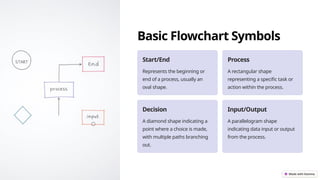
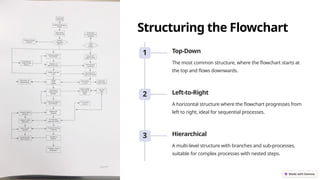
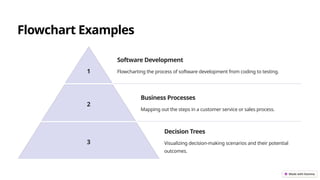
This presentation introduces flowcharts as a visual representation of processes that enhance clarity, improve efficiency, and facilitate collaboration. It outlines basic flowchart symbols, creation steps, structuring methods, best practices, and common troubleshooting tips. Key takeaways include the importance of visualization in understanding processes and optimizing workflows.