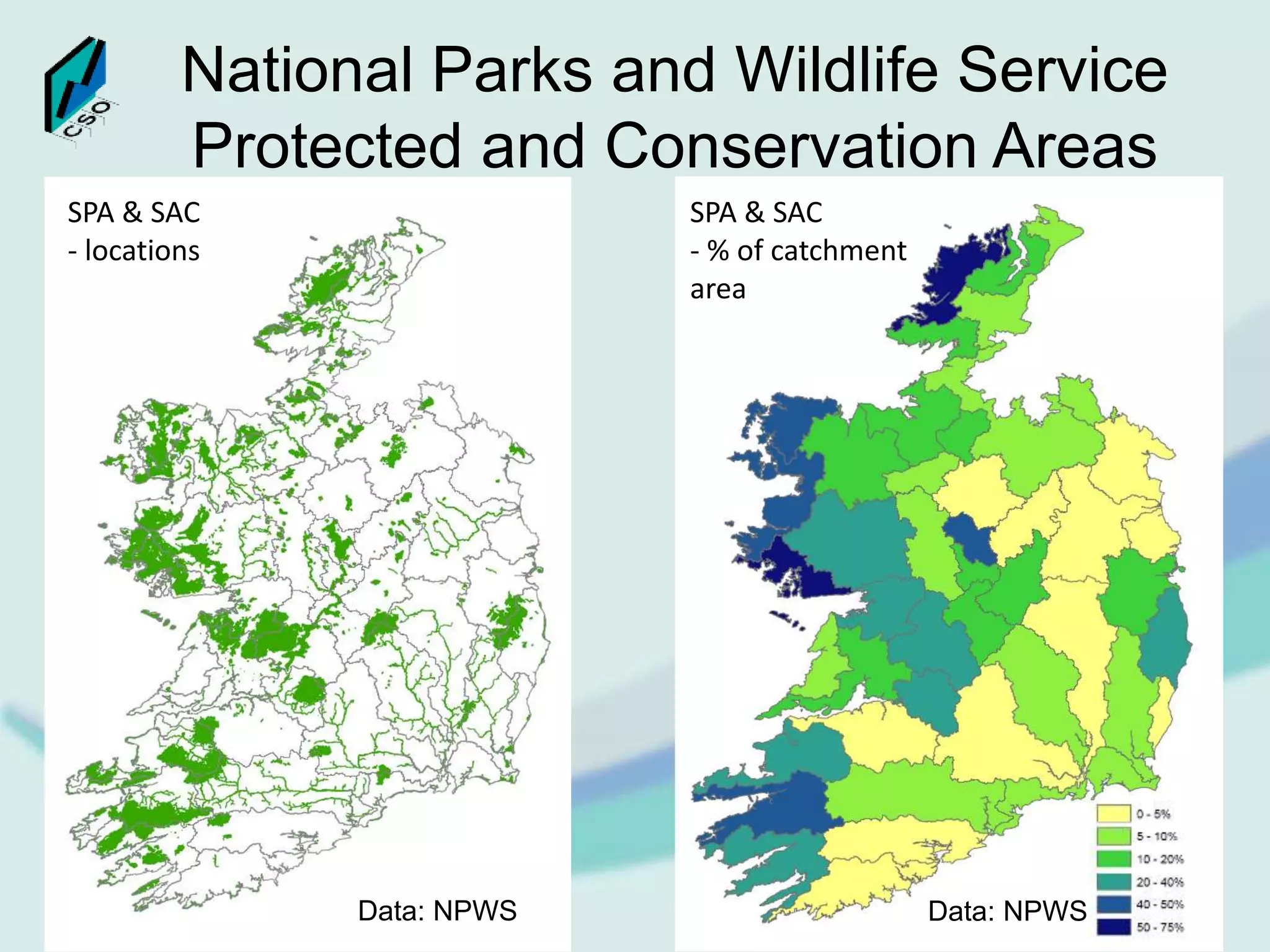
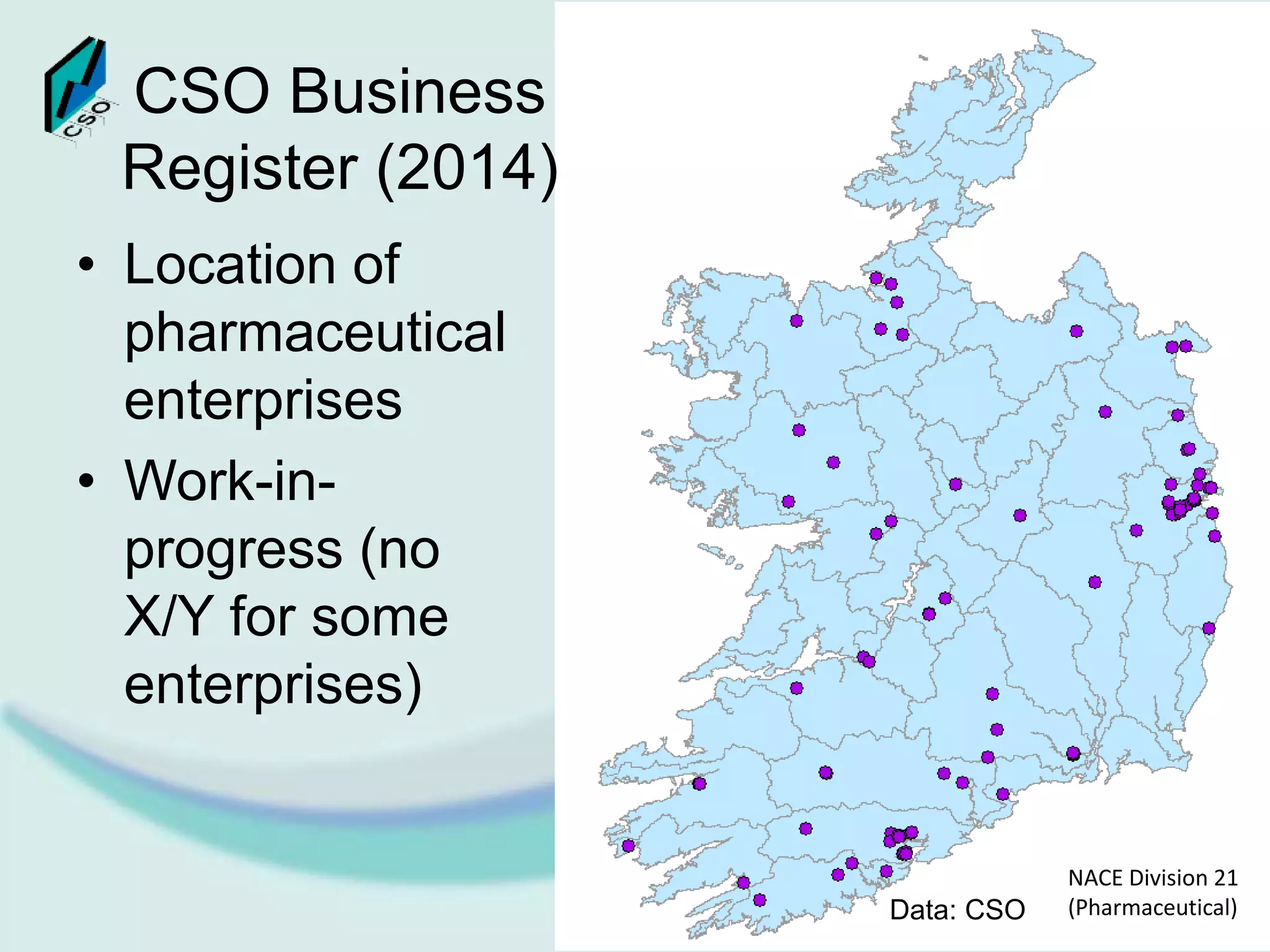
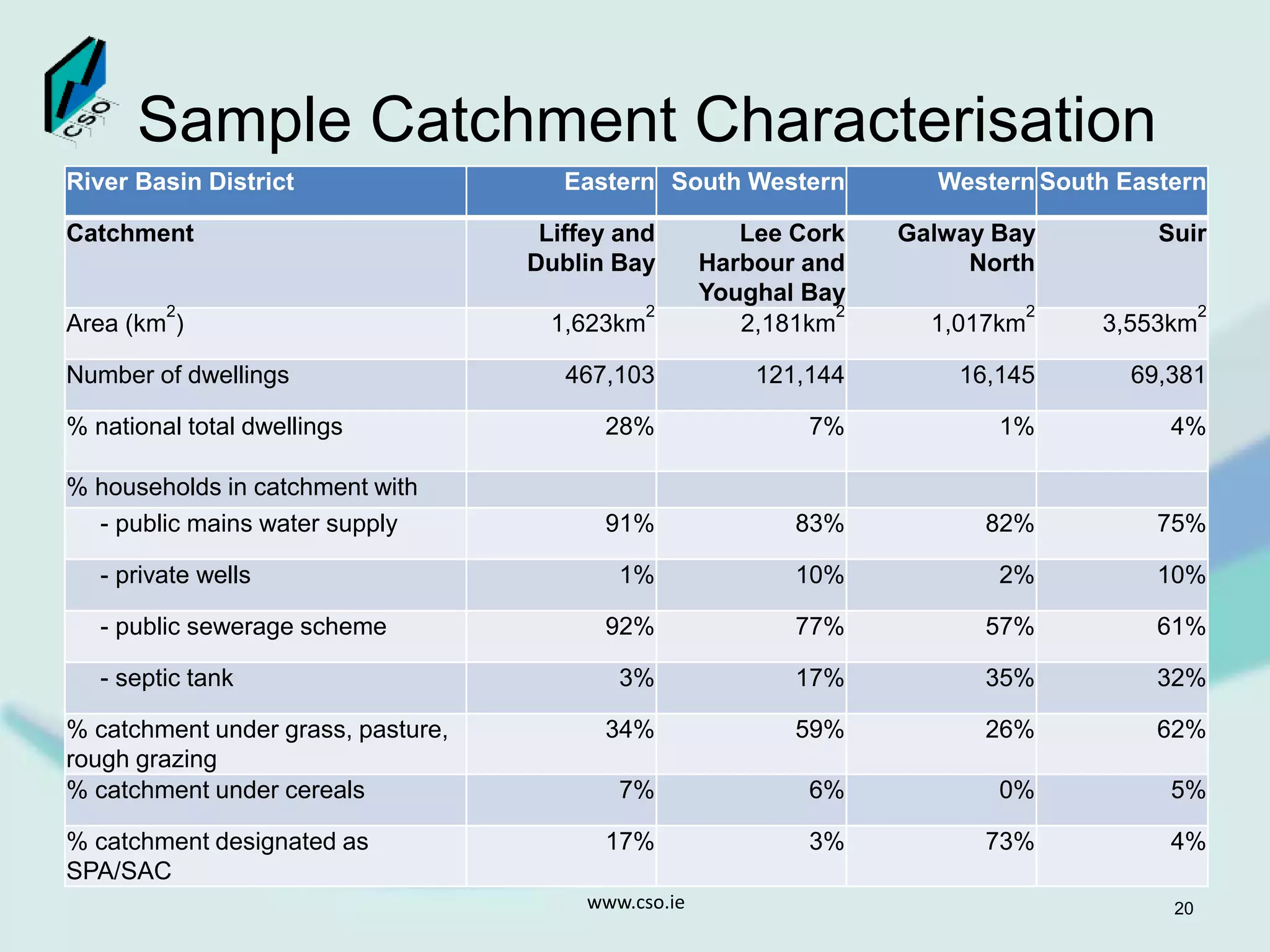
The document discusses the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) within the Central Statistics Office (CSO) of Ireland, highlighting its historical use for census visualizations and recent applications in environmental statistics. It details various GIS-related projects, notably in land cover and use, and emphasizes the need for accessing geocoded microdata to support ecosystem accounting and analysis. It concludes with a call for collaboration among agencies and the importance of long-term archiving of geocoded data for future analyses.