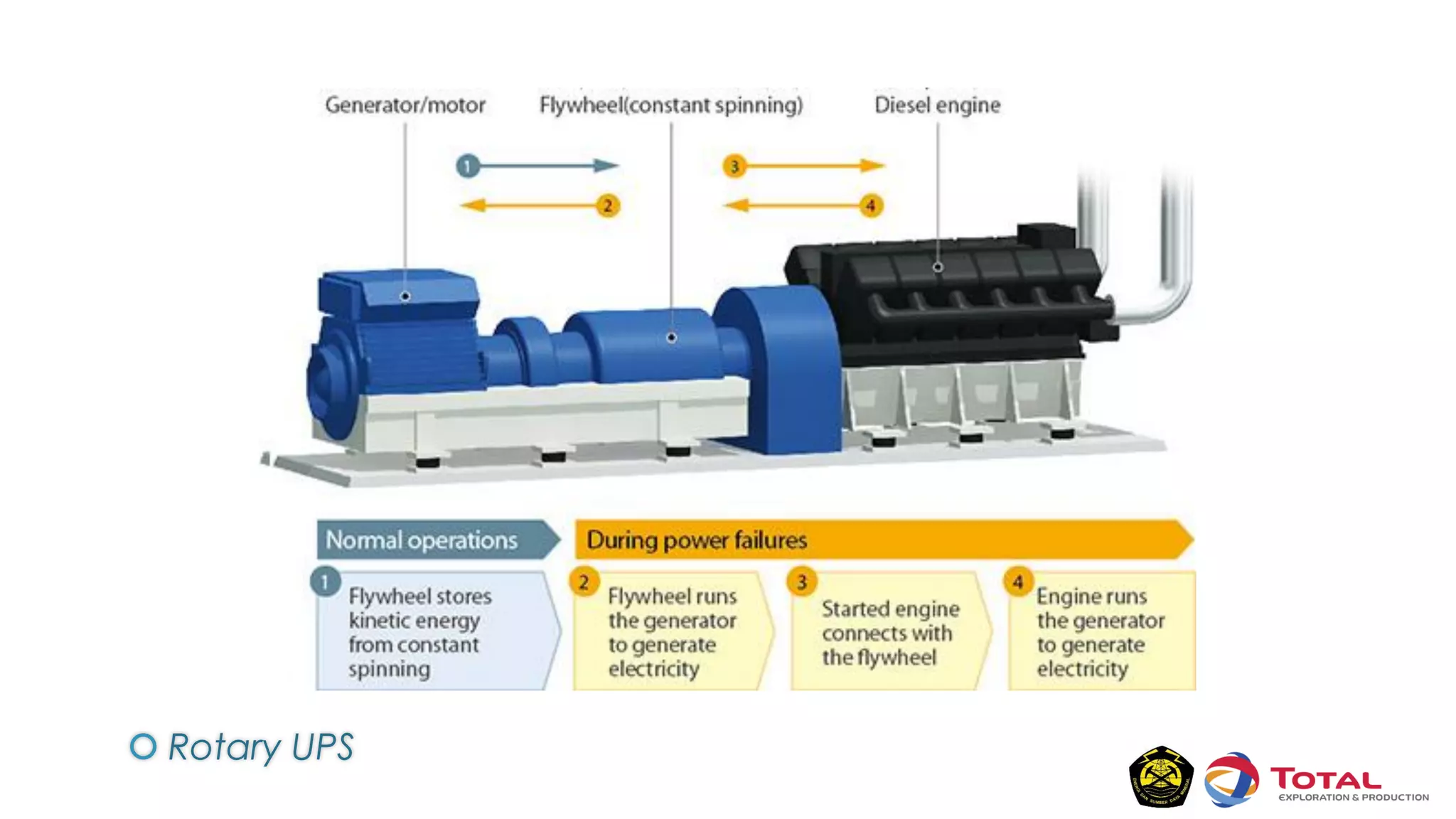
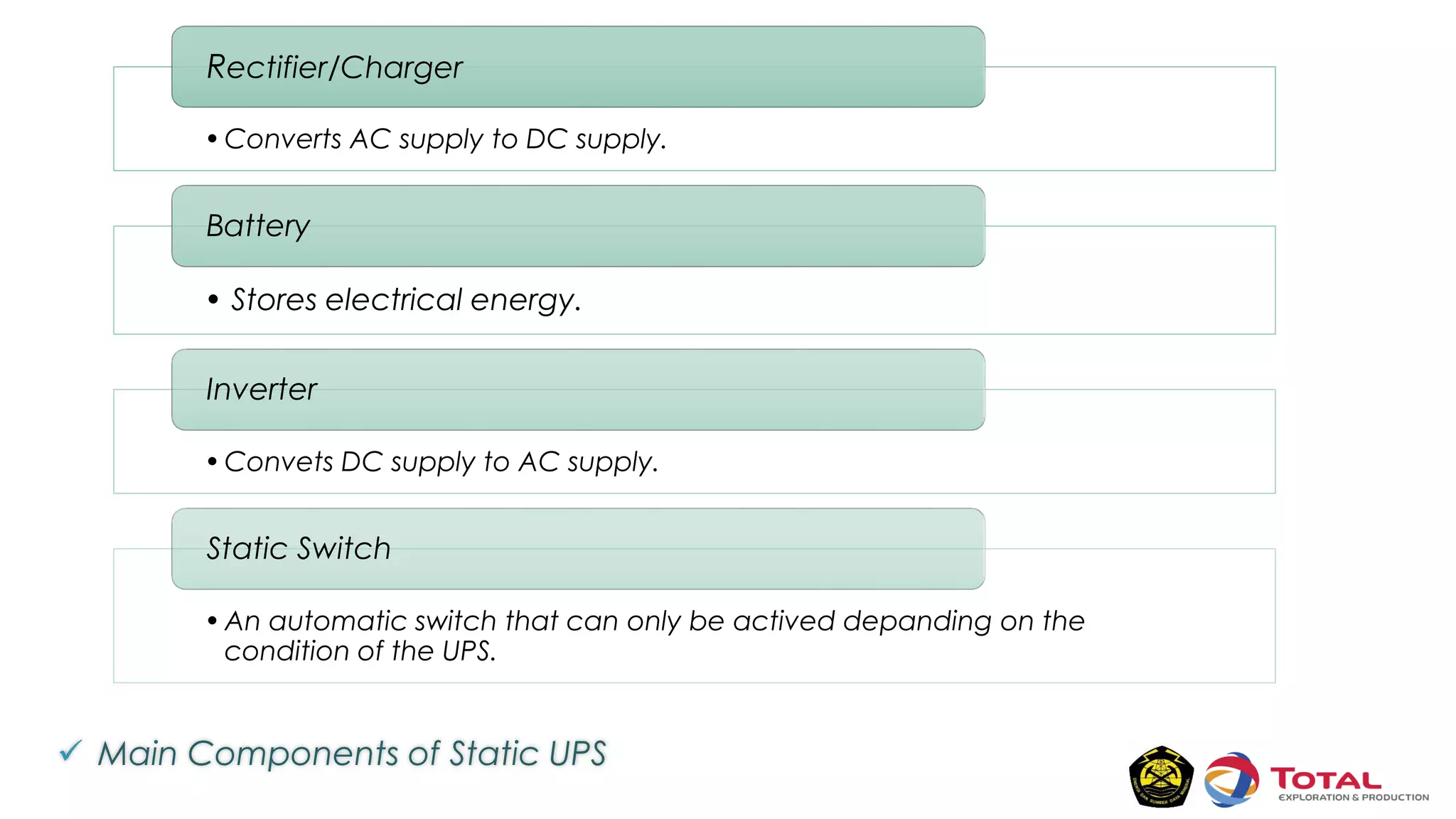
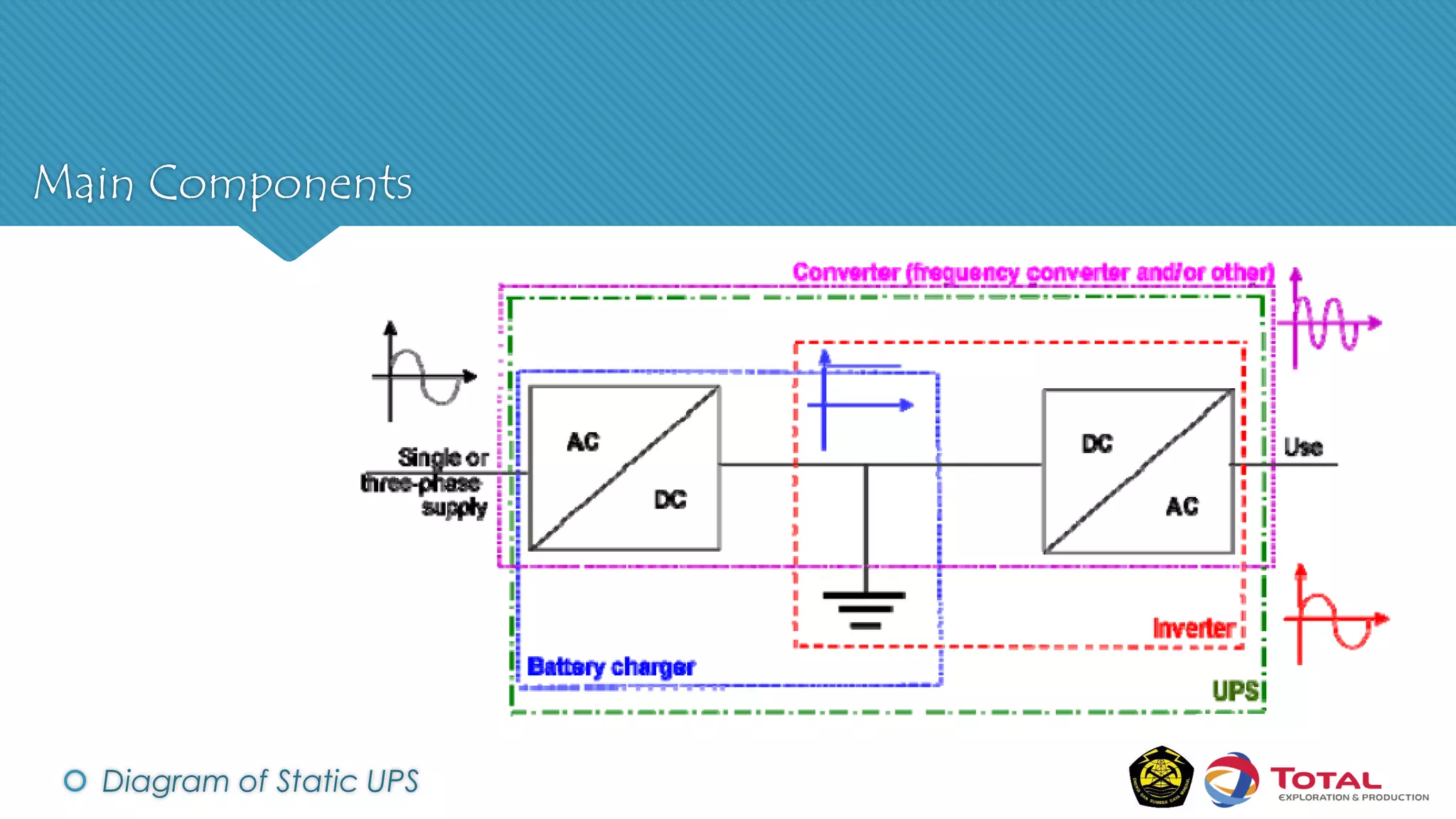
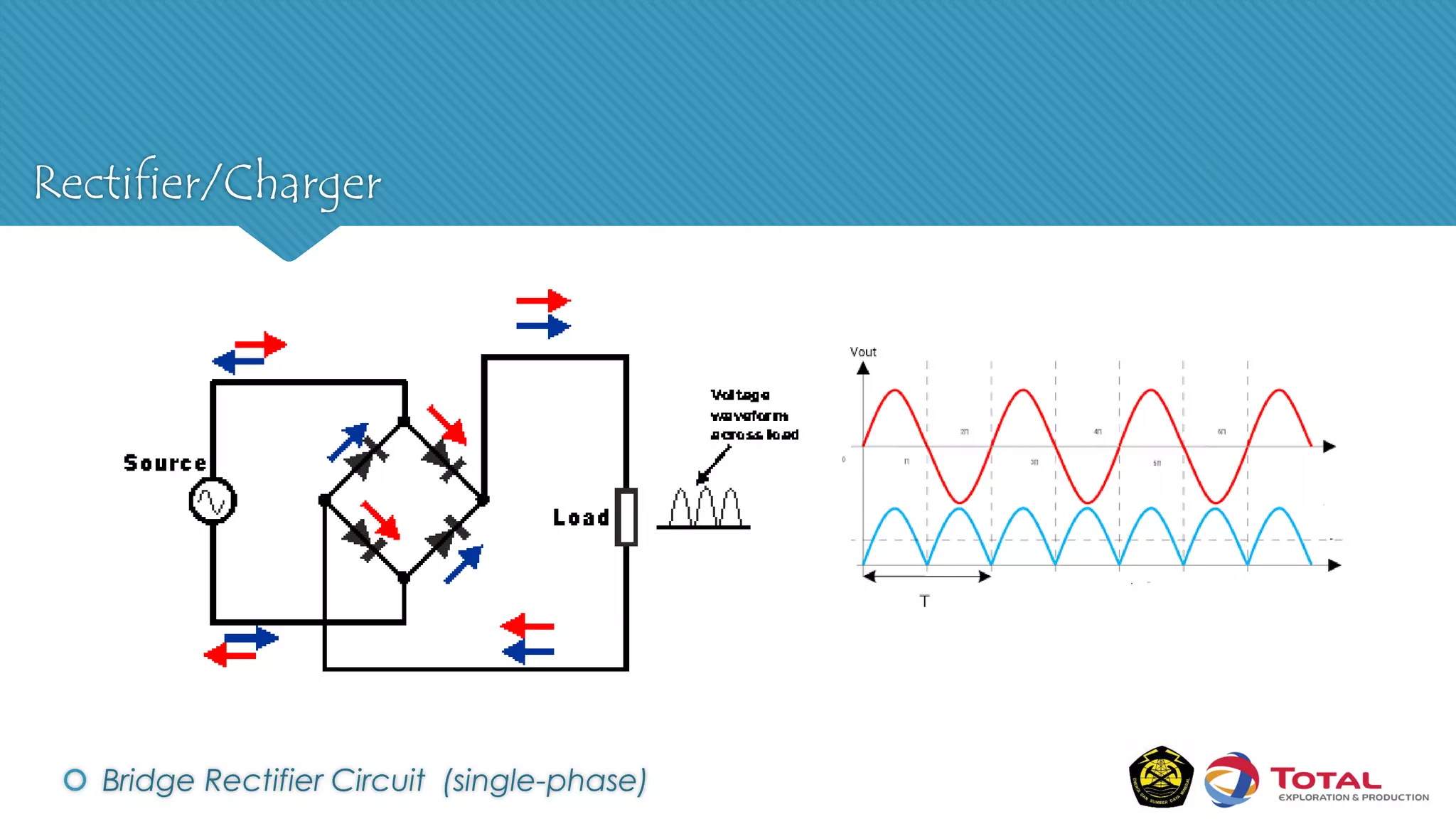
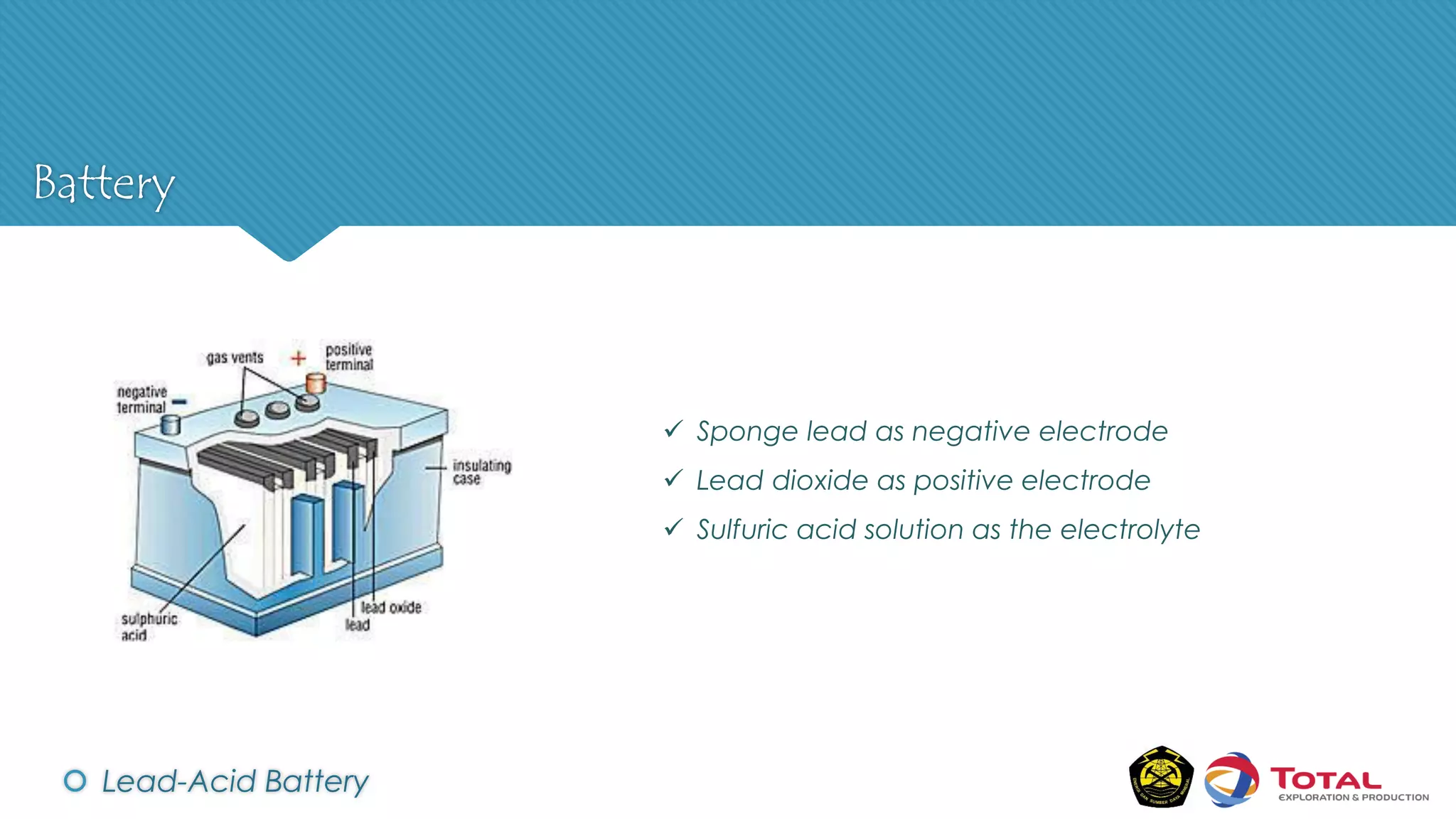
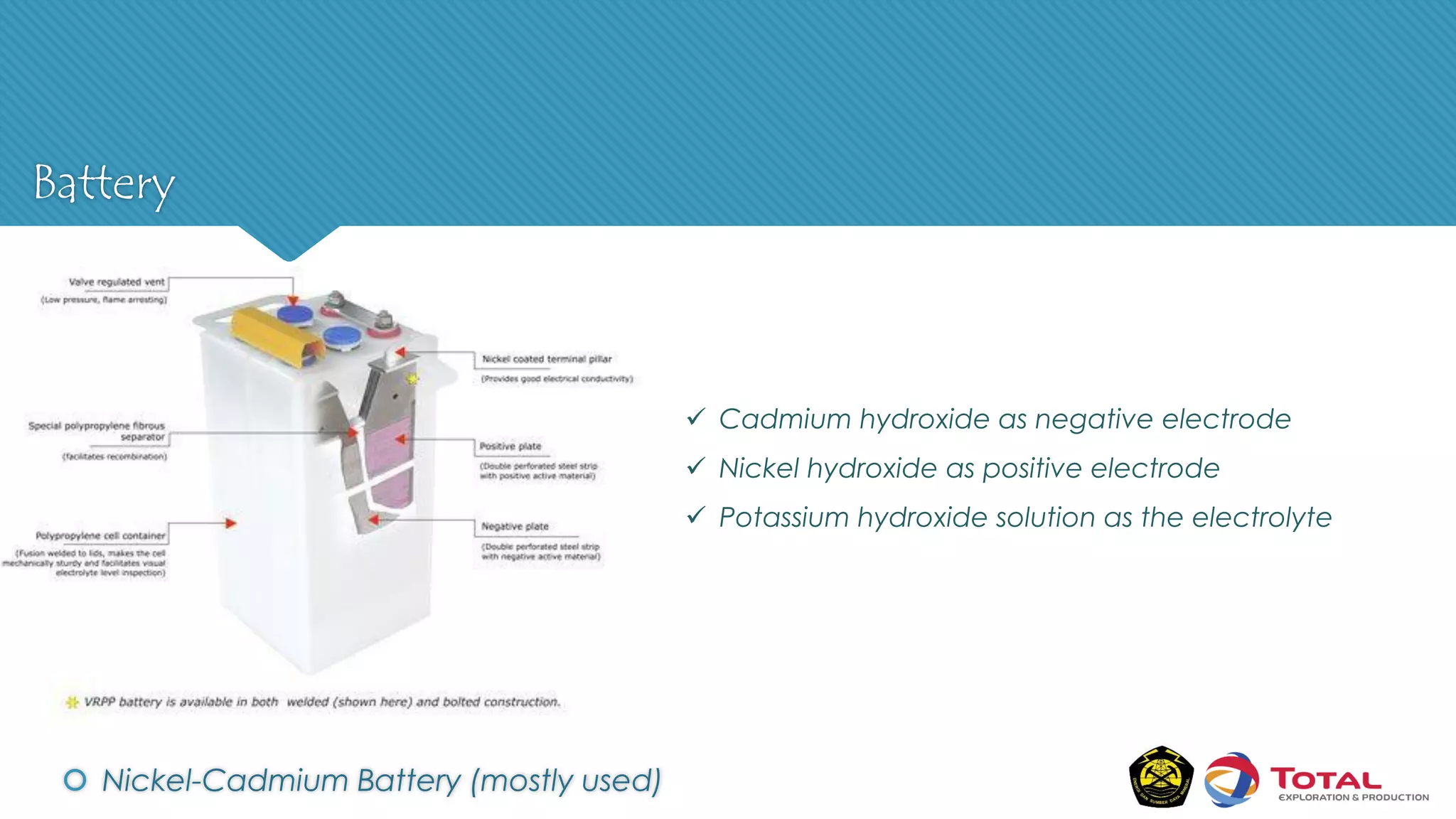
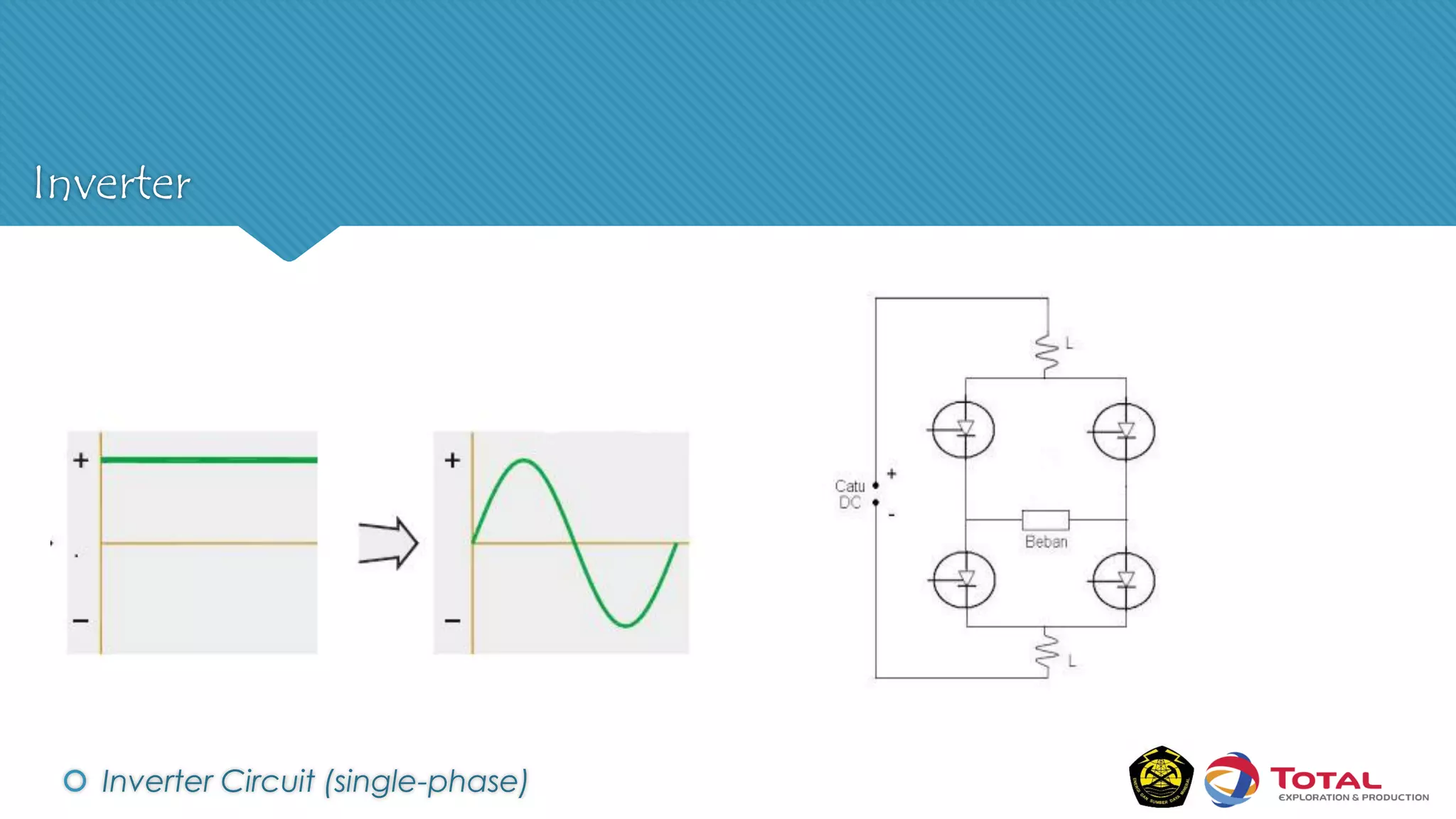
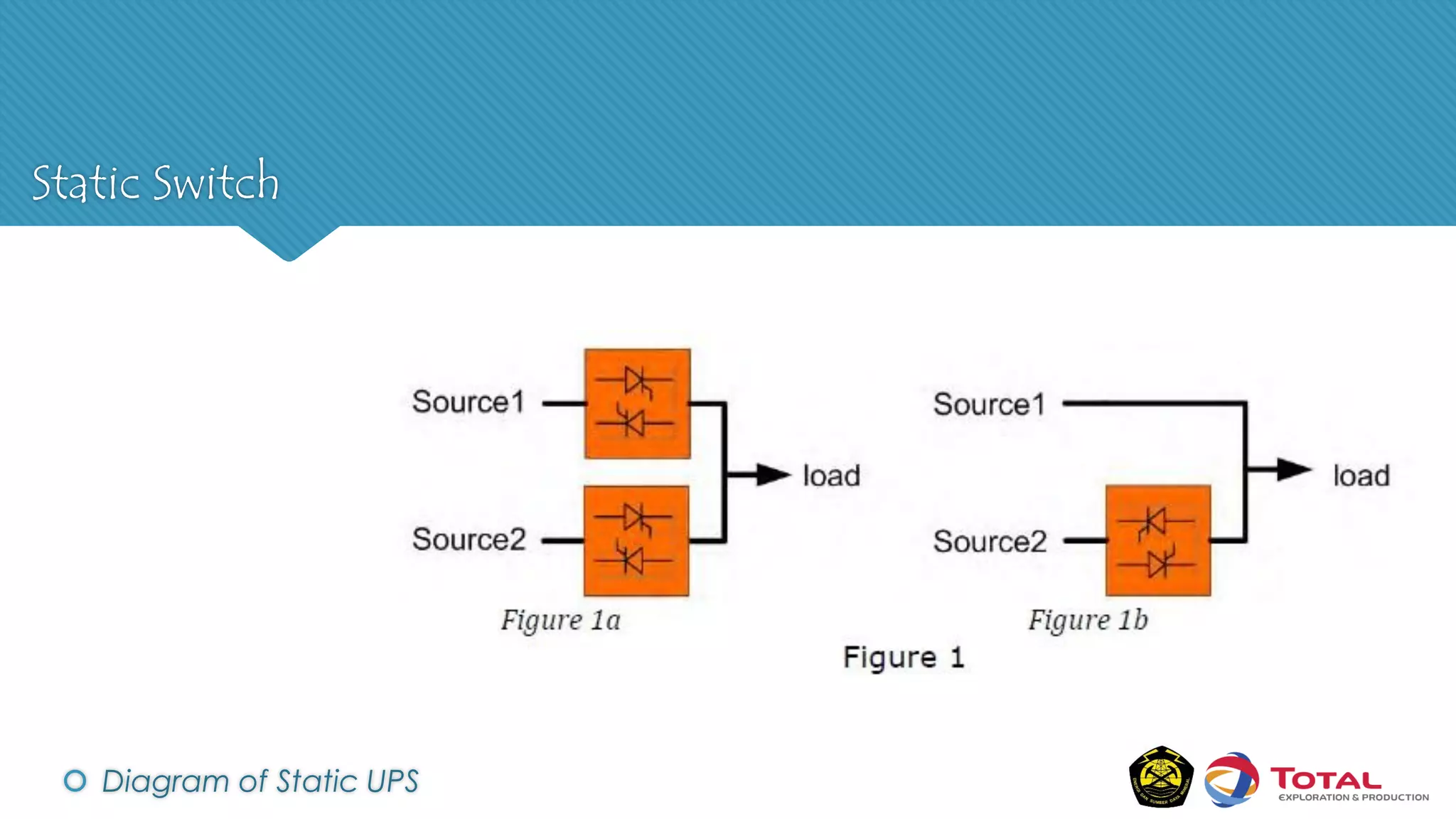
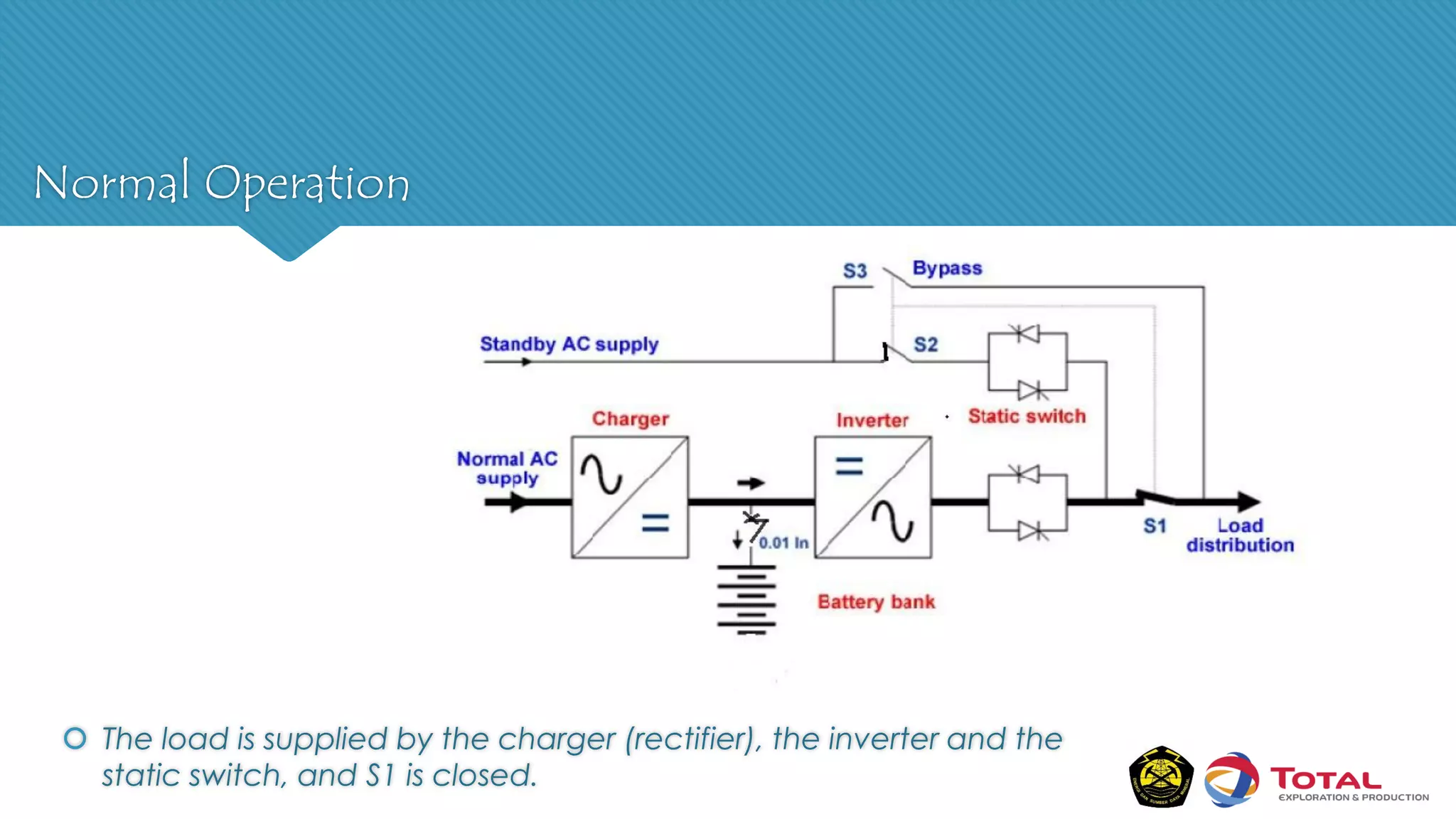
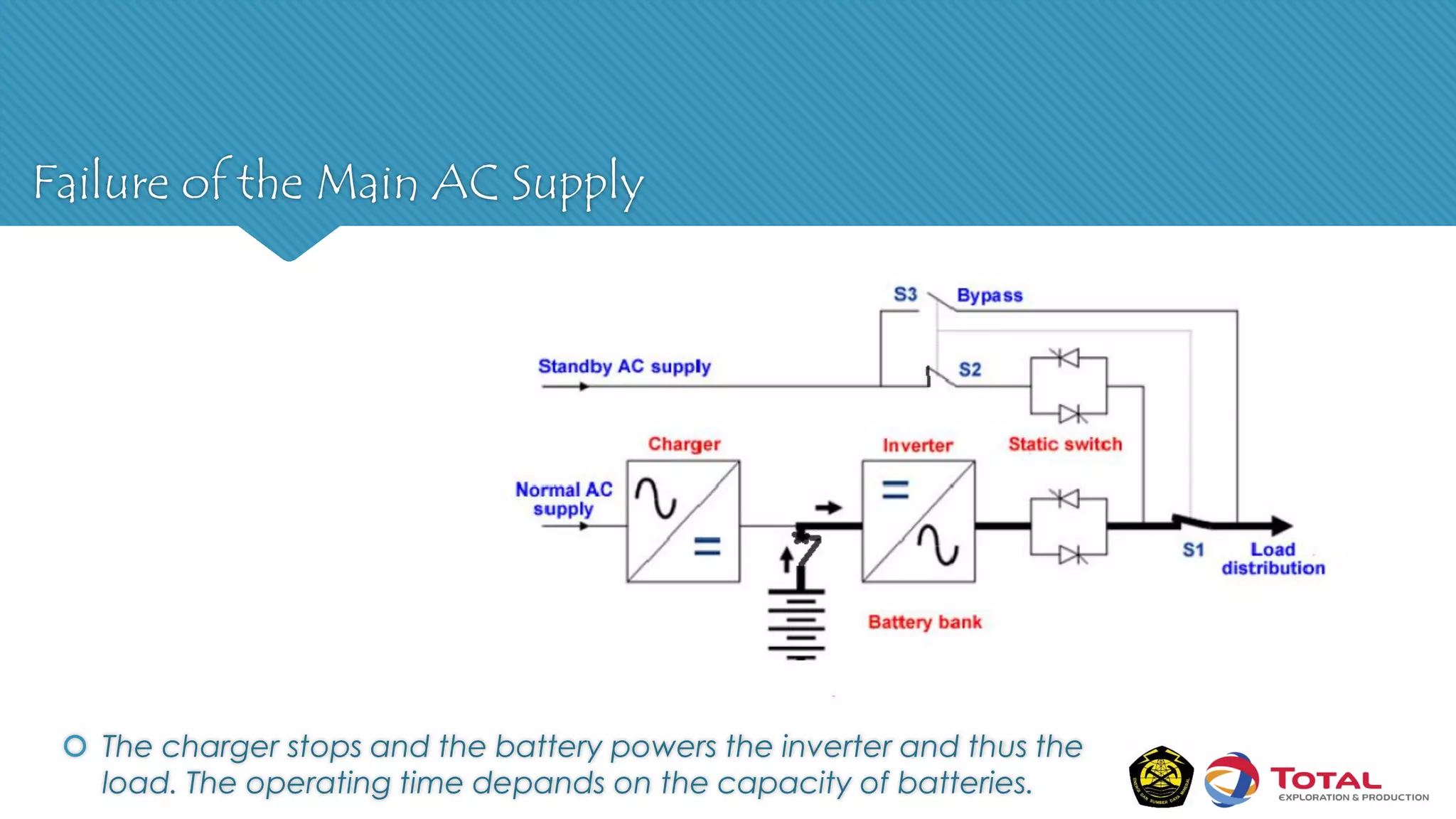
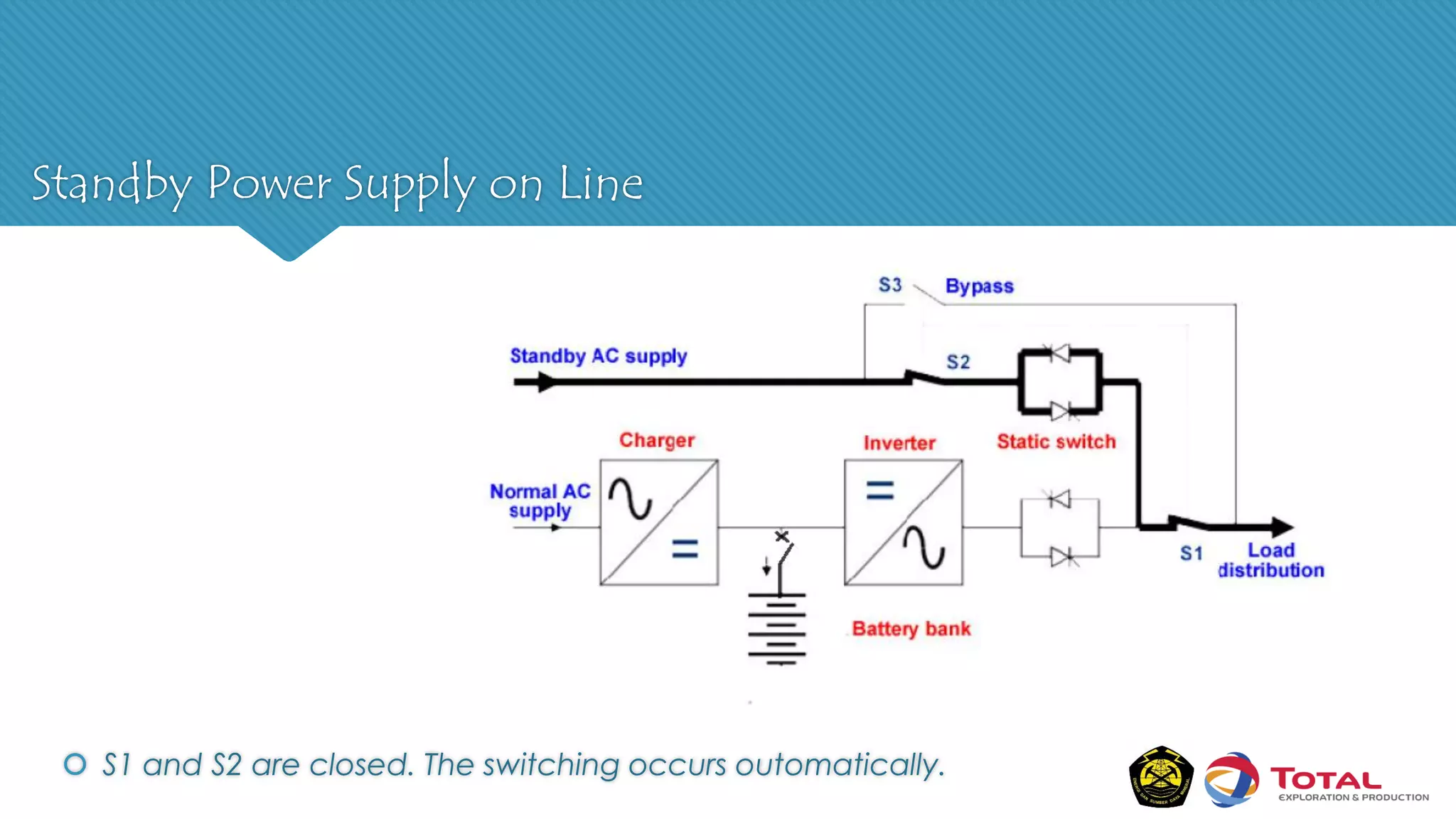
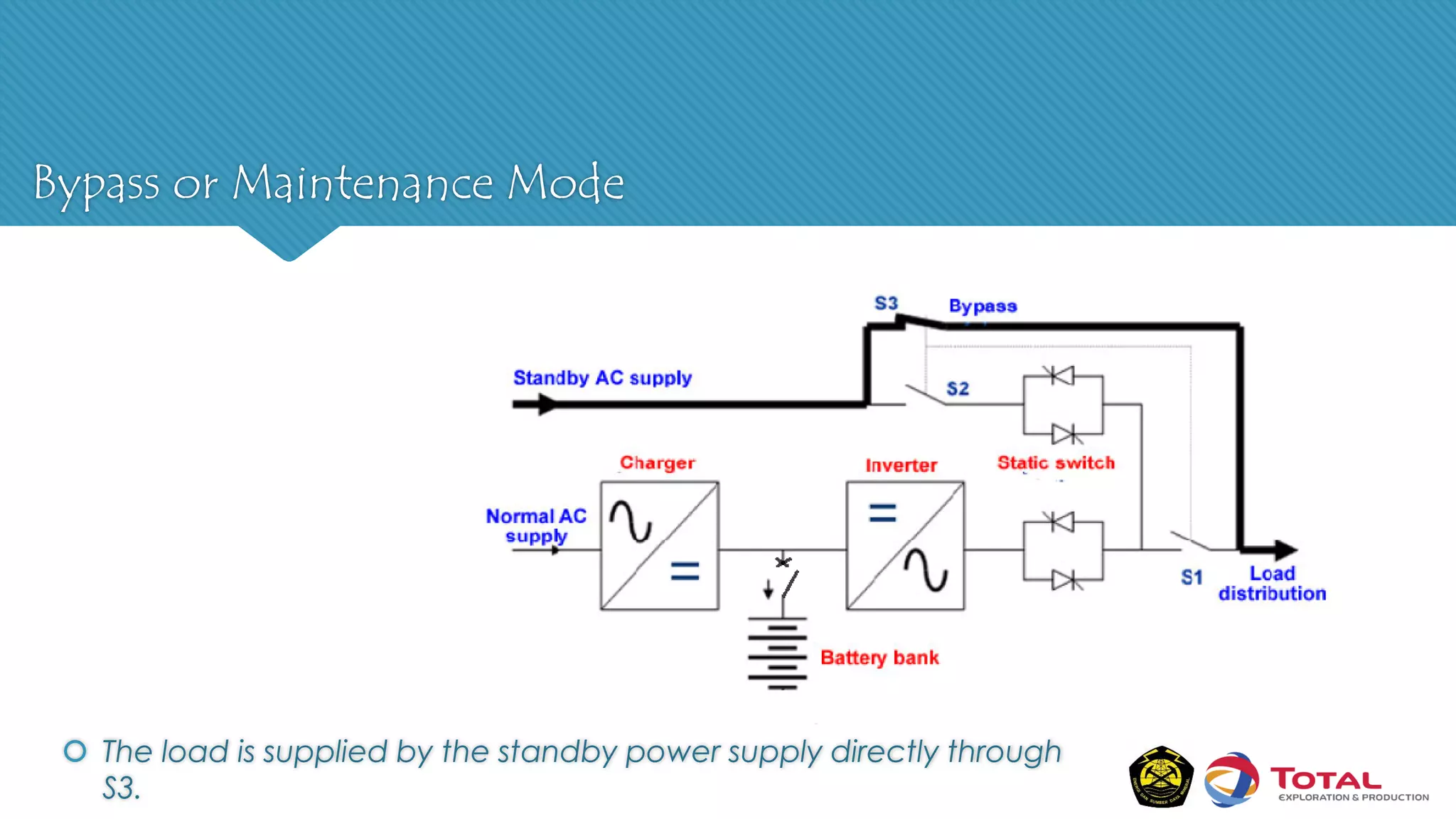
An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) provides backup electrical power when the primary power source fails. It has three main components: a rectifier that converts AC to DC power, batteries that store the energy, and an inverter that converts the stored DC back to AC power. There are two main types of UPS - rotary UPS uses an alternator while static UPS uses solid-state components without rotating parts. A static UPS has four operating modes including normal operation from the main power, backup from batteries if the main fails, switching to a standby power source, and bypass for maintenance. The UPS ensures critical systems have continuous power for processes, safety and data protection.